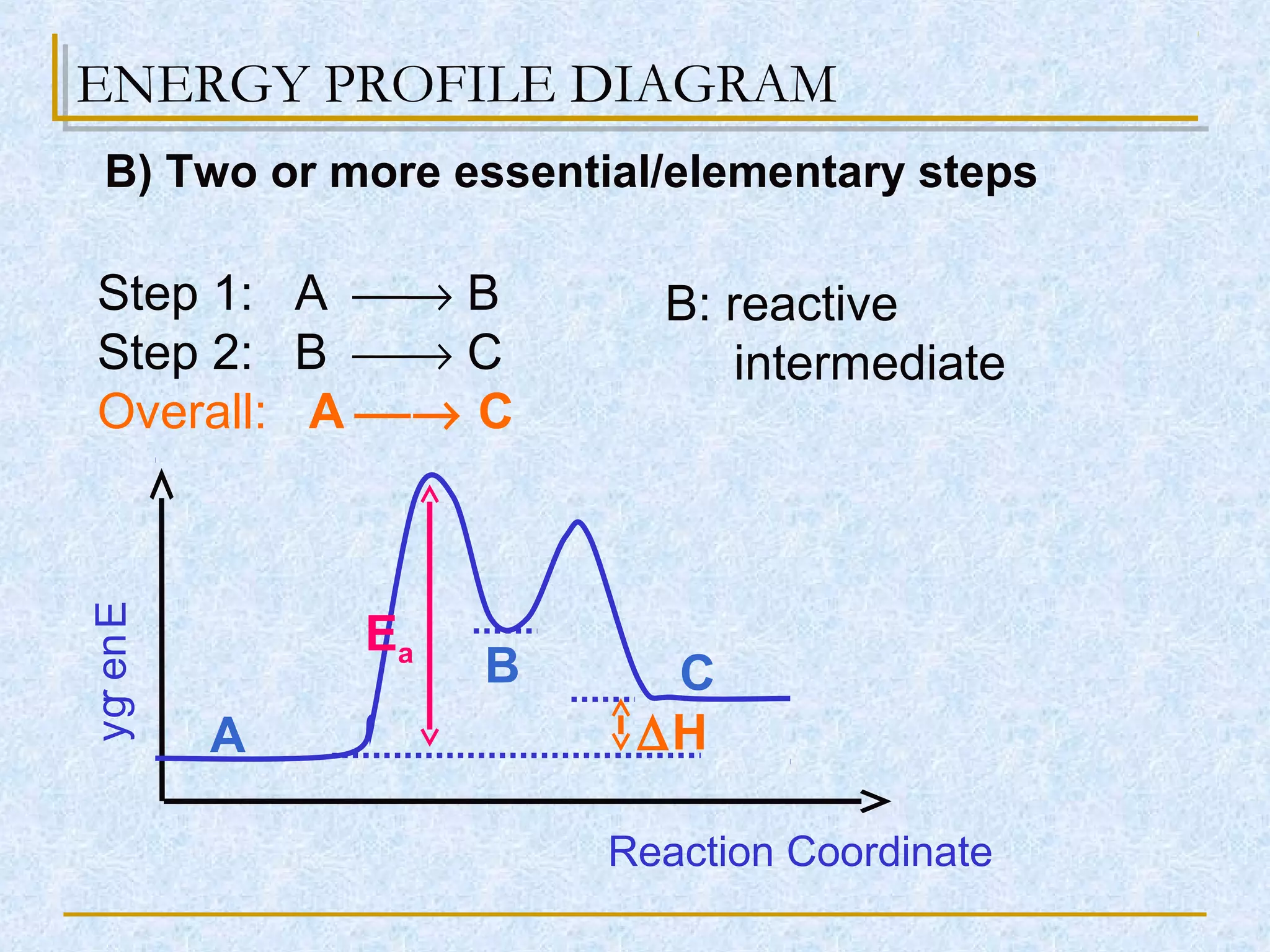
