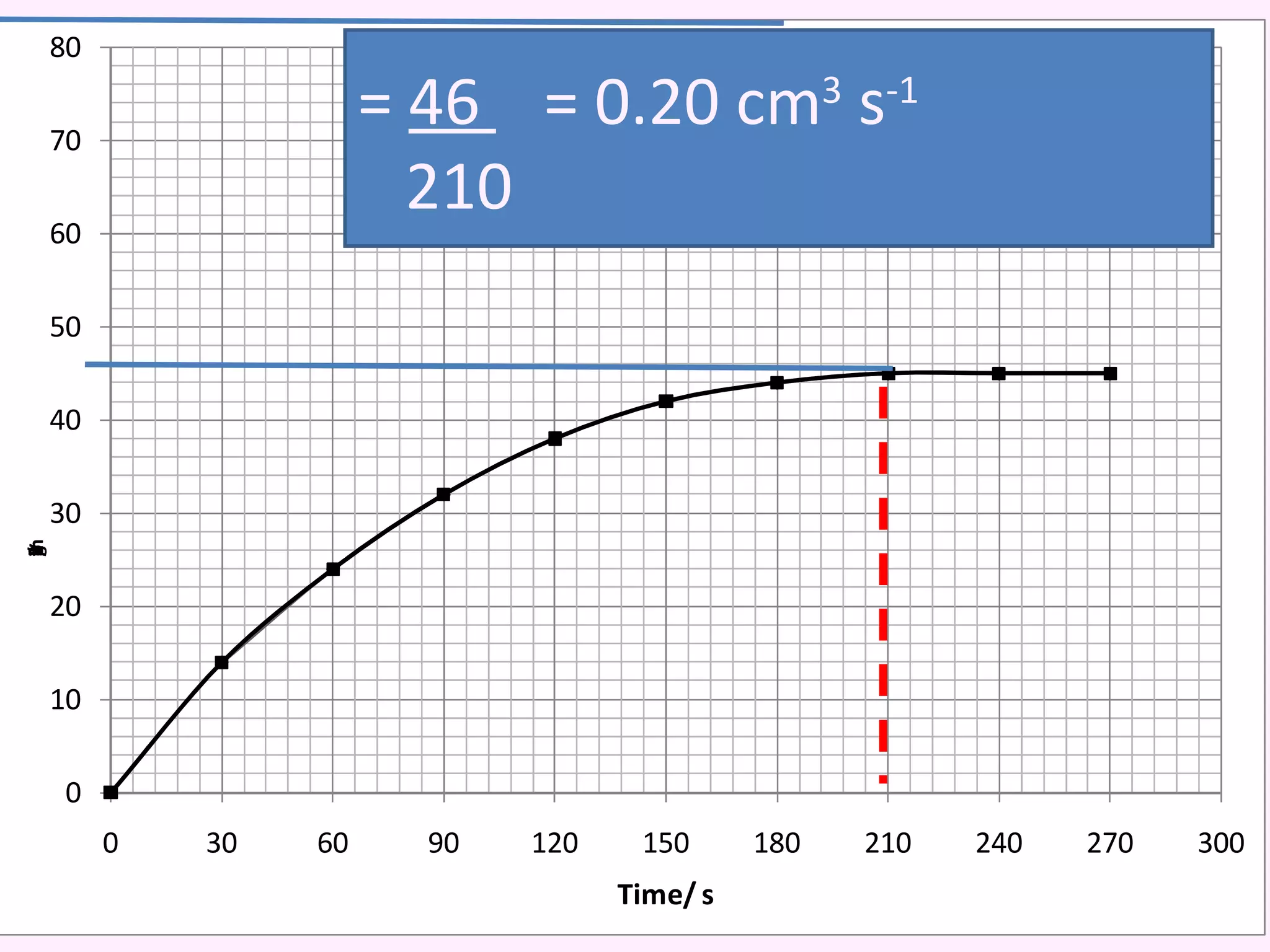
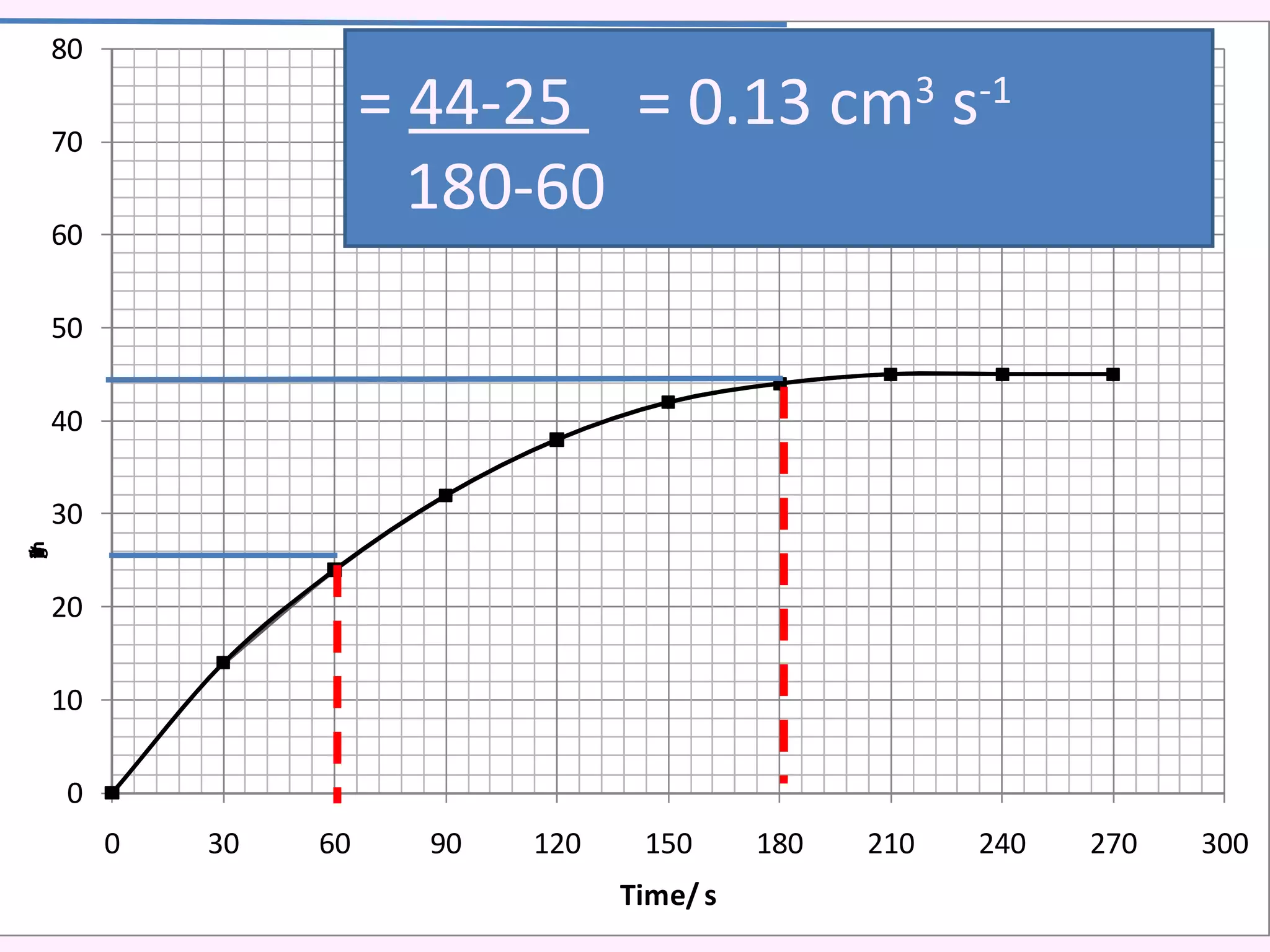
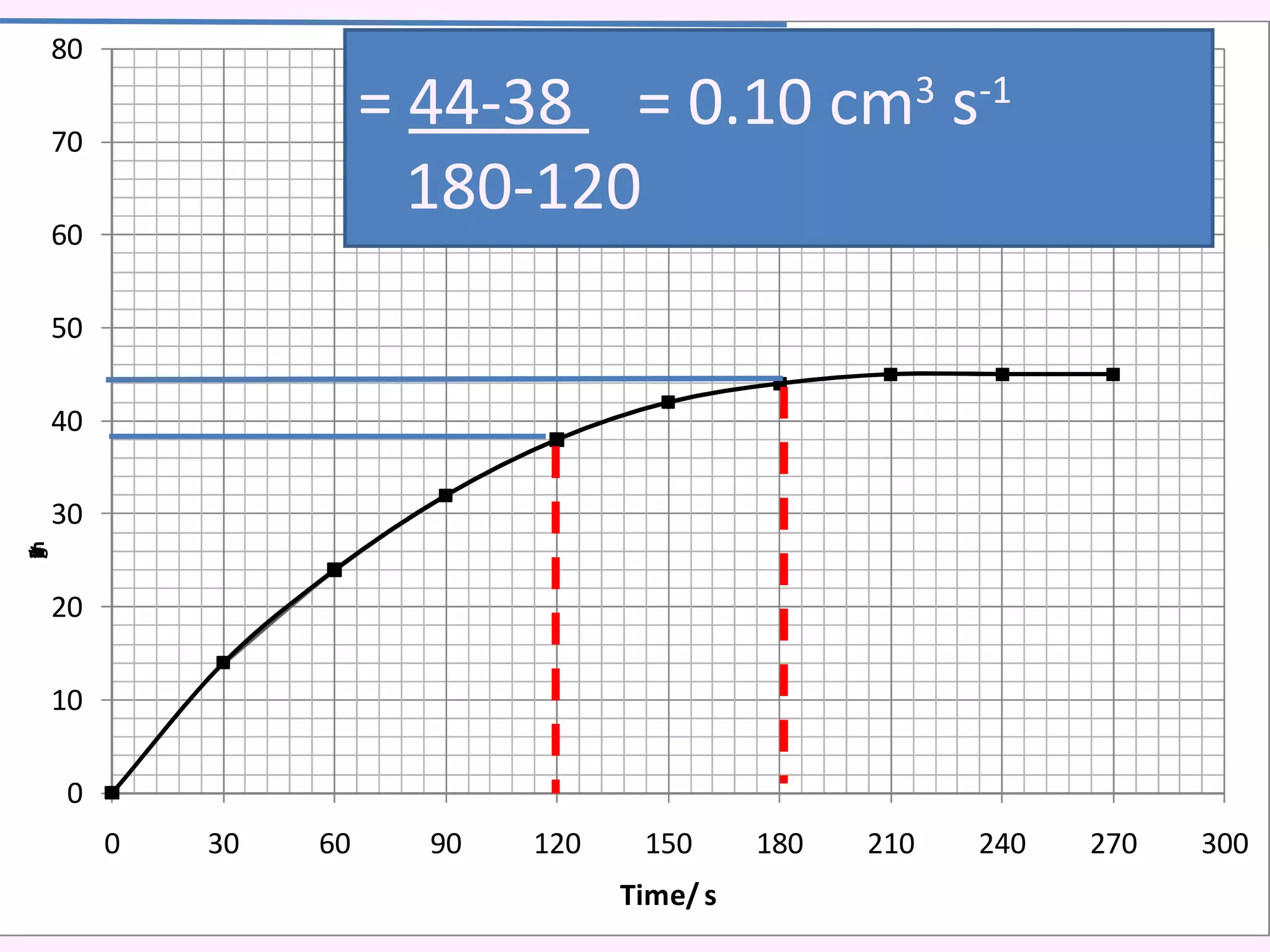
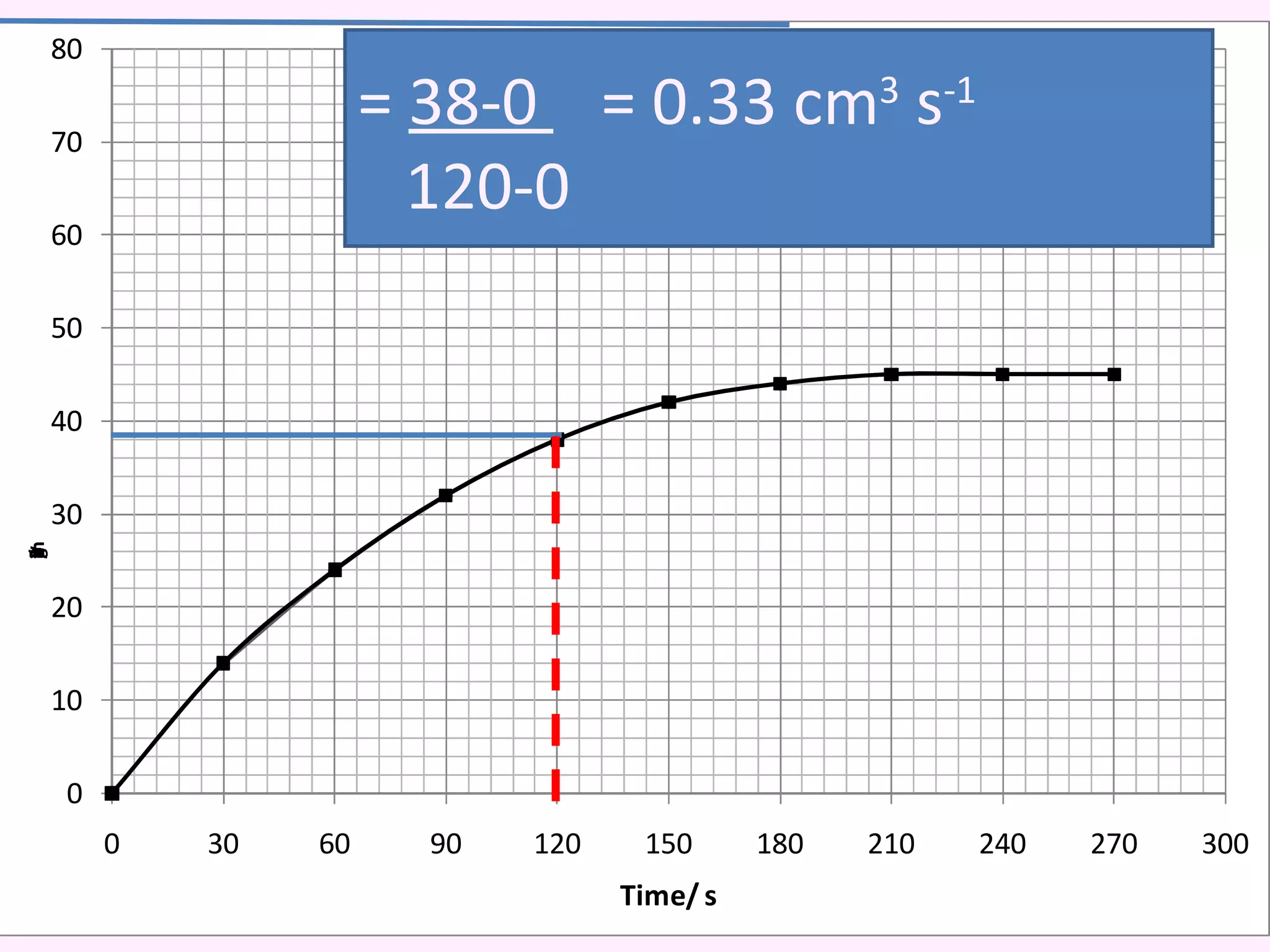
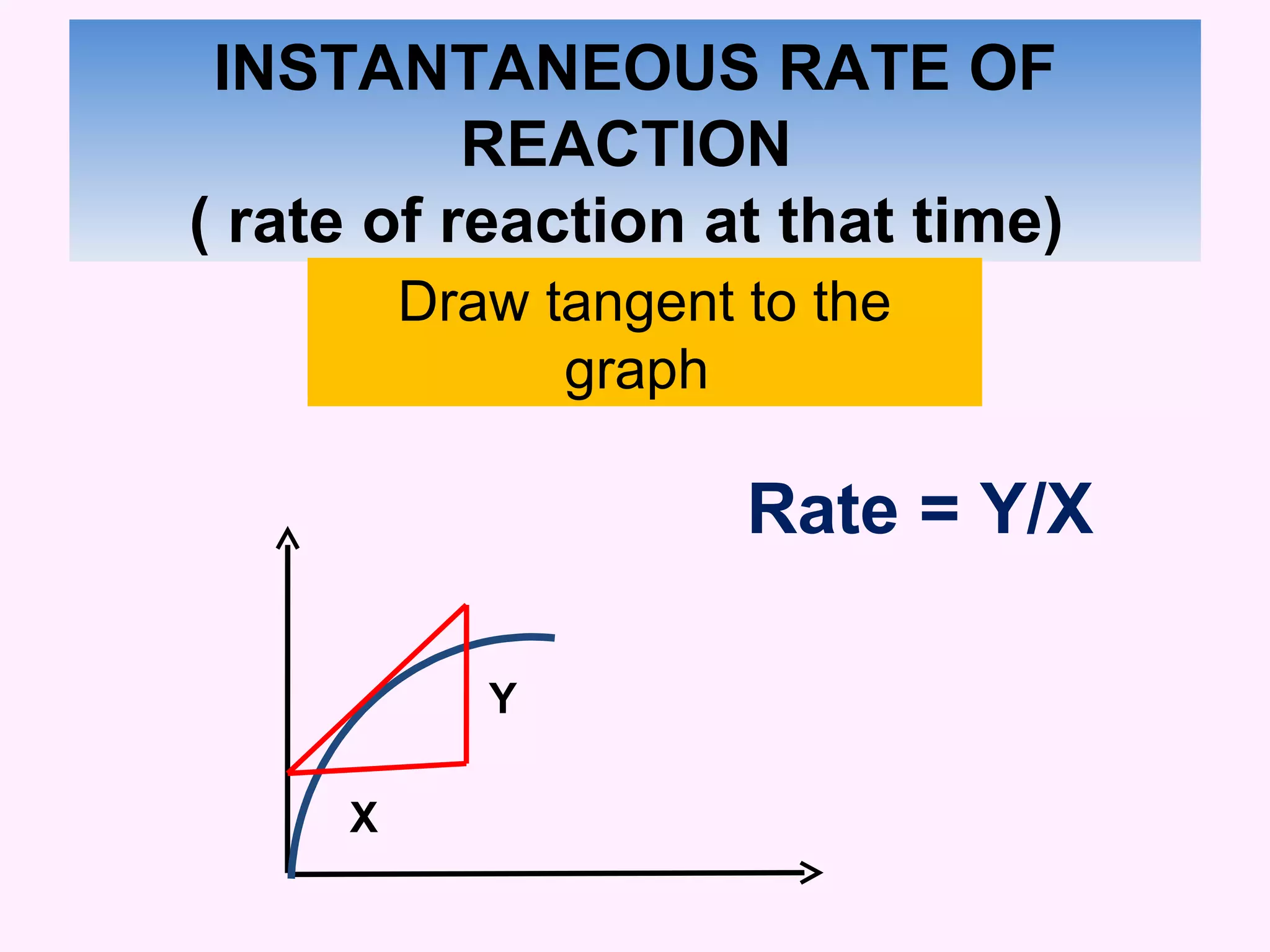
