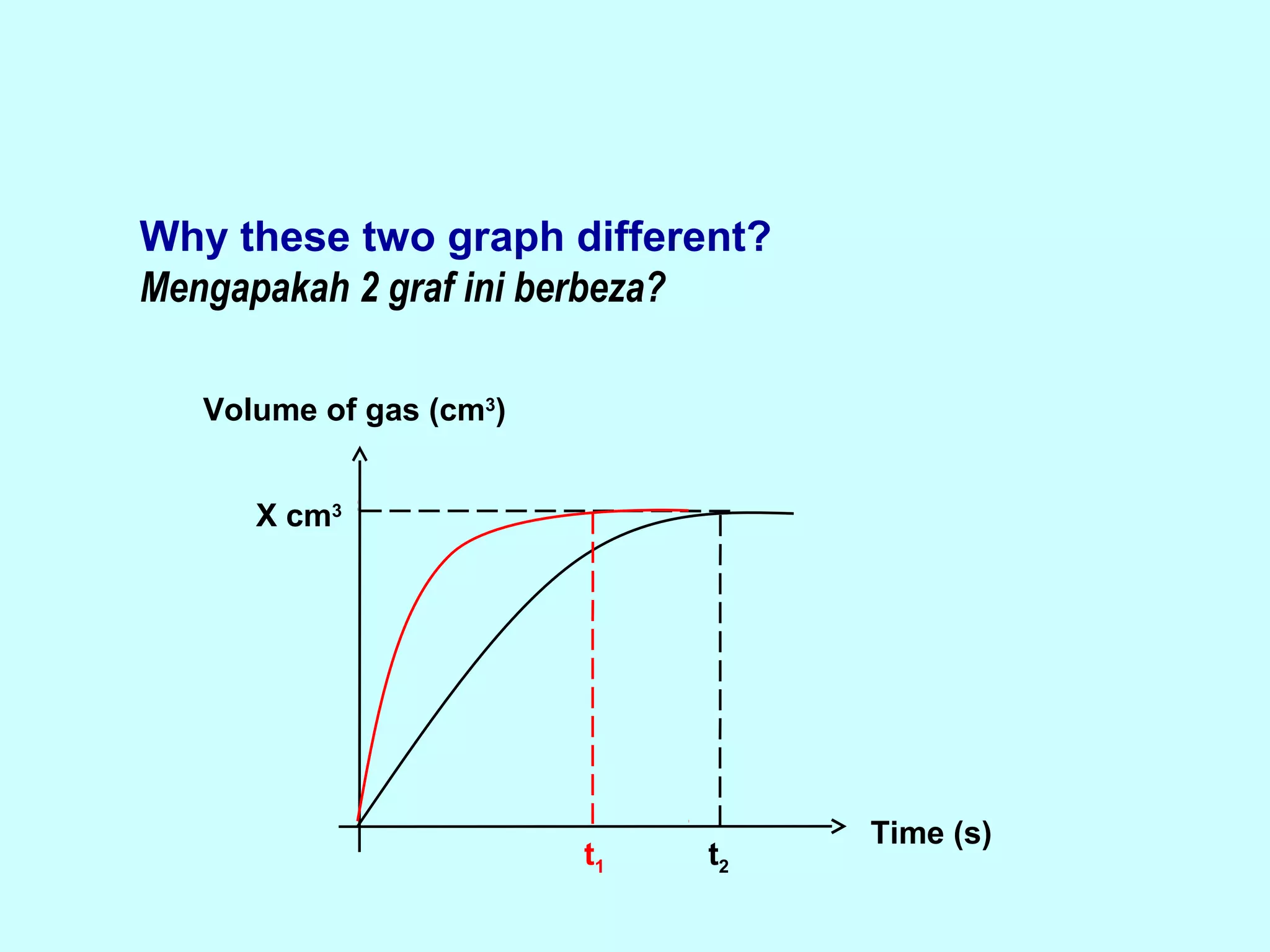
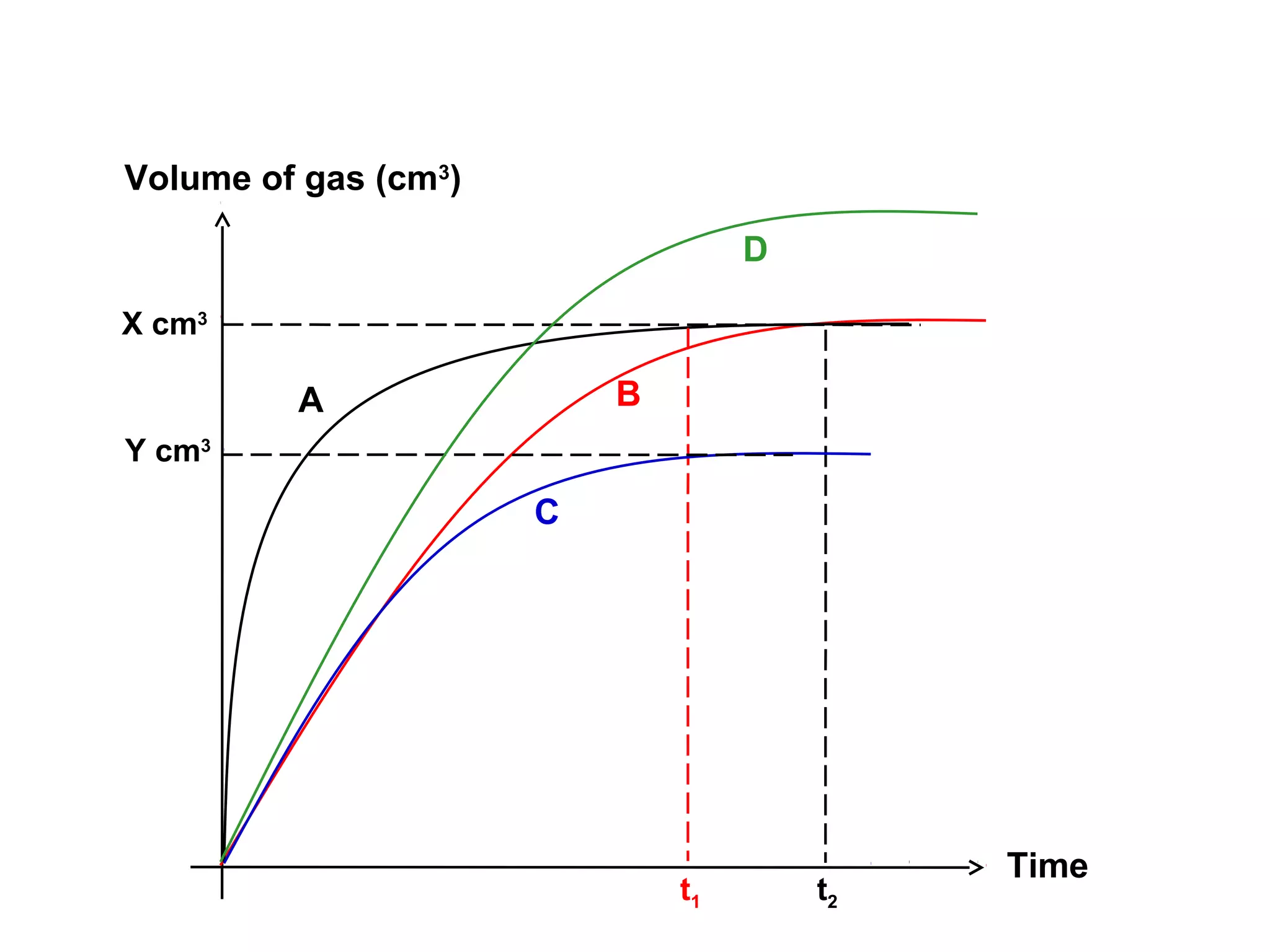
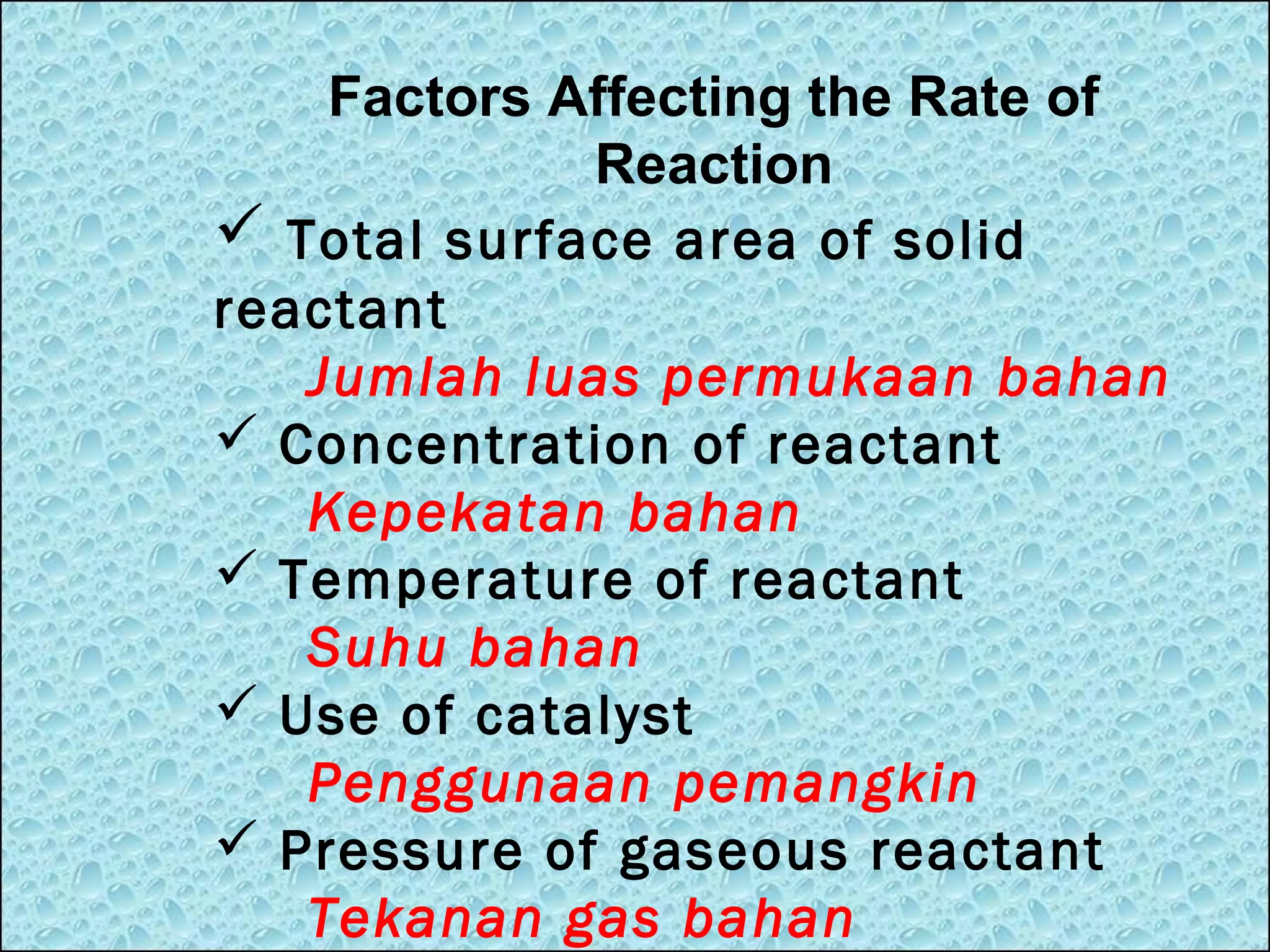
