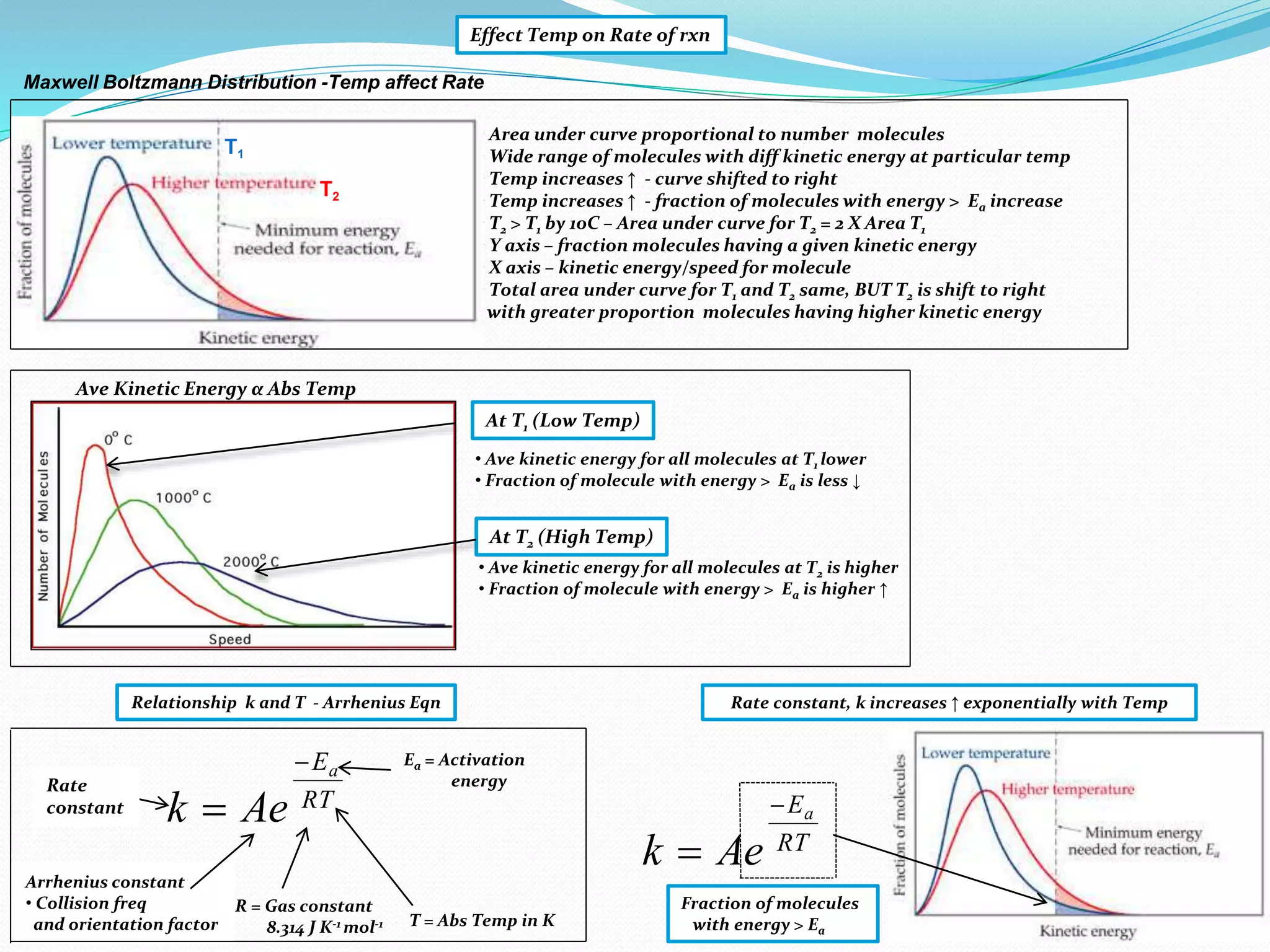
This document provides a tutorial on collision theory, the Arrhenius equation, and the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution curve. It explains that for a chemical reaction to occur, molecules must collide with the correct orientation and with energy greater than the activation energy. It also discusses how increasing the temperature or concentration of reactants increases the rate of reaction by increasing the frequency and energy of collisions. The Arrhenius equation quantitatively describes the relationship between reaction rate and temperature. The Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution curve illustrates how more molecules have energy above the activation energy at higher temperatures, explaining the temperature dependence of reaction rates.