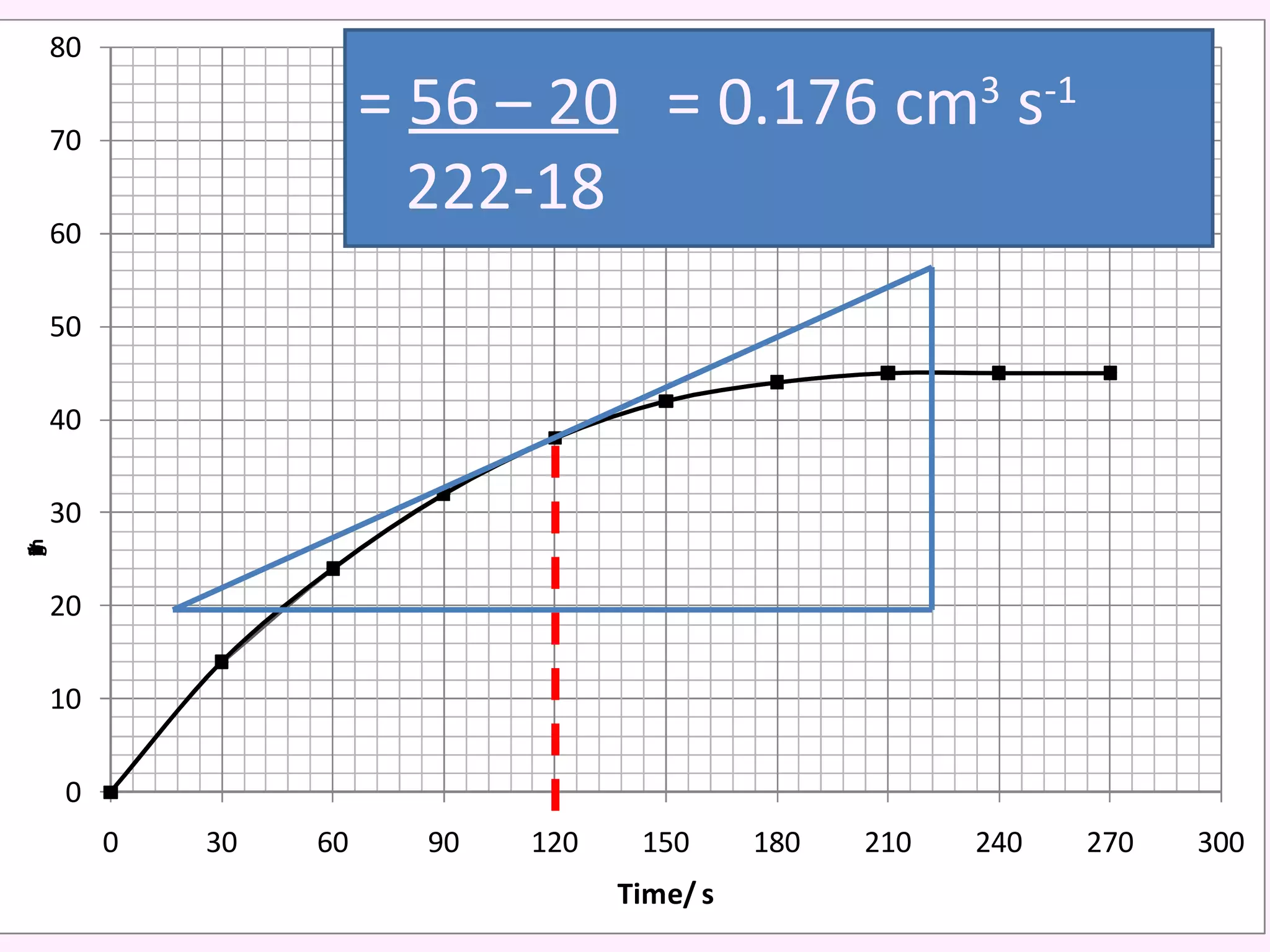
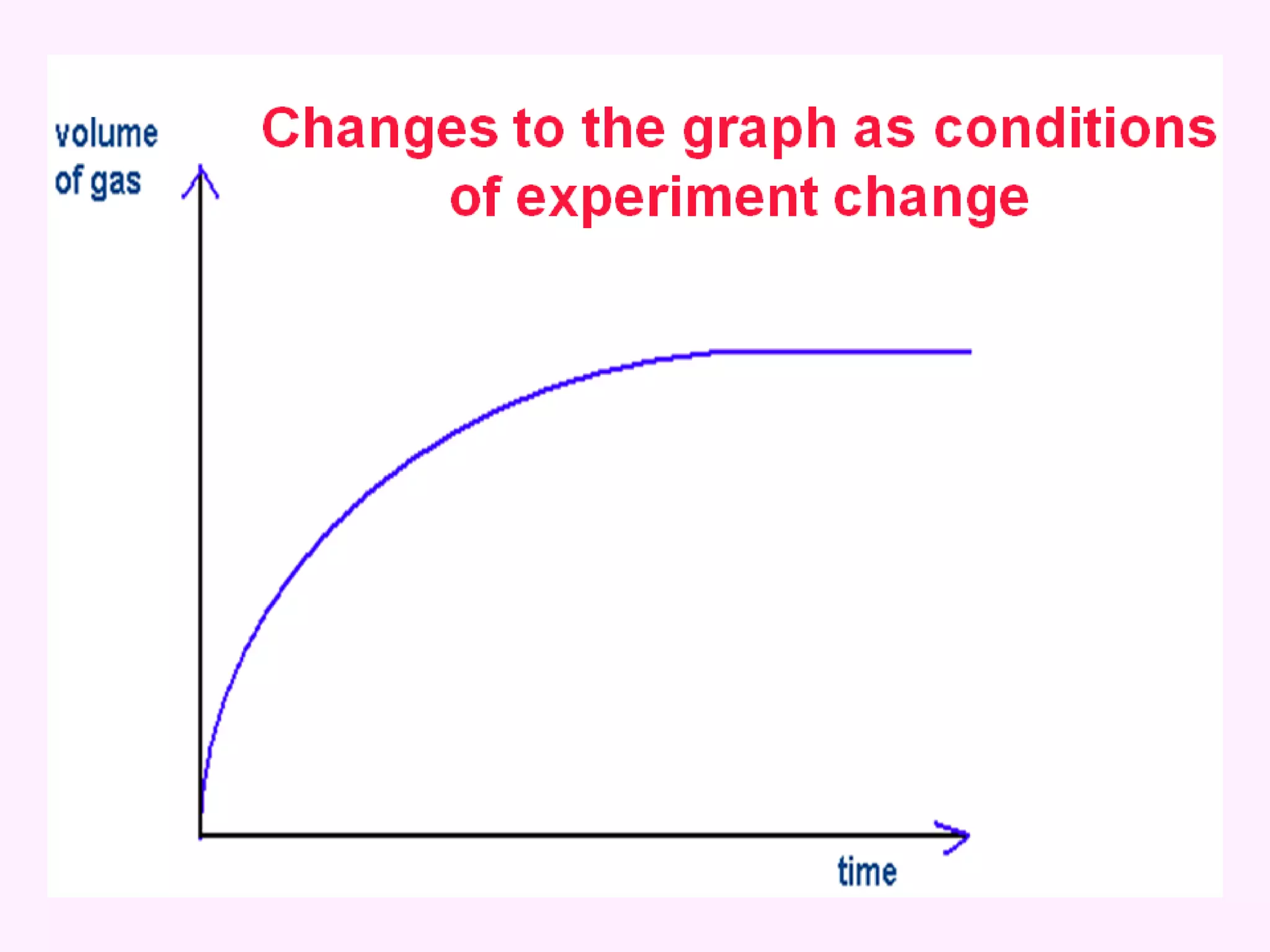
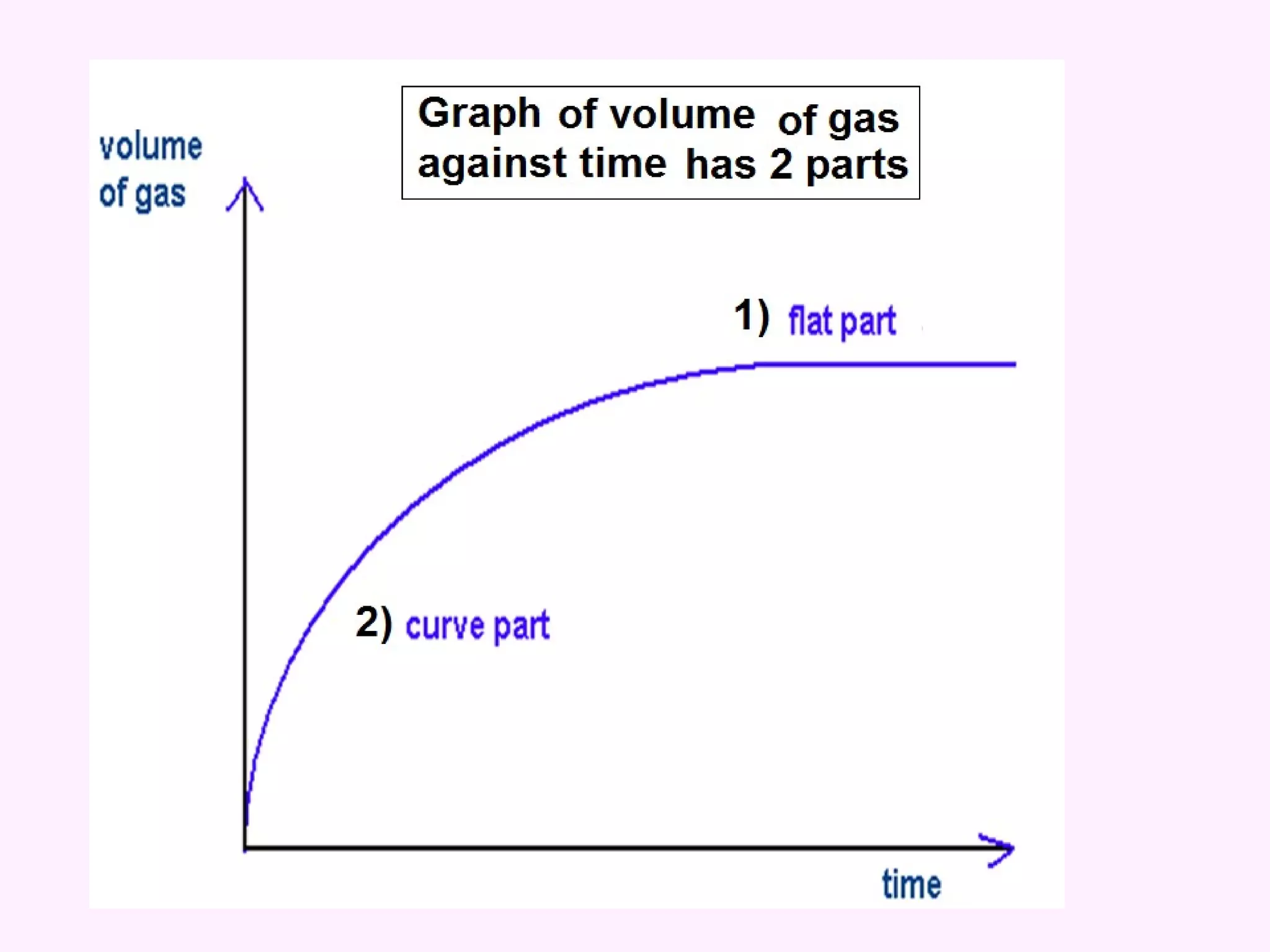
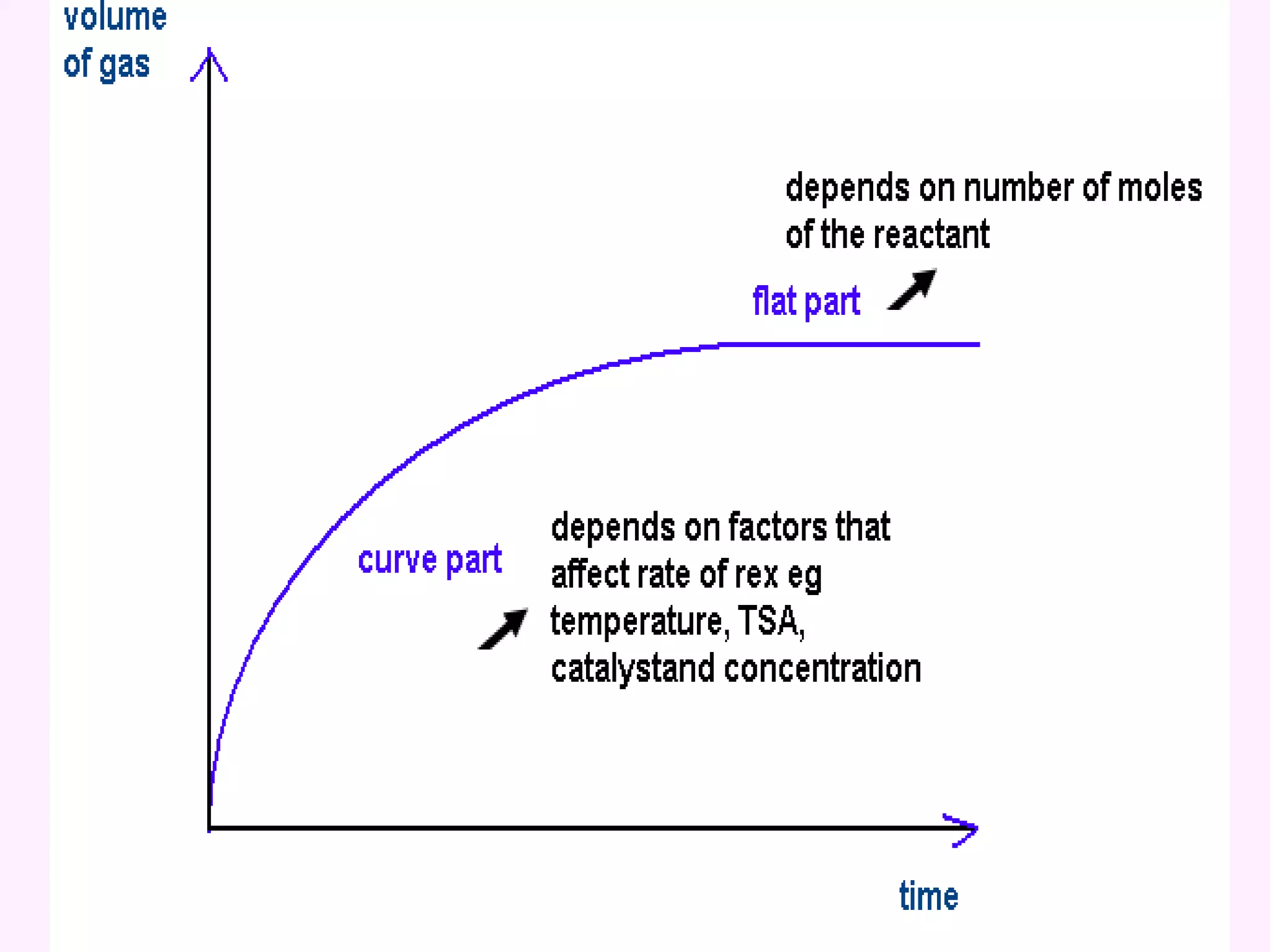
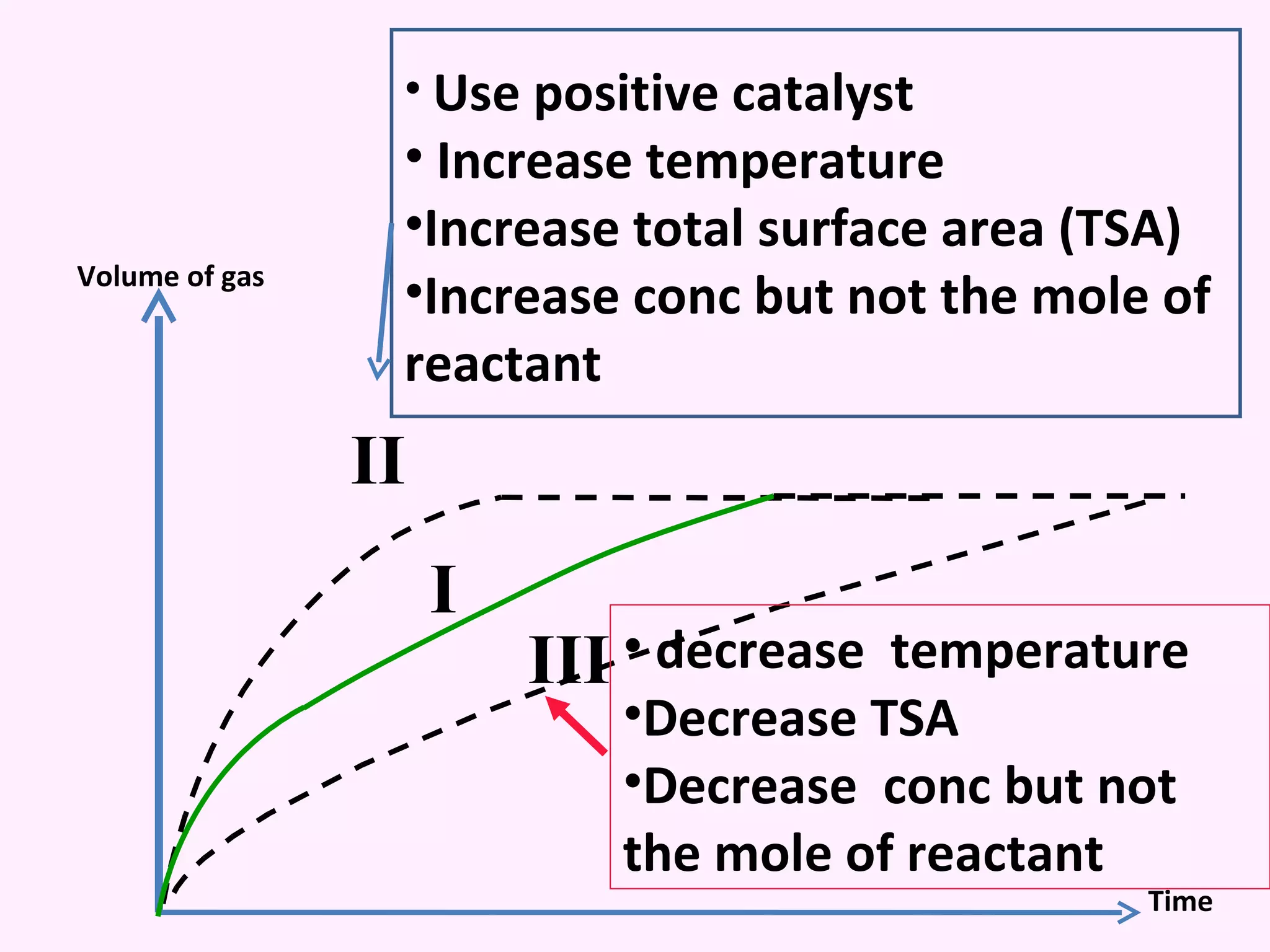
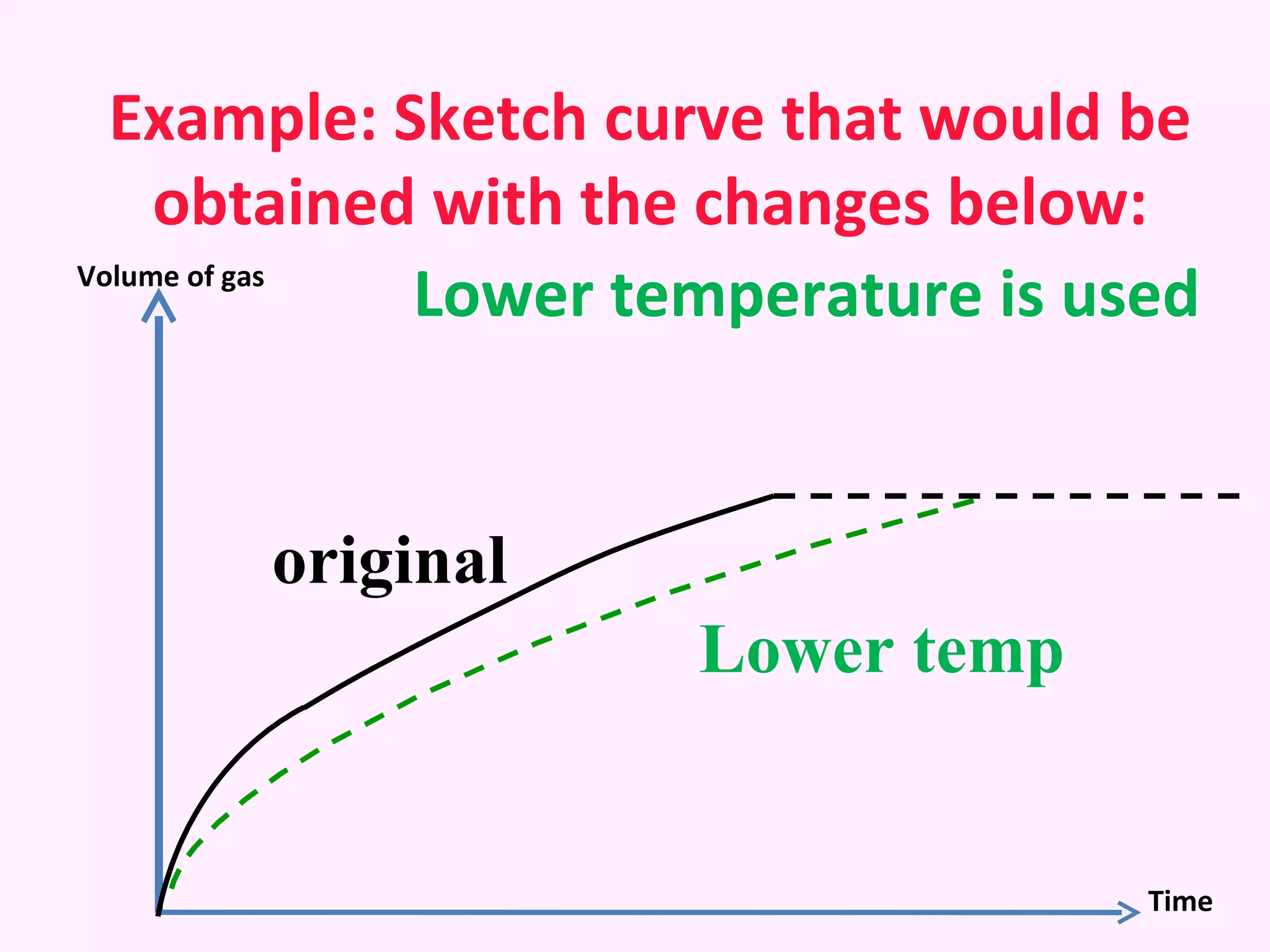
