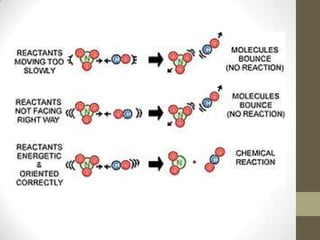
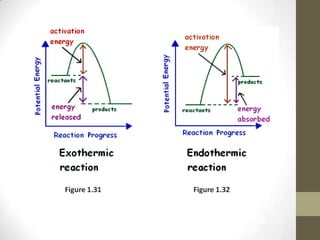
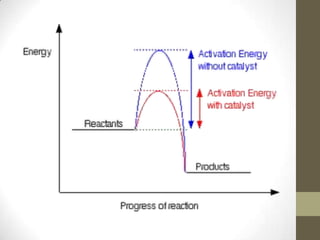
This document discusses factors that affect the rate of chemical reactions according to the collision theory. It explains that for a reaction to occur, reactant particles must collide with sufficient kinetic energy to overcome the activation energy barrier. The rate of reactions depends on both the frequency of collisions between reactants and the activation energy. It then analyzes how increasing the surface area, concentration, temperature, use of catalysts, and pressure can increase the collision frequency, leading to more effective collisions and higher reaction rates.