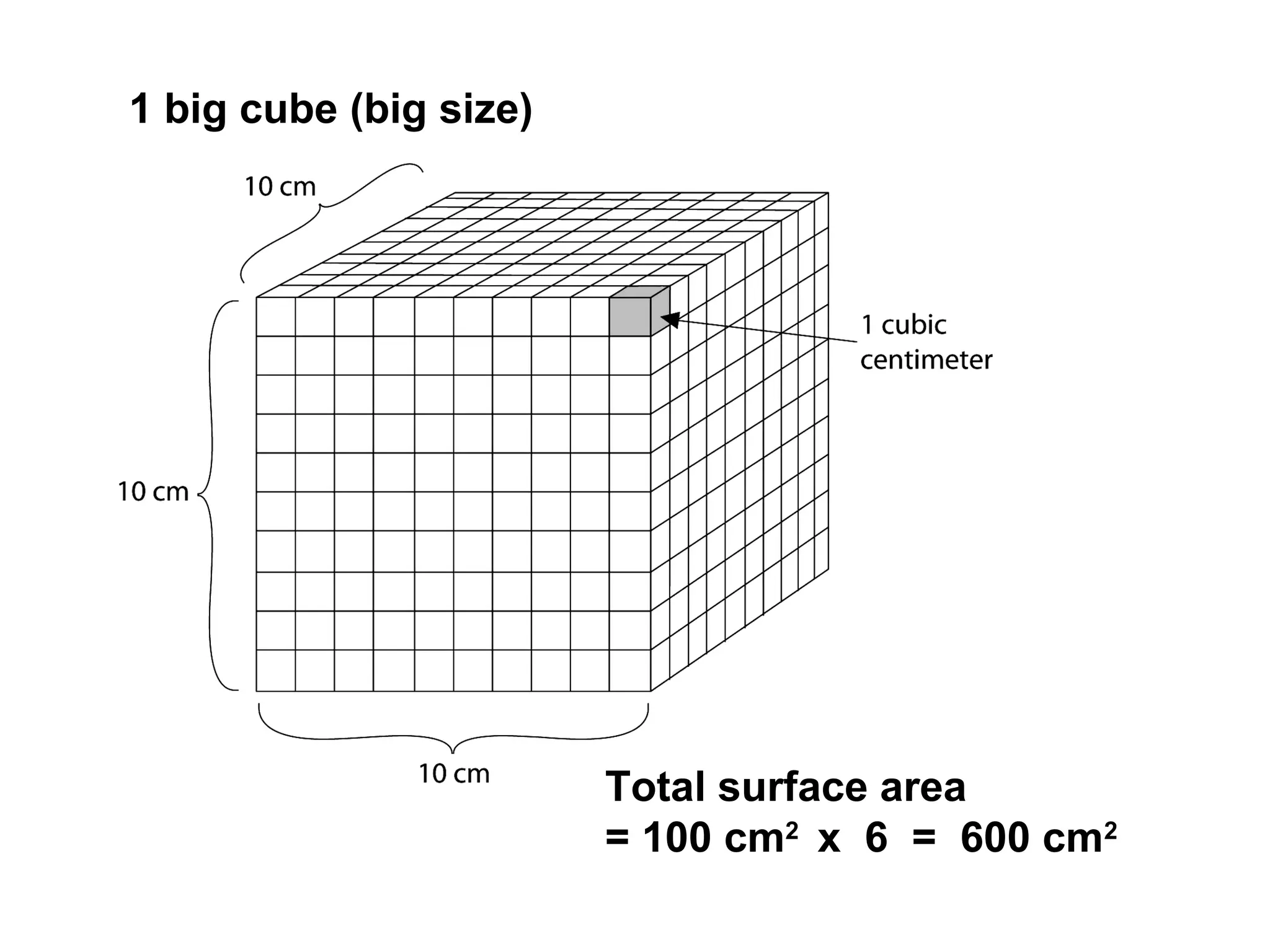
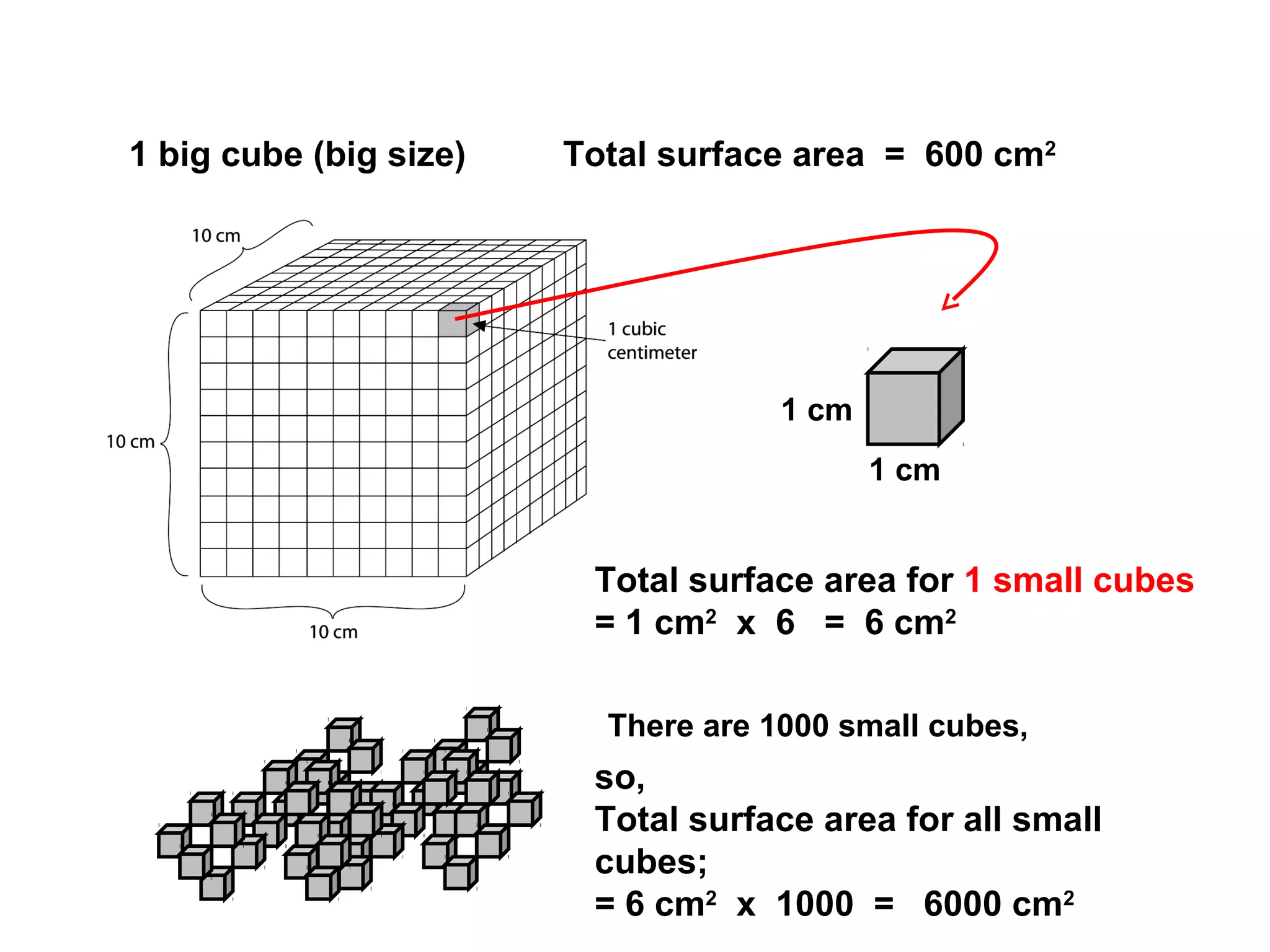
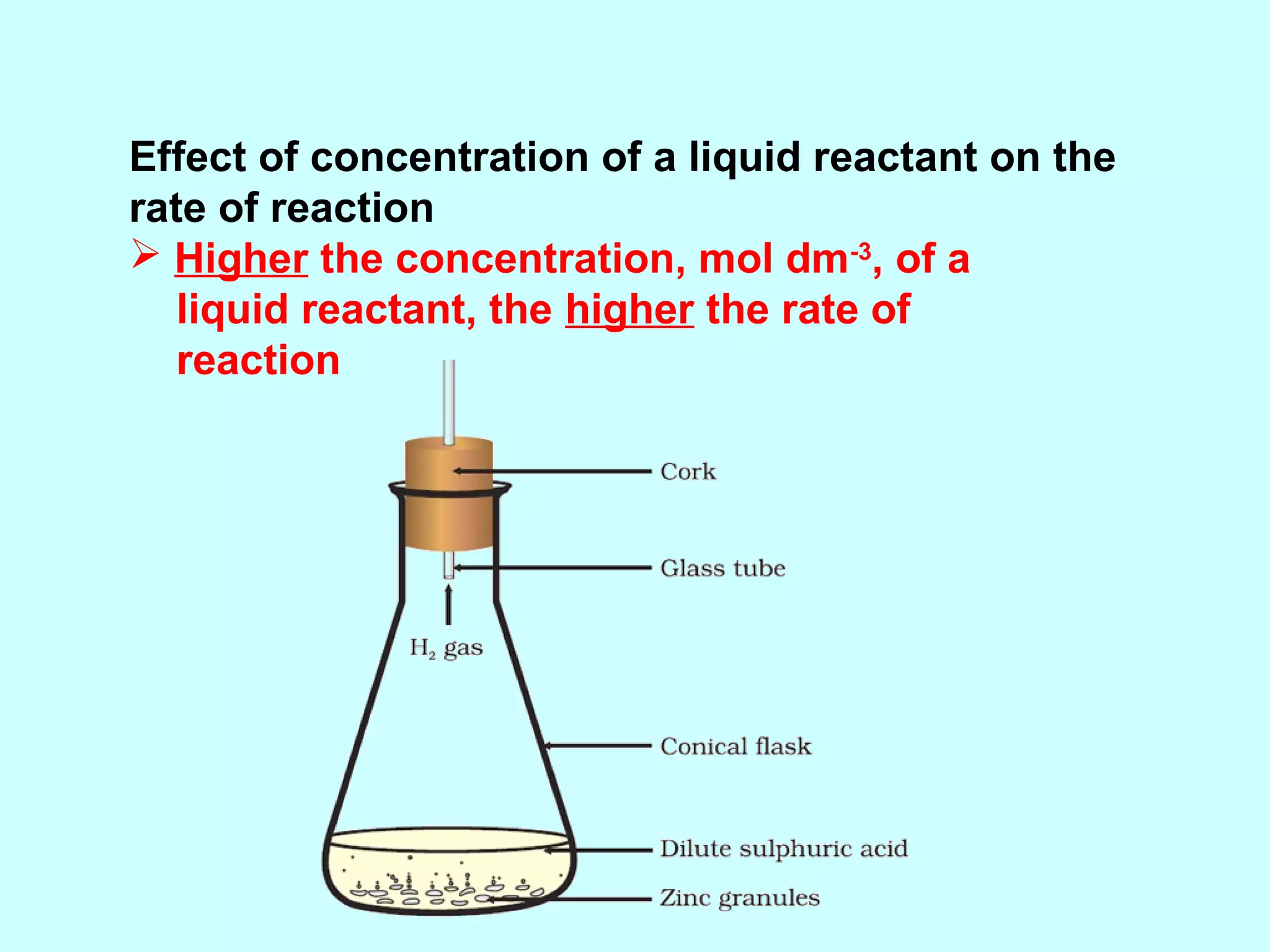