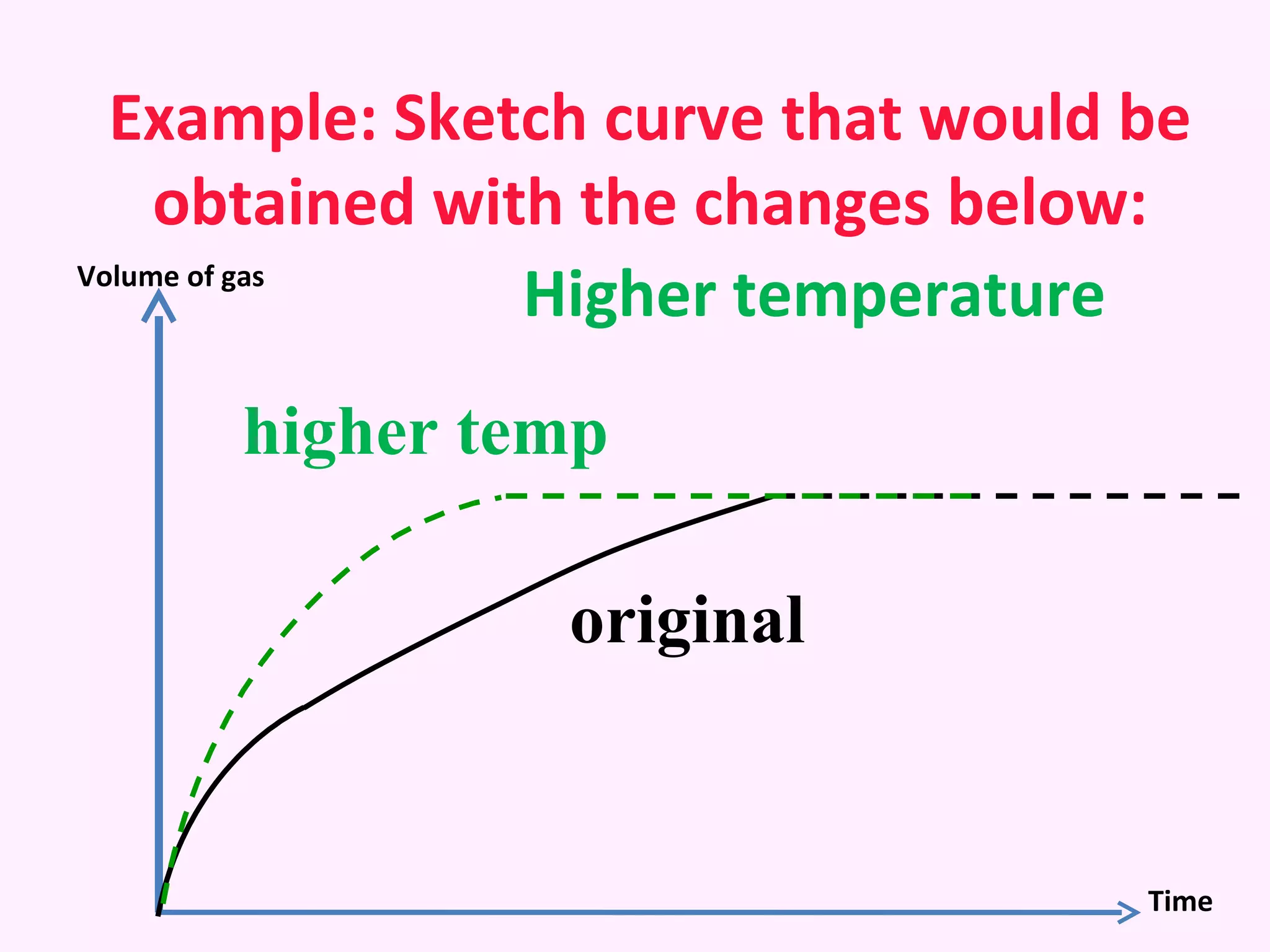
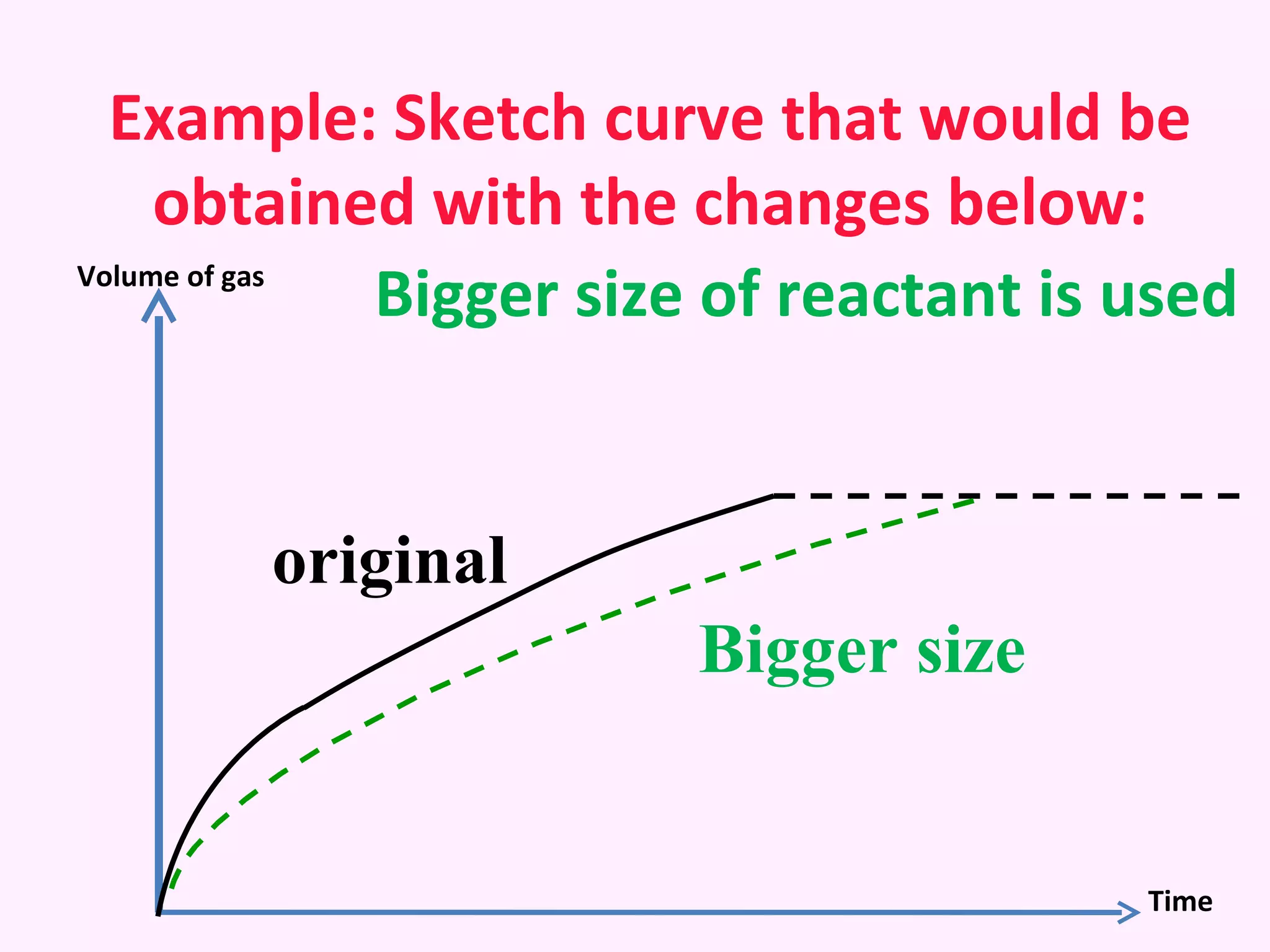
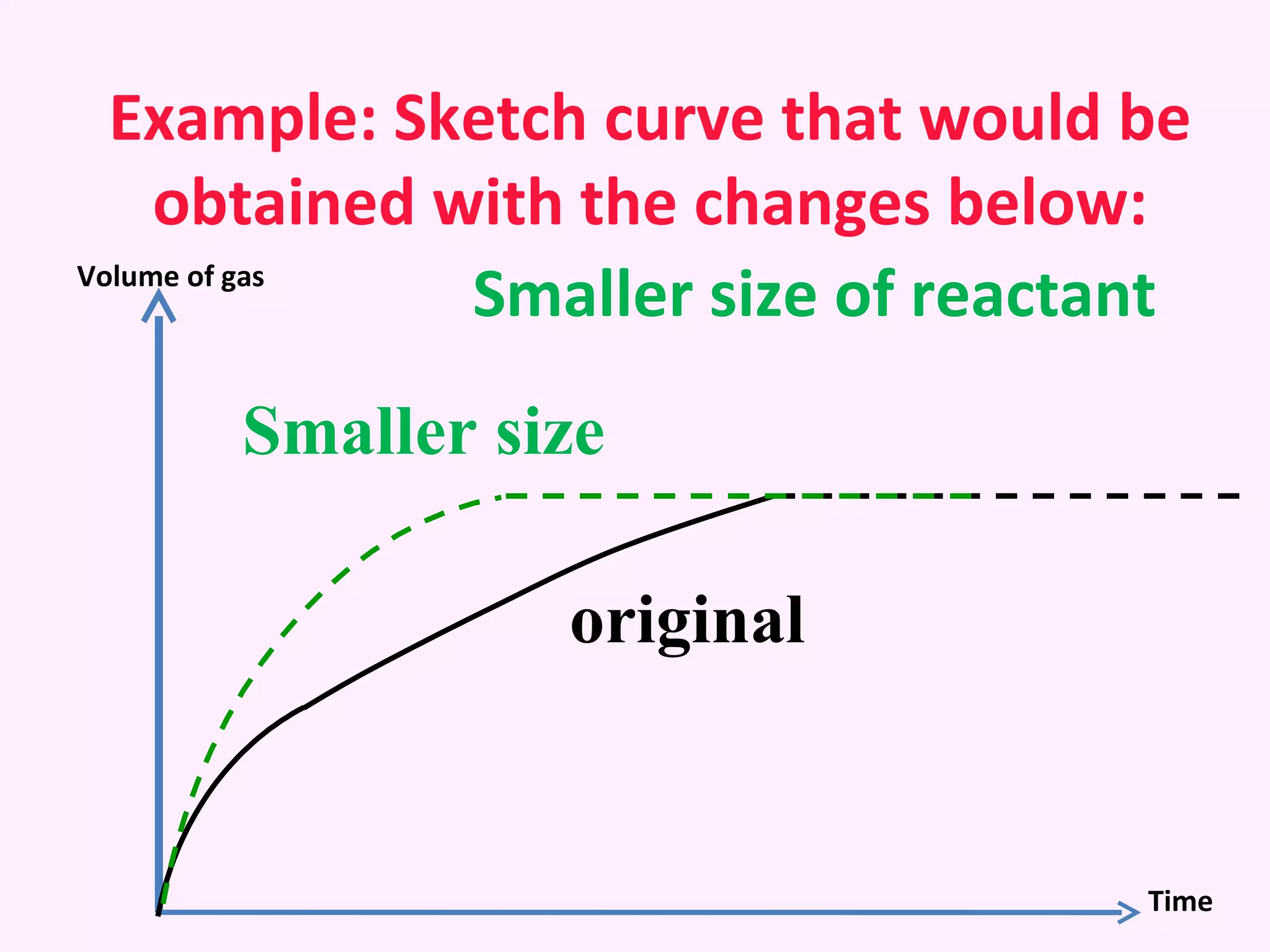
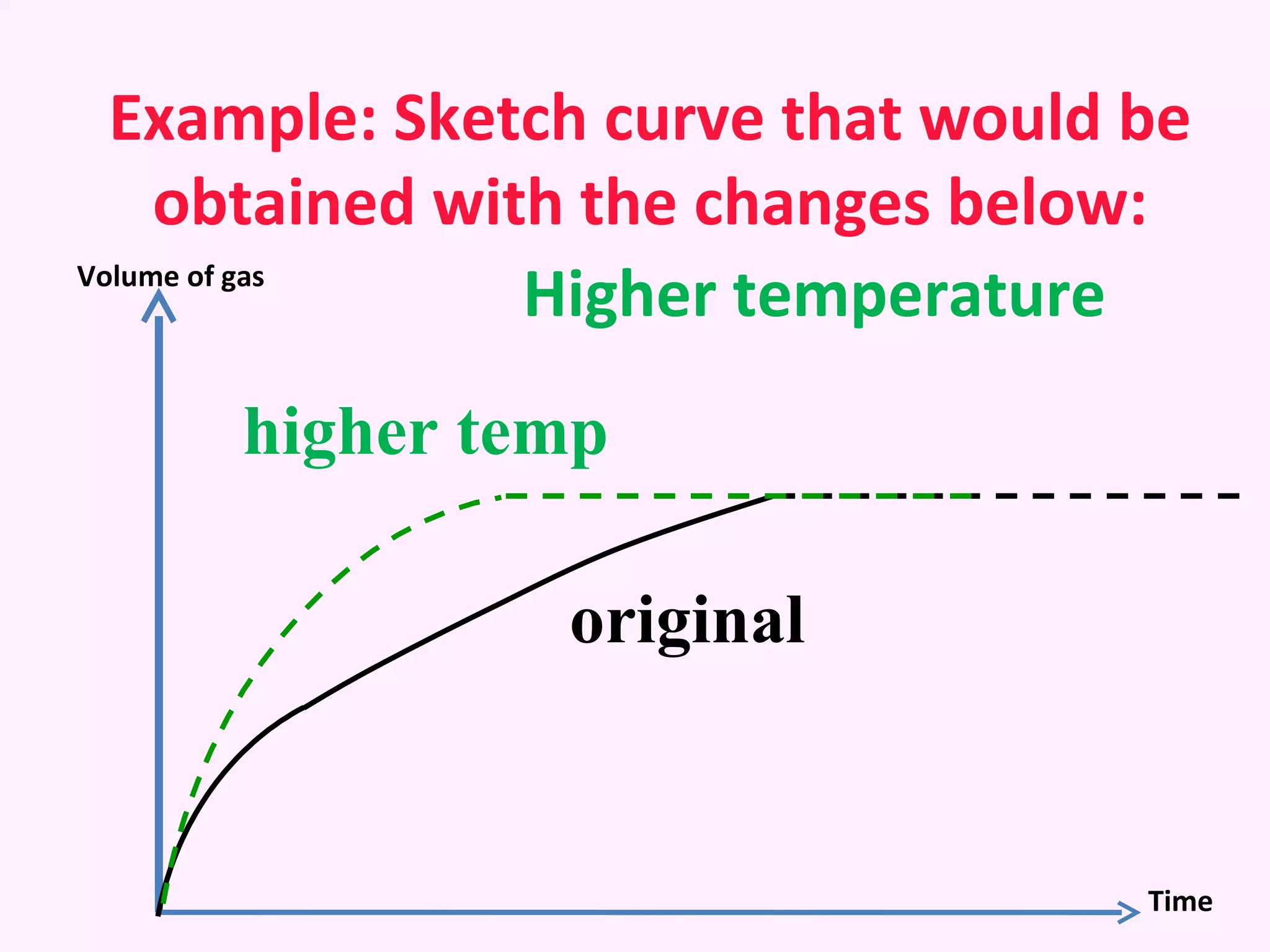
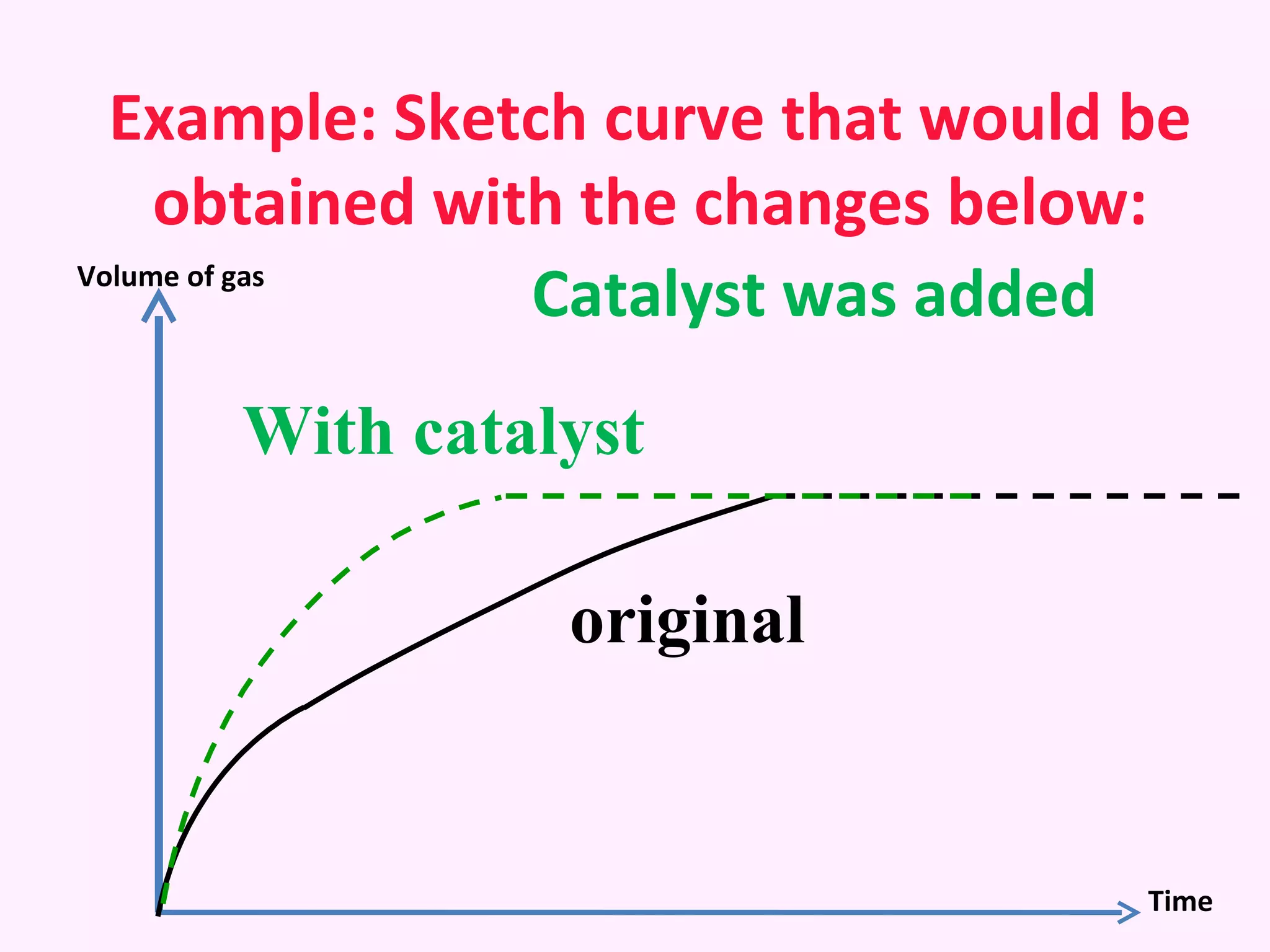