![Collision Theory
Chemical rxn to occur bet A +B
• Molecule collide with right orientation (geometry)
( effective collision take place)
• Molecule collide with total energy greater > activation energy
• Effective collision will lead to product formation
Collision bet A + B
No product formation
• Energy collision < activation energy
• Collision not in correct orientation
or energetic enough to overcome Ea
Product formation
• Energy collision > activation energy
• Collision energetic enough to overcome Ea
Rate of Reaction
• Conc reactant increase ↑
• Freq of collision increase ↑
• Freq of effective collision increase ↑
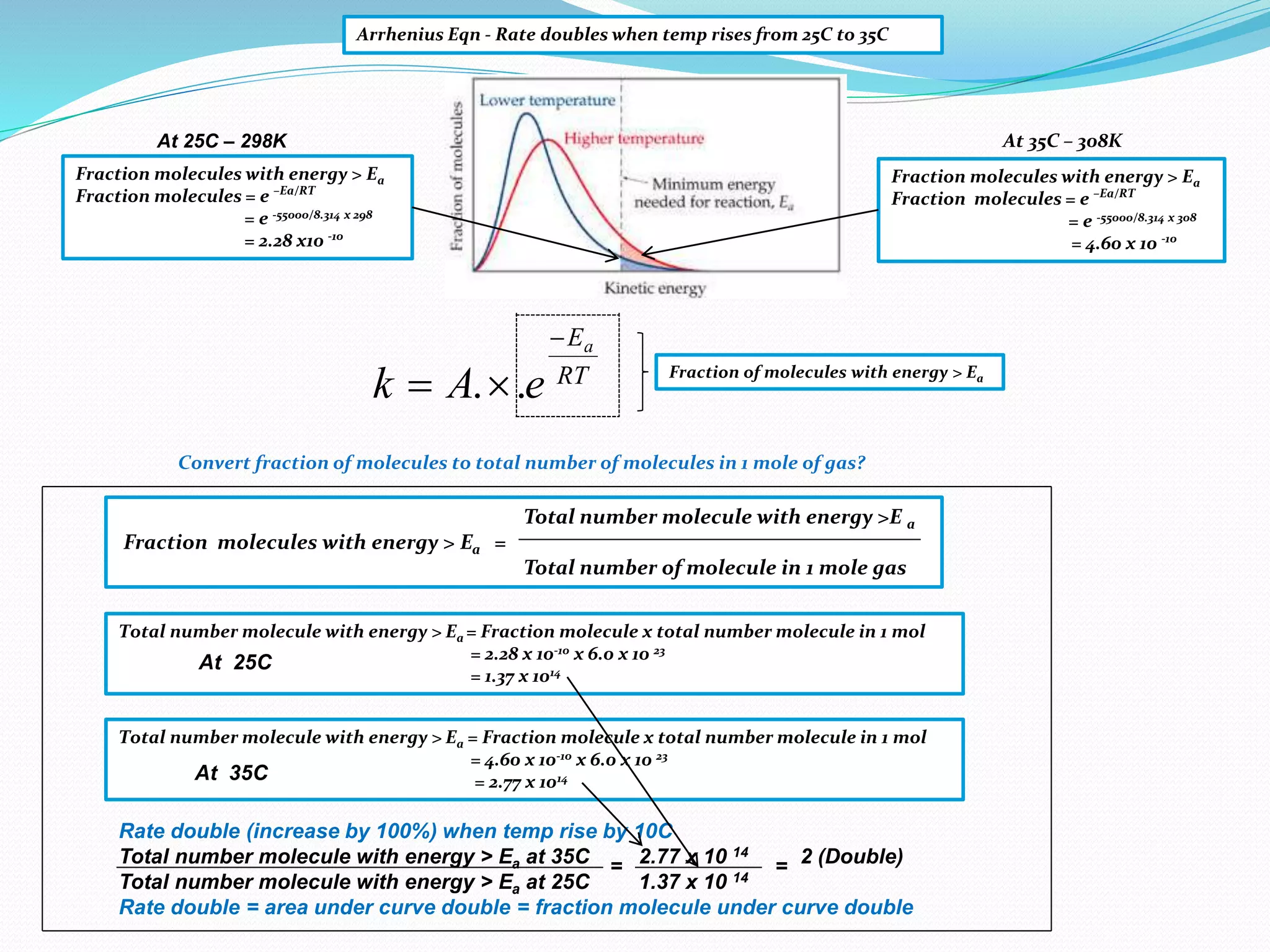
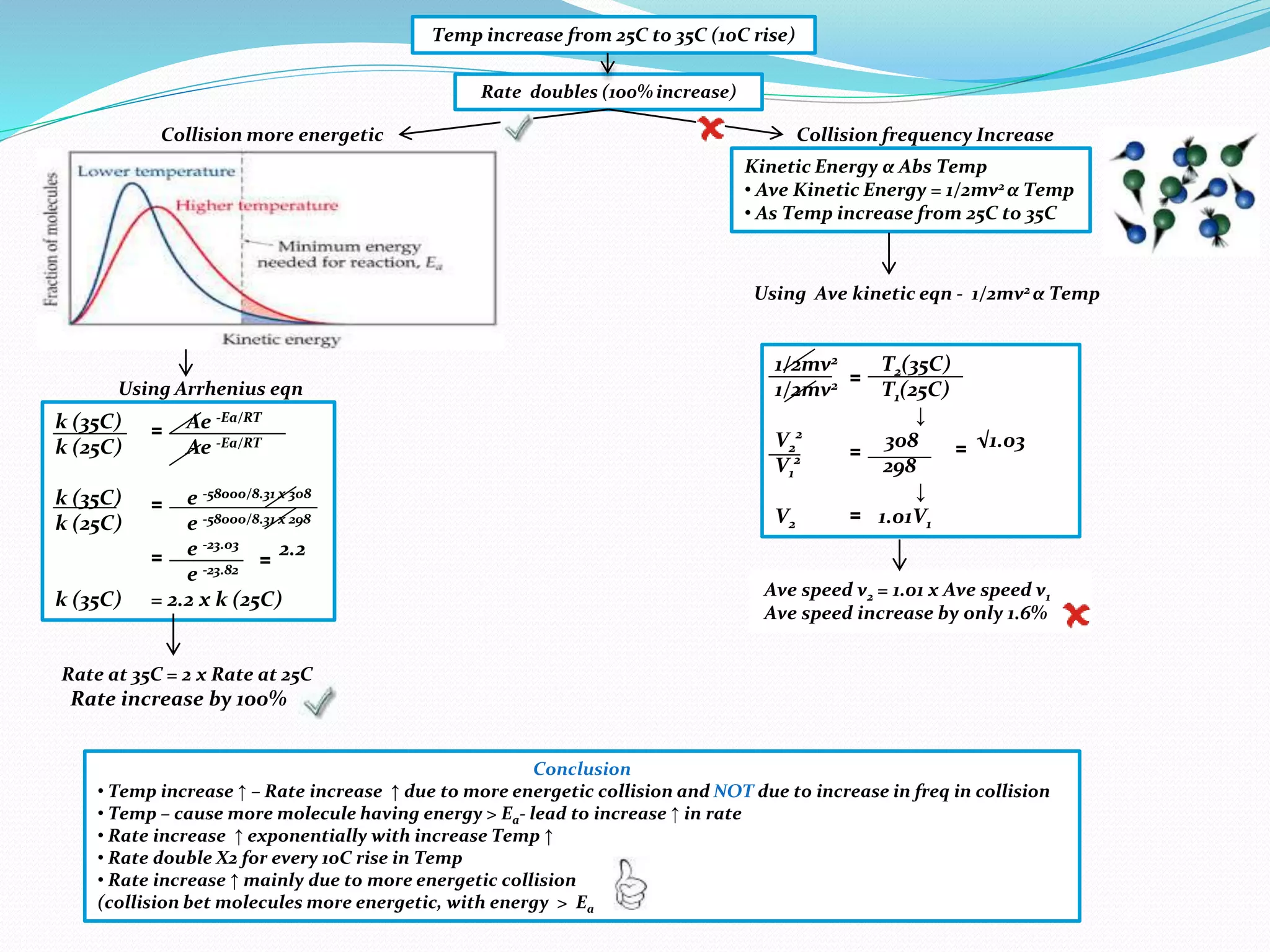
• Temp increase ↑ by 10 C
• Rate increase ↑ by 100%
• Exponential relationship
bet Temp and Rate
Rate = k [A]1[B]1 1st order – A
1st order – B
Conc A doubles x2 – Rate x2
Conc A triples x3 – Rate x3
Collision Theory
• Temp increase ↑ by 10C
• Fraction of molecules with
energy > Ea doubles
• Rate increases ↑ by 100%
Ineffective collision Effective collision