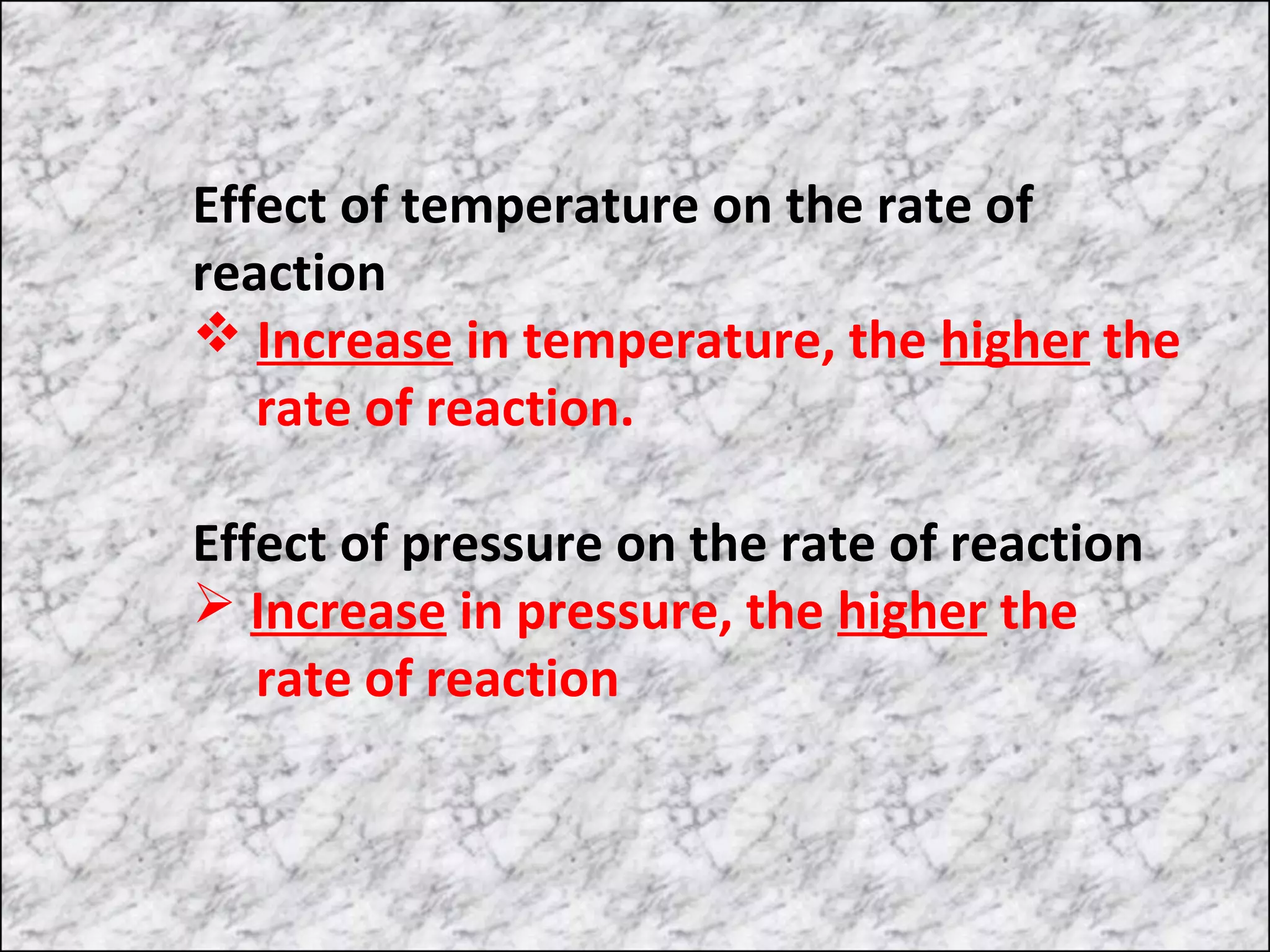
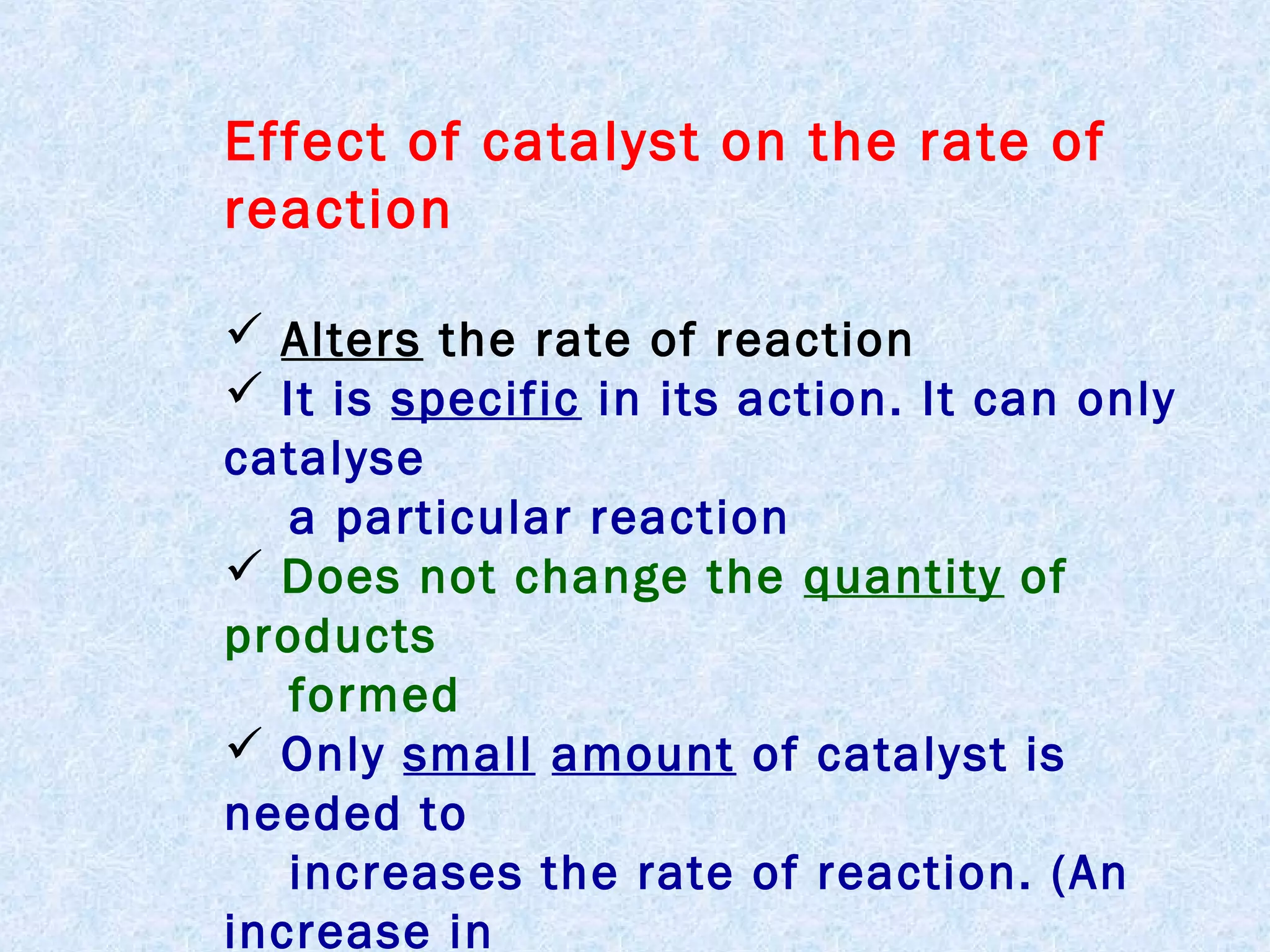