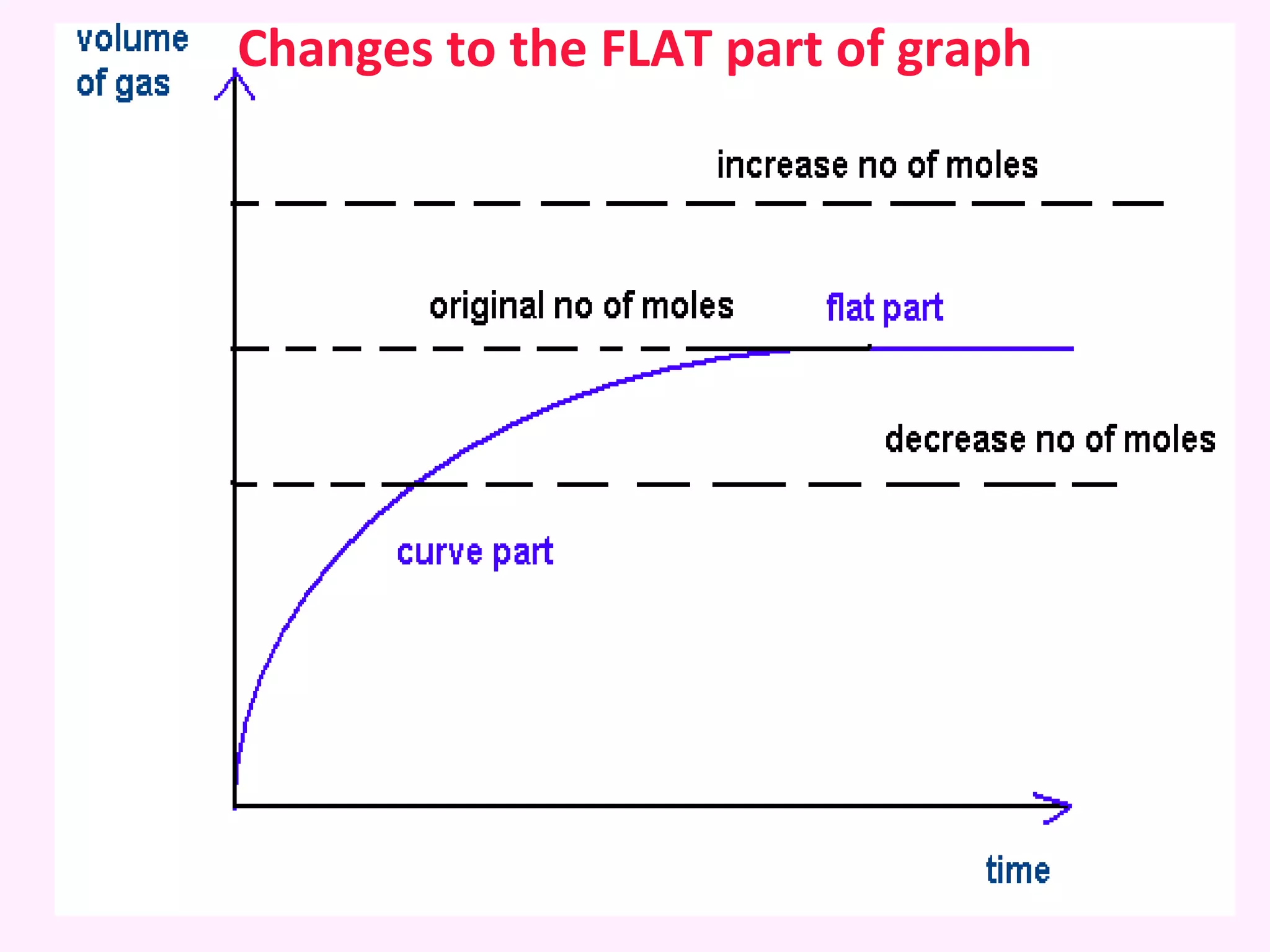
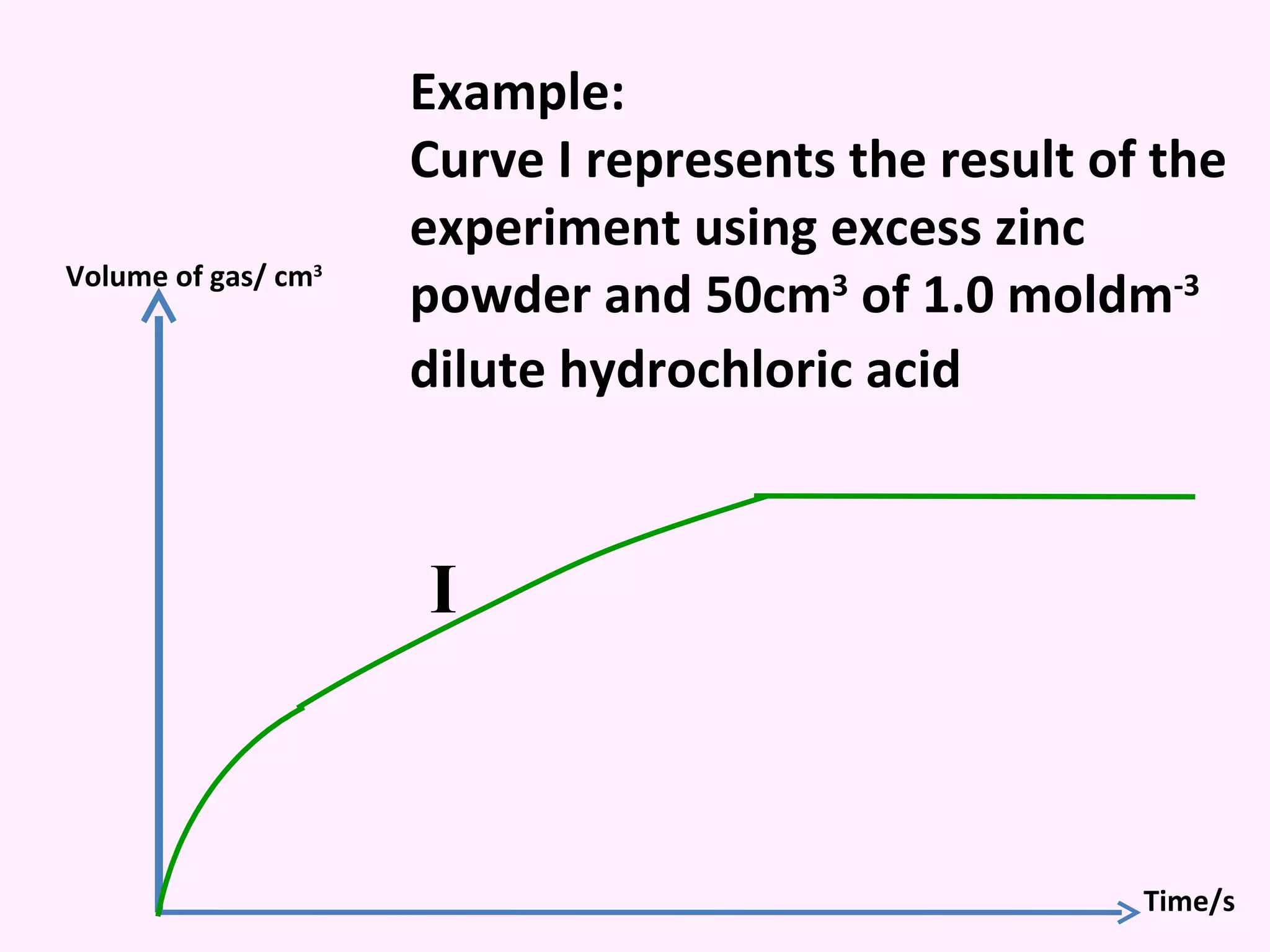
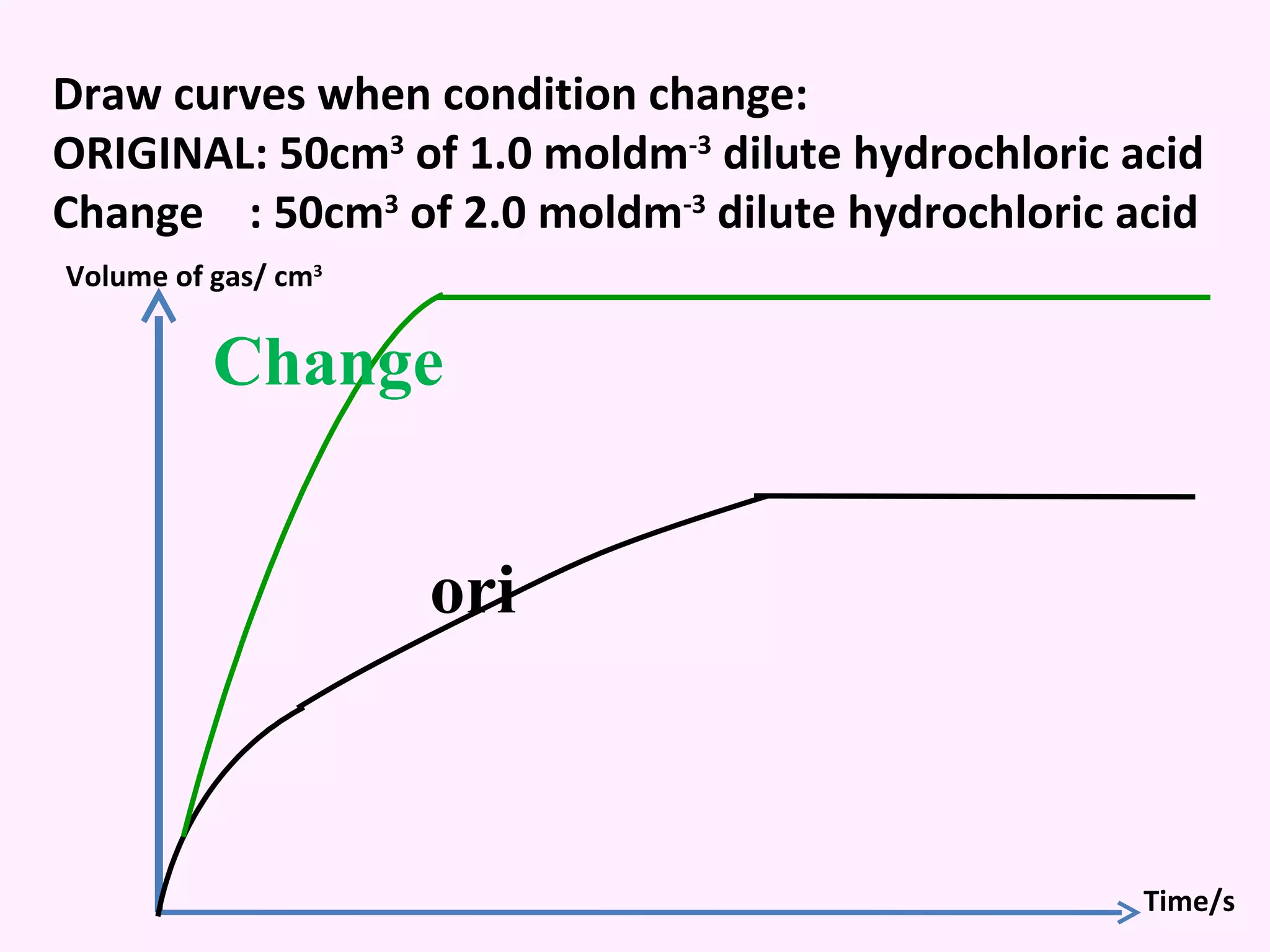
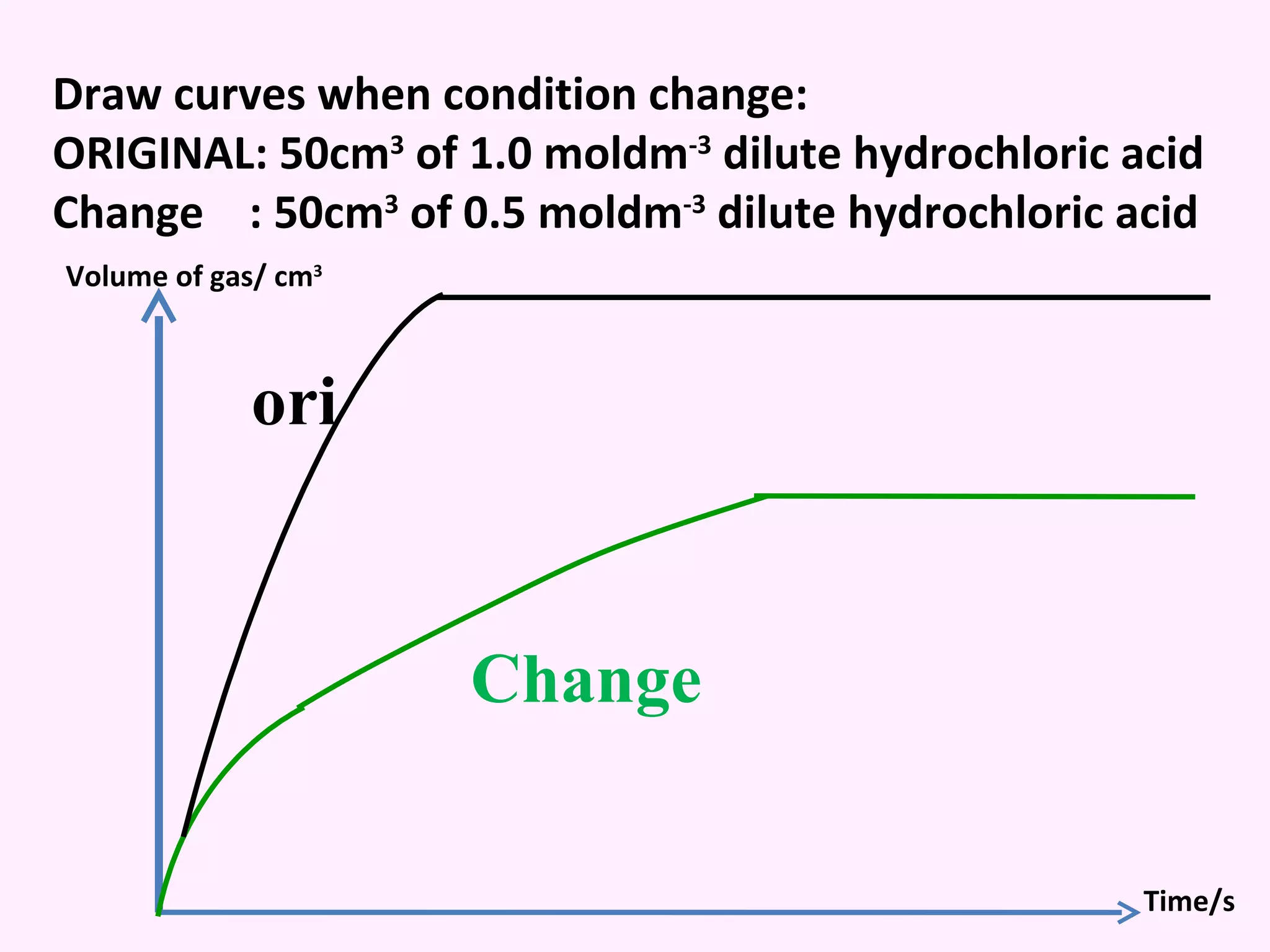
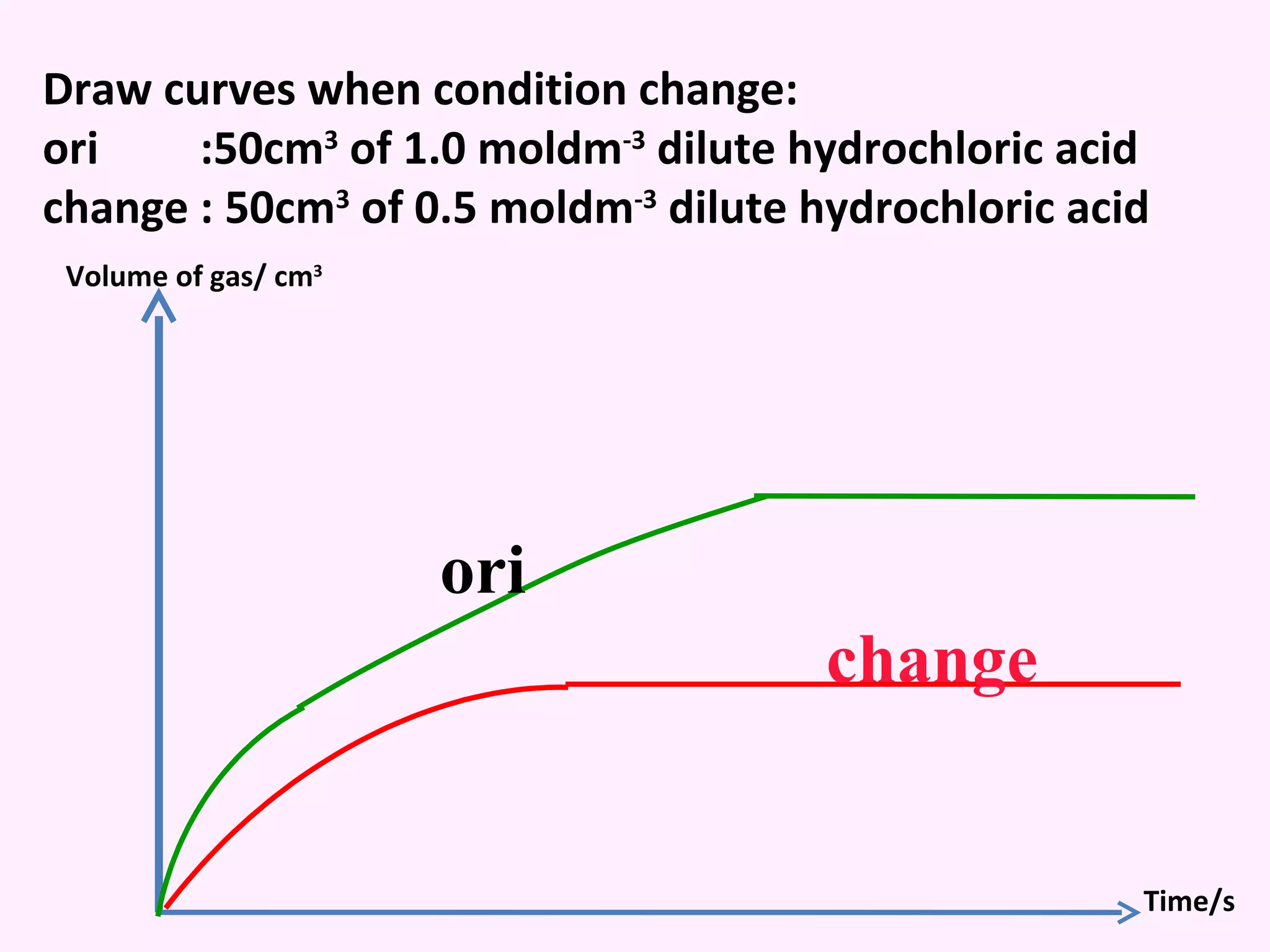
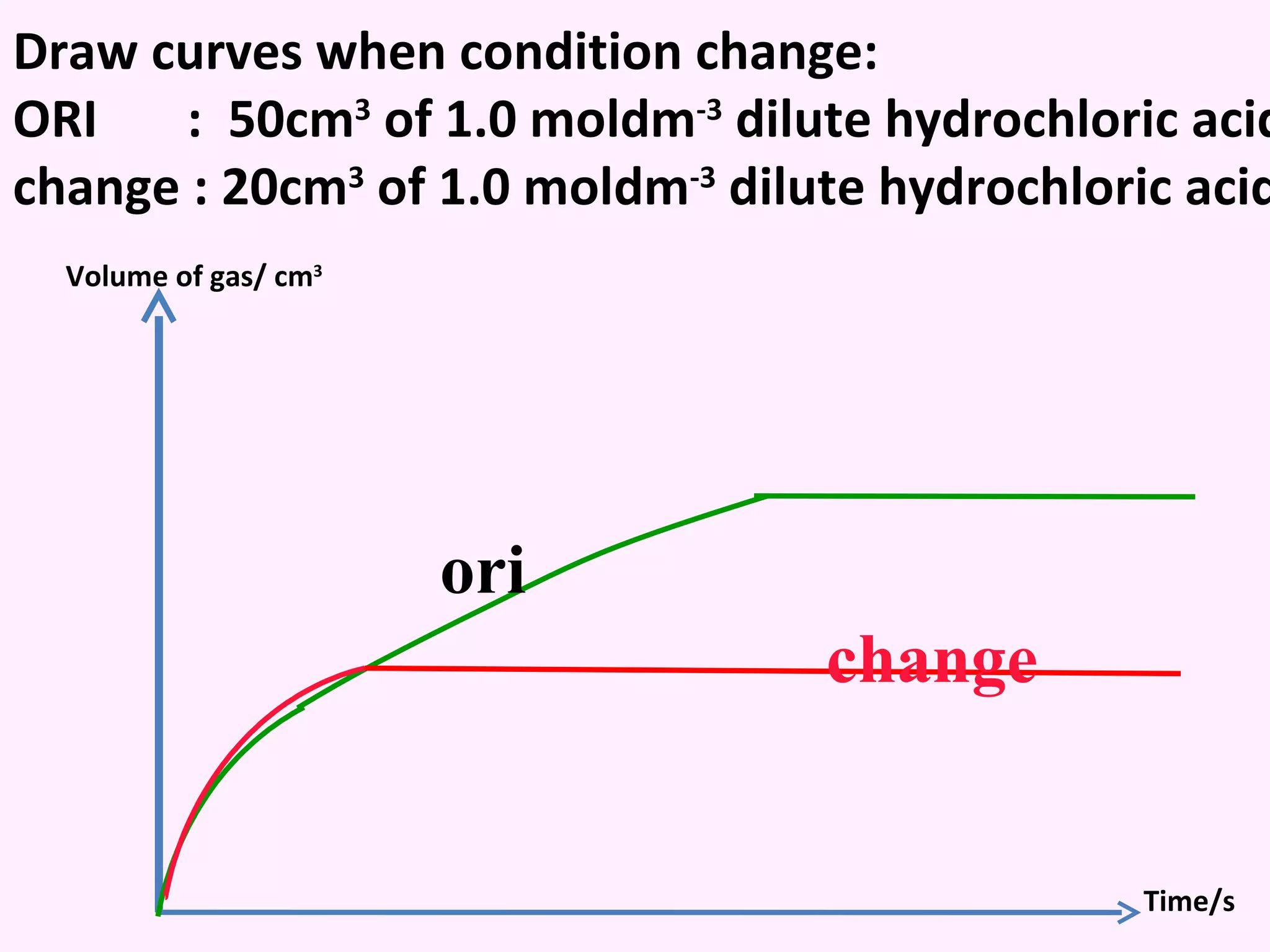
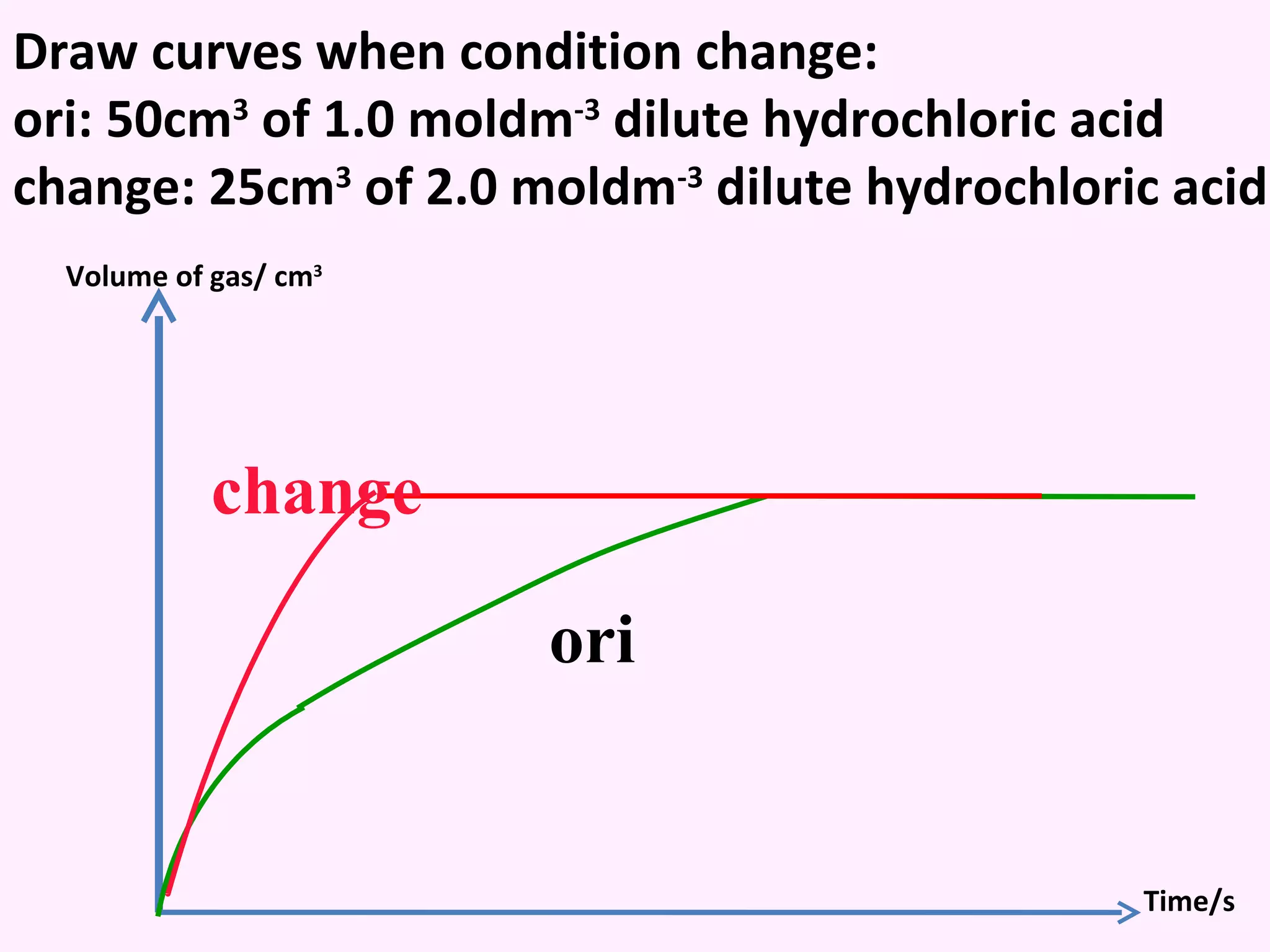
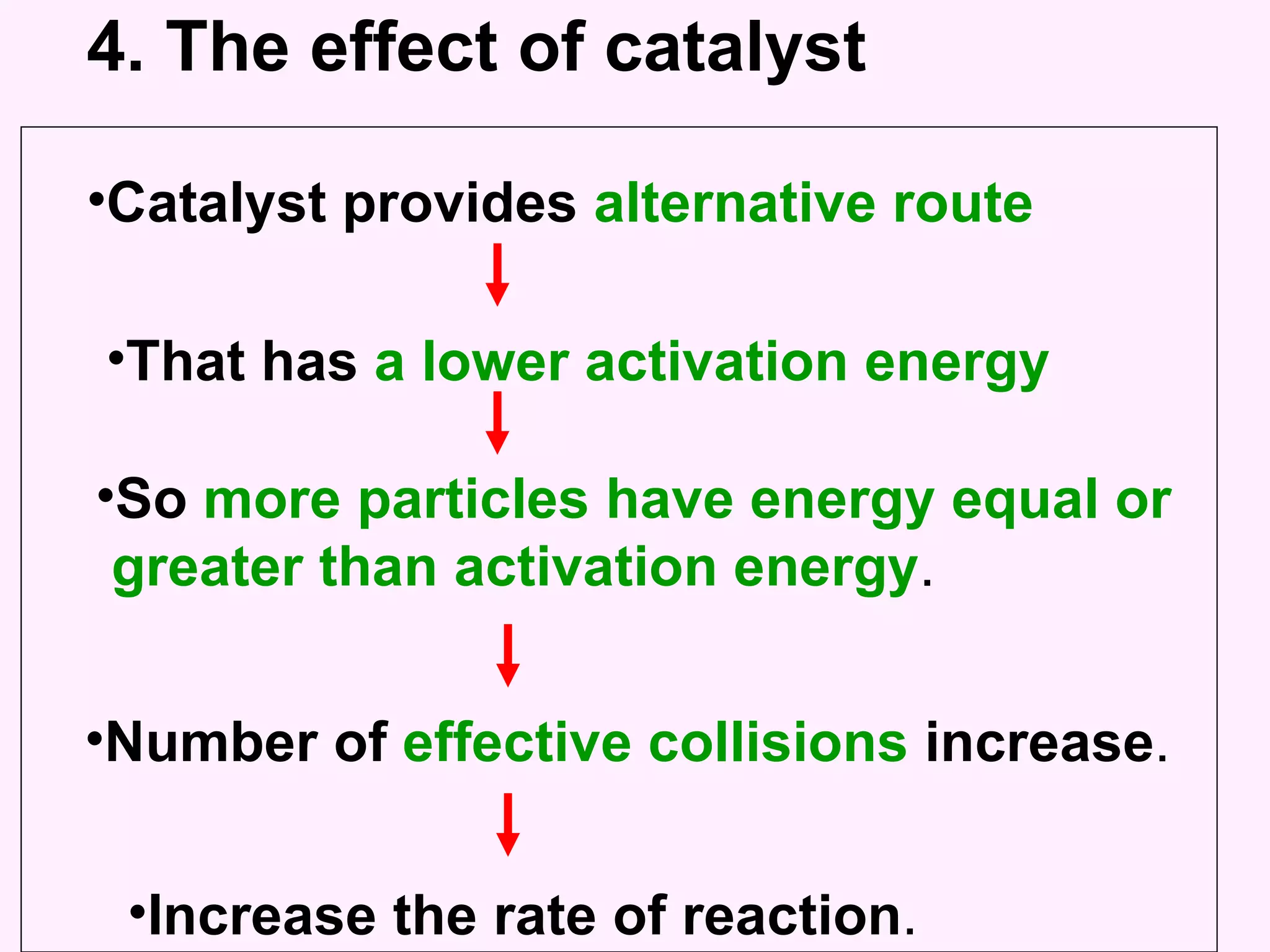
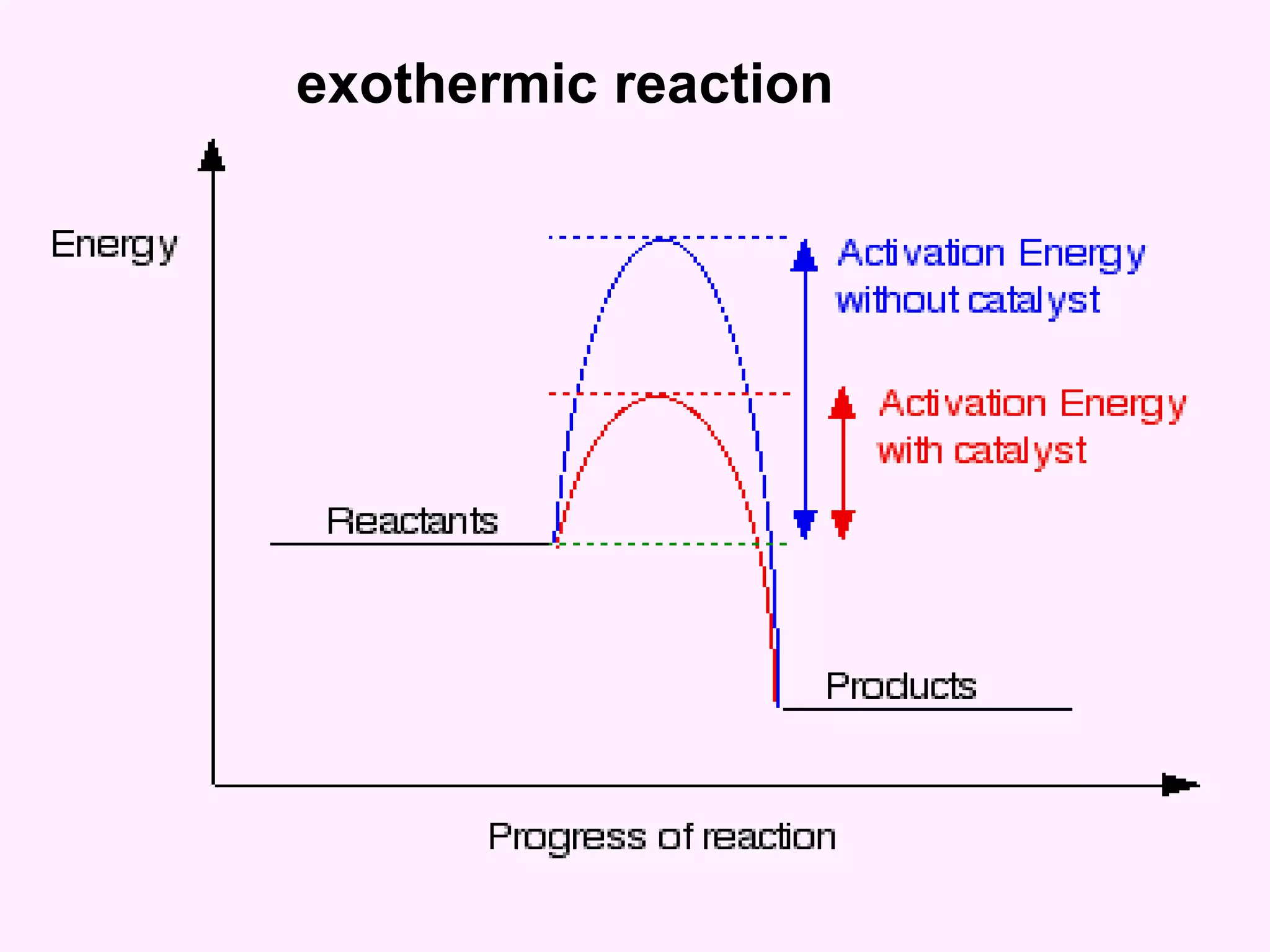
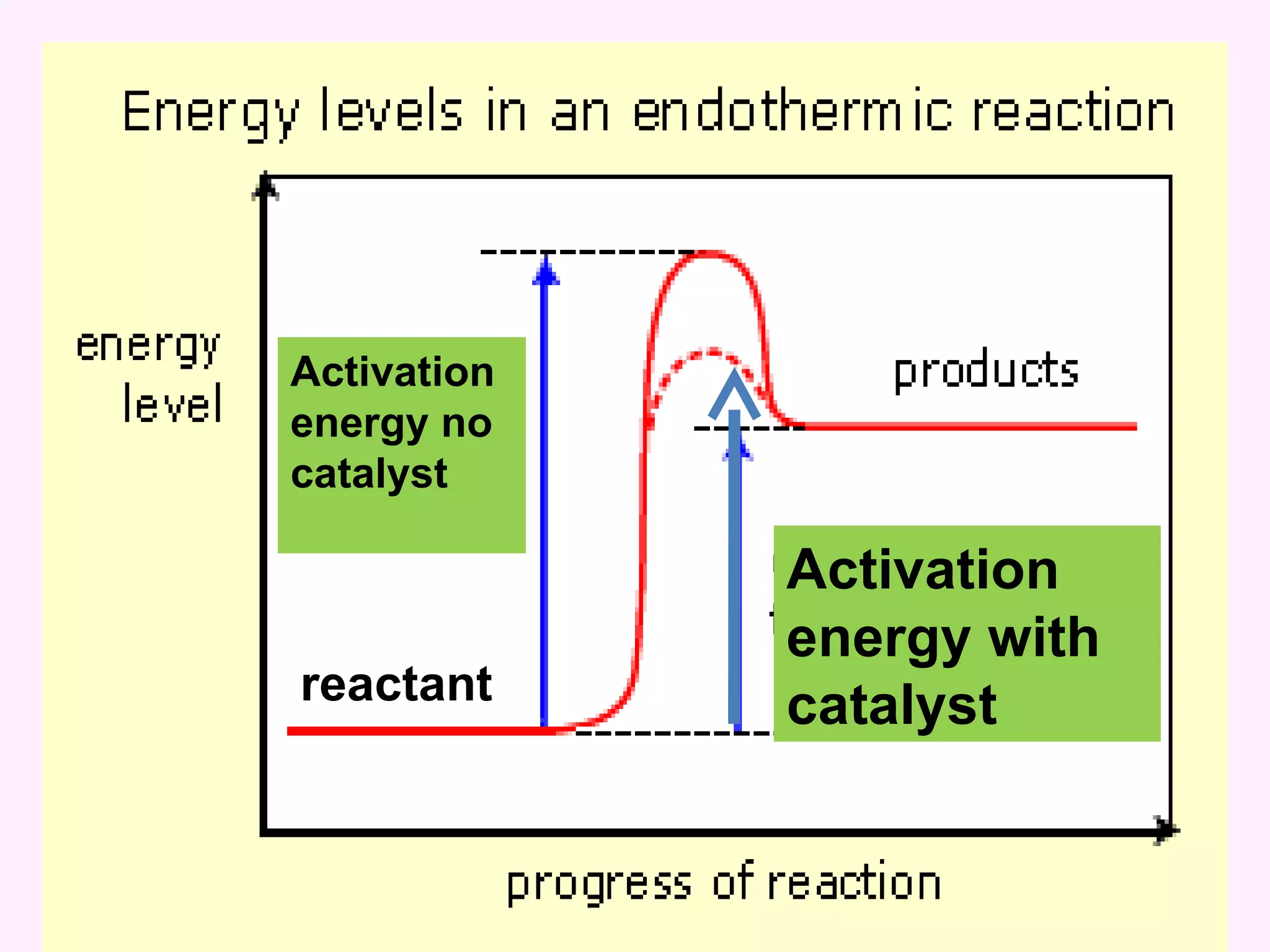
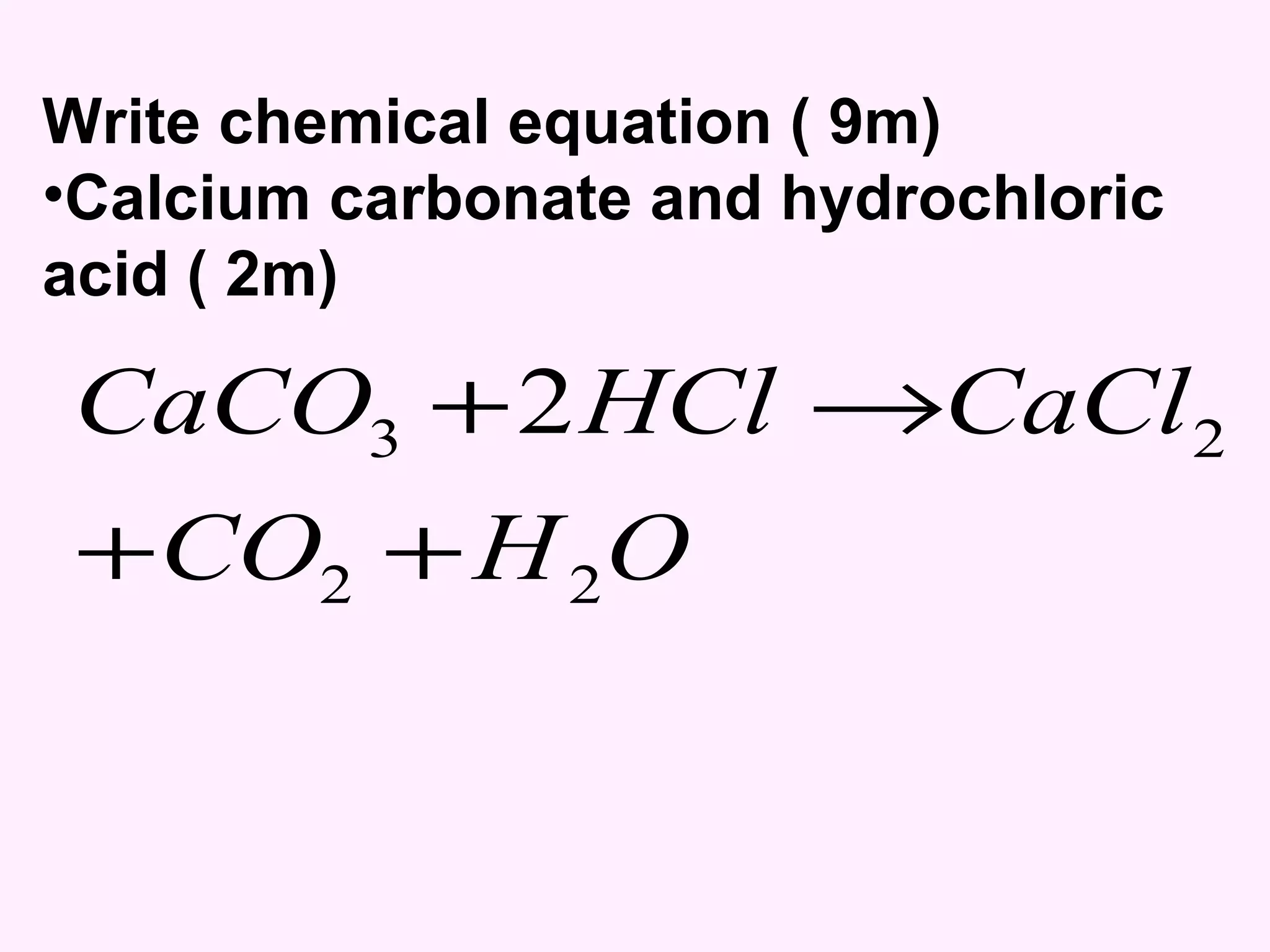
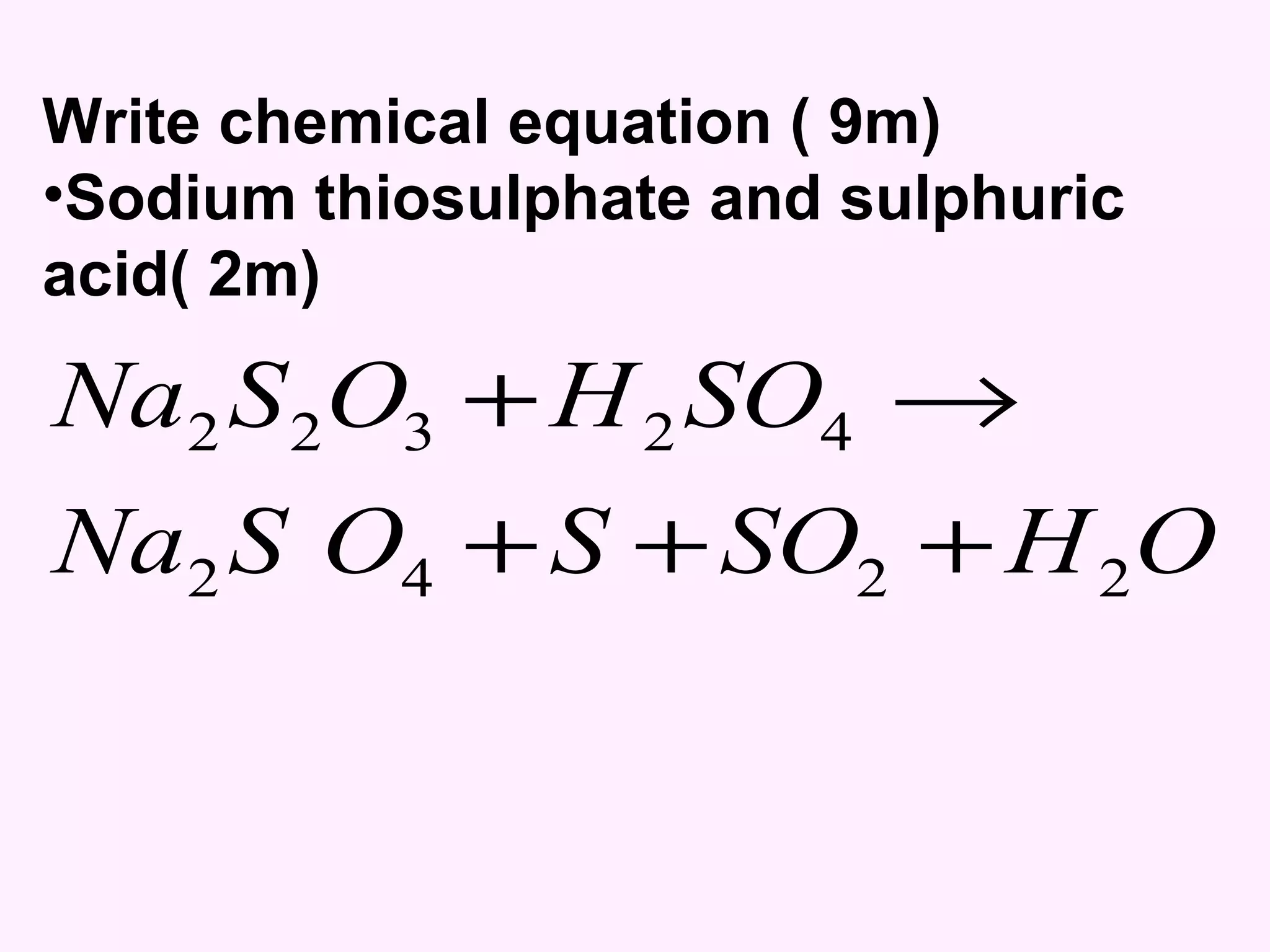
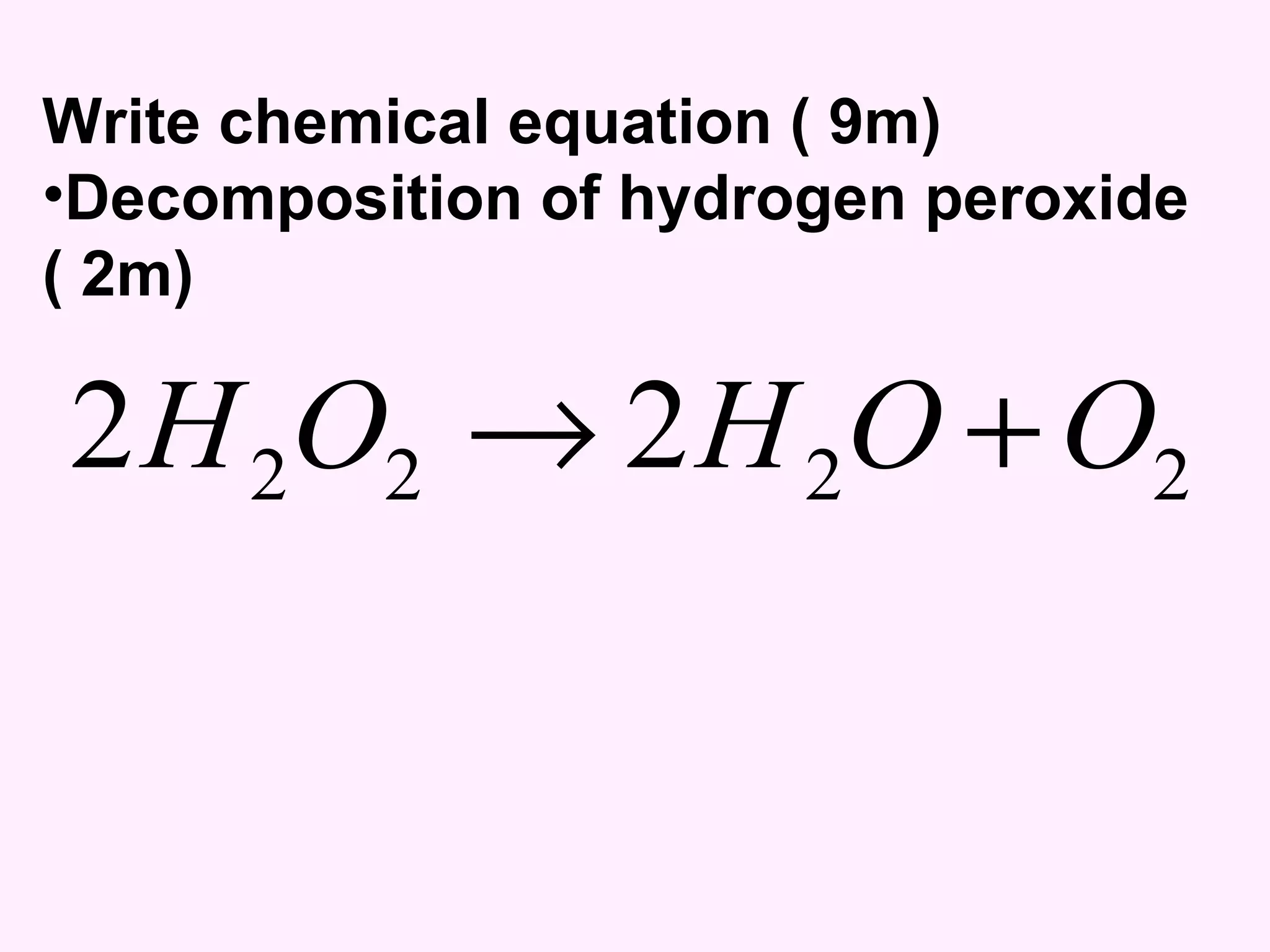The document discusses factors that affect the rate of chemical reactions including temperature, concentration, surface area, and the use of catalysts. It explains how increasing temperature, concentration, or surface area increases the frequency of particle collisions, leading to a faster reaction rate. Catalysts provide an alternative reaction pathway with lower activation energy, allowing more particles to have sufficient energy for reaction. Examples are provided of calculating reaction rates from graphs and sketching how rate curves would change with different conditions.