Concentration
Temperaturedepends](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hrbvwvicsruuuk9vkm50-signature-cdec9f1aa9eed97523dcd574ea6276a5e8badb947cf0fcd46c5051e8f72bb3d6-poli-160312012922/75/IB-Chemistry-Collision-Theory-Arrhenius-Equation-and-Maxwell-Boltzmann-Distribution-2-2048.jpg)
![Temp and rate constant link by Arrhenius Eqn
X + Y → Z
Rate of rxn = (Total number collision) x ( fraction collision, energy >Ea) x ( [X] [Y] )
Arrhenius Constant
A
Fraction molecule energy > Ea
e –Ea/RT
Conc
[X][Y]
Rate of rxn = A e –Ea/RT [X][Y]
Rate of rxn = k [X] [Y]
If conc constant BUT Temp changes, combine eqn 1 and 2
Rate of rxn = k [X]1
[Y]1
= A e –Ea/RT [X][Y]
k = A e –Ea/RT
Rate rxn written in TWO forms
Rate of rxn = A e –Ea/RT [X] [Y]
Eqn 1 Eqn 2
Cancel both sides
Rate of rxn = A e –Ea/RT [X][Y]
Fraction molecule energy > Ea
e –Ea/RT
Conc
[X][Y]
Temp increase
Fraction with energy > Ea increase
Rate increase exponentially
Conc increase
Freq collision increase
Rate increase
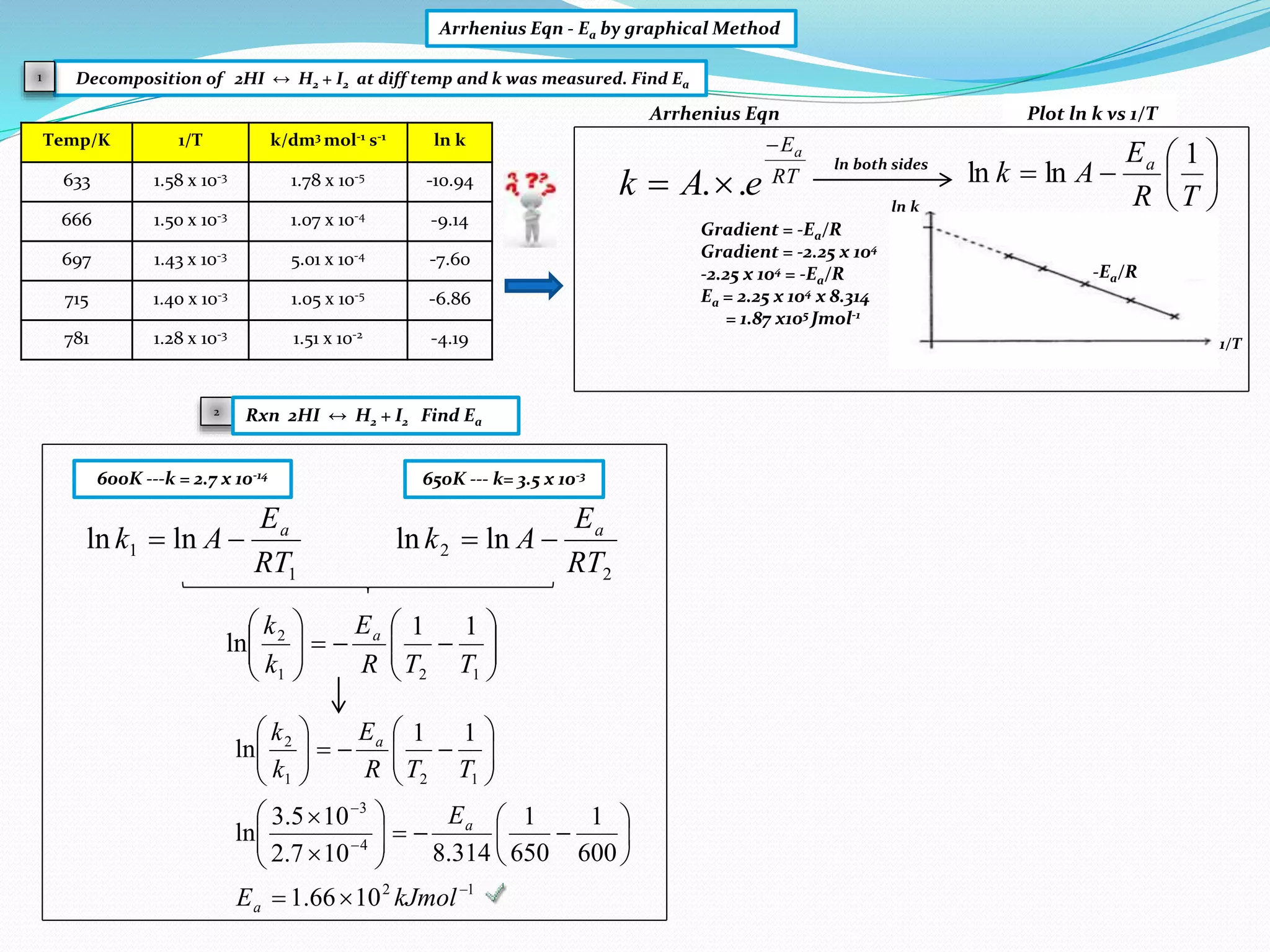
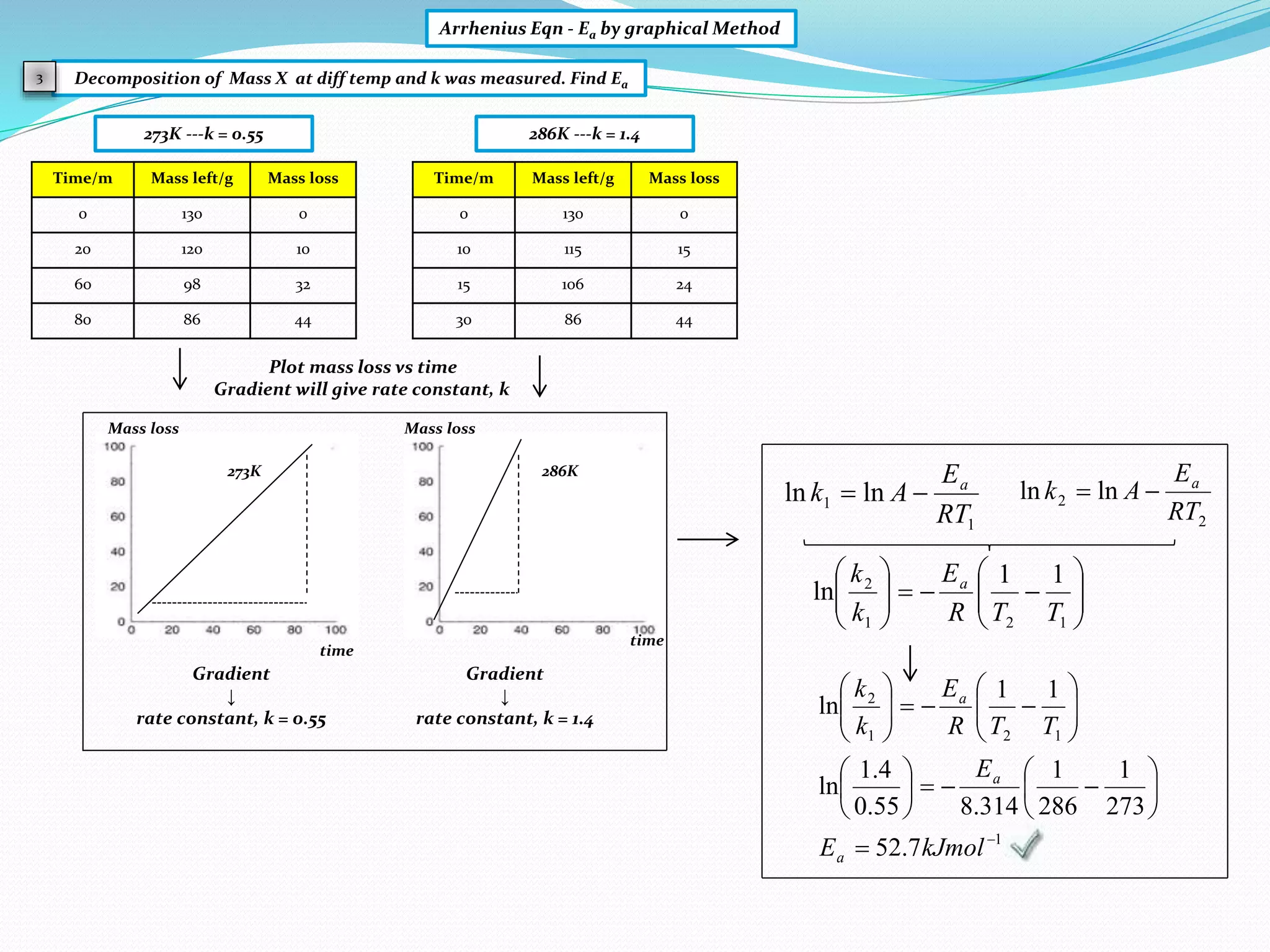
Arrhenius Eqn - Ea by graphical Method
RT
Ea
eAk
..
TR
E
Ak a 1
lnln
TR
E
Ak a 1
303.2
lglg
Plot ln k vs 1/T
• Gradient = -Ea/R
• ln A = intercept y axis
Plot log k vs 1/T
• Gradient = -Ea/R
• log A = intercept y axis
ln both sides log both sides
ln k lg k
1/T1/T
-Ea/R -Ea/R](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hrbvwvicsruuuk9vkm50-signature-cdec9f1aa9eed97523dcd574ea6276a5e8badb947cf0fcd46c5051e8f72bb3d6-poli-160312012922/75/IB-Chemistry-Collision-Theory-Arrhenius-Equation-and-Maxwell-Boltzmann-Distribution-6-2048.jpg)