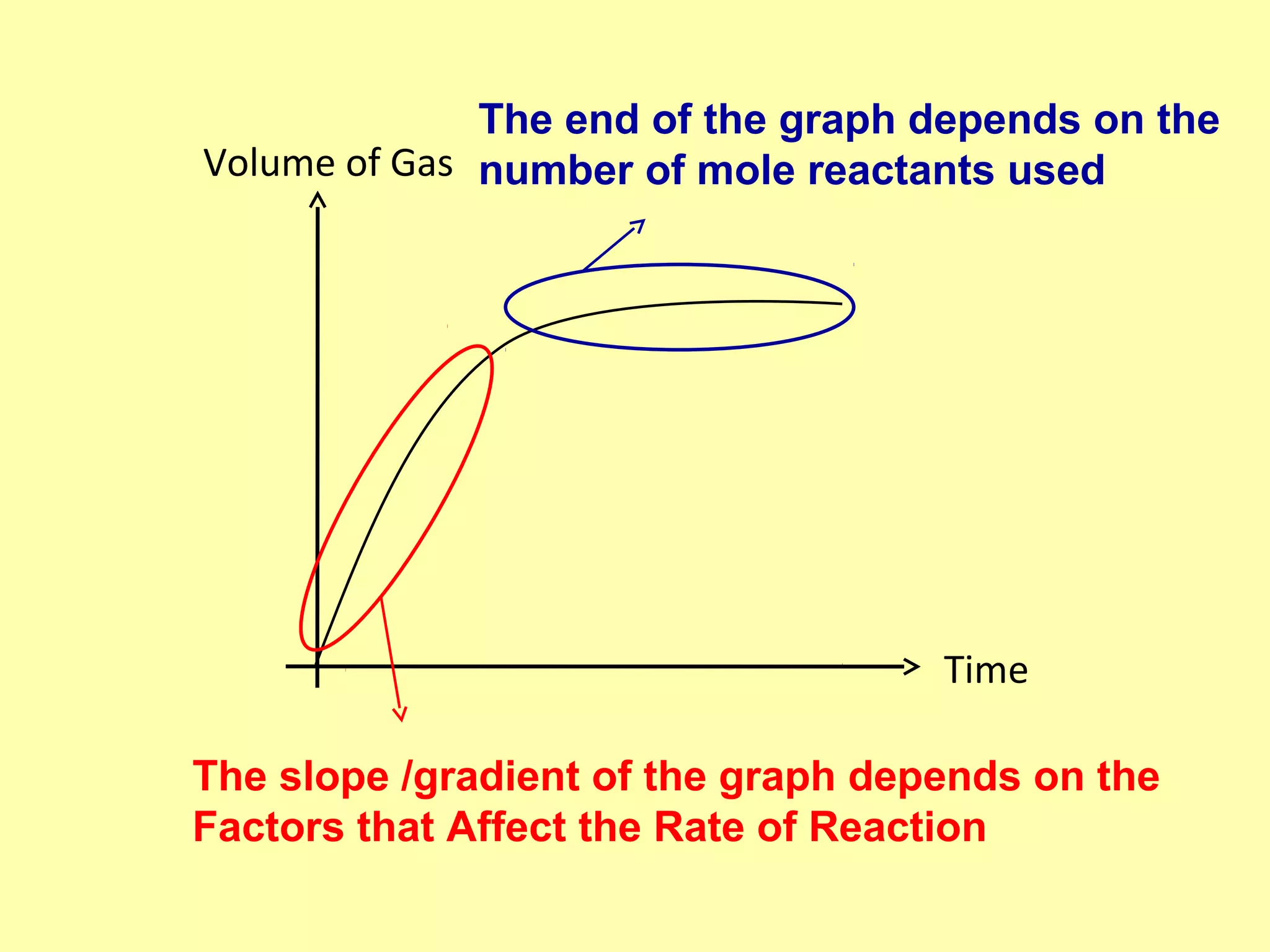
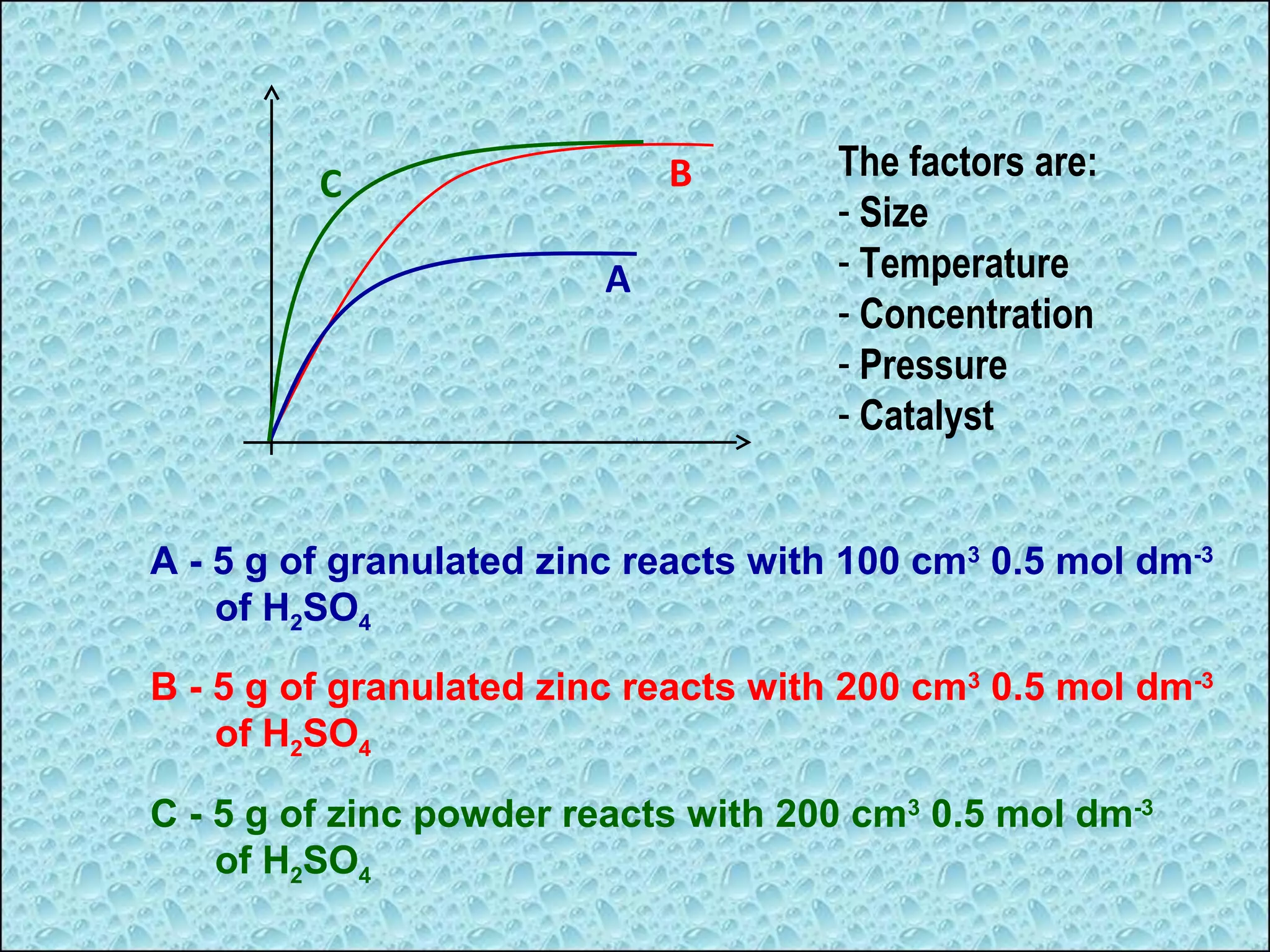
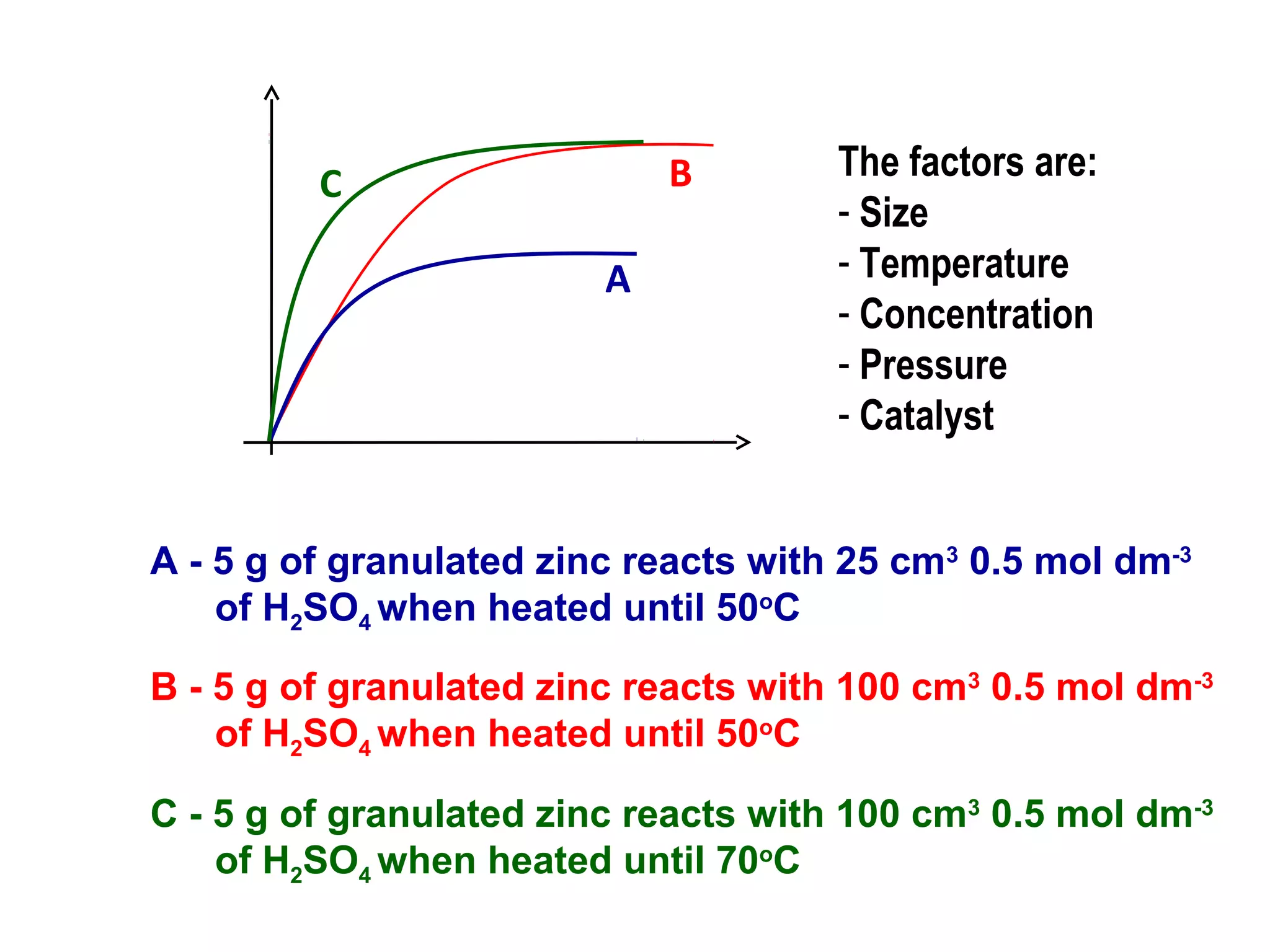
The document outlines various factors that affect the rate of chemical reactions, including surface area, concentration, temperature, pressure, and the use of catalysts. It specifically notes that smaller solid reactants, higher concentrations, elevated temperatures, and increased pressure generally lead to faster reactions. Additionally, it explains that catalysts can enhance reaction rates without changing the quantity of products and are specific in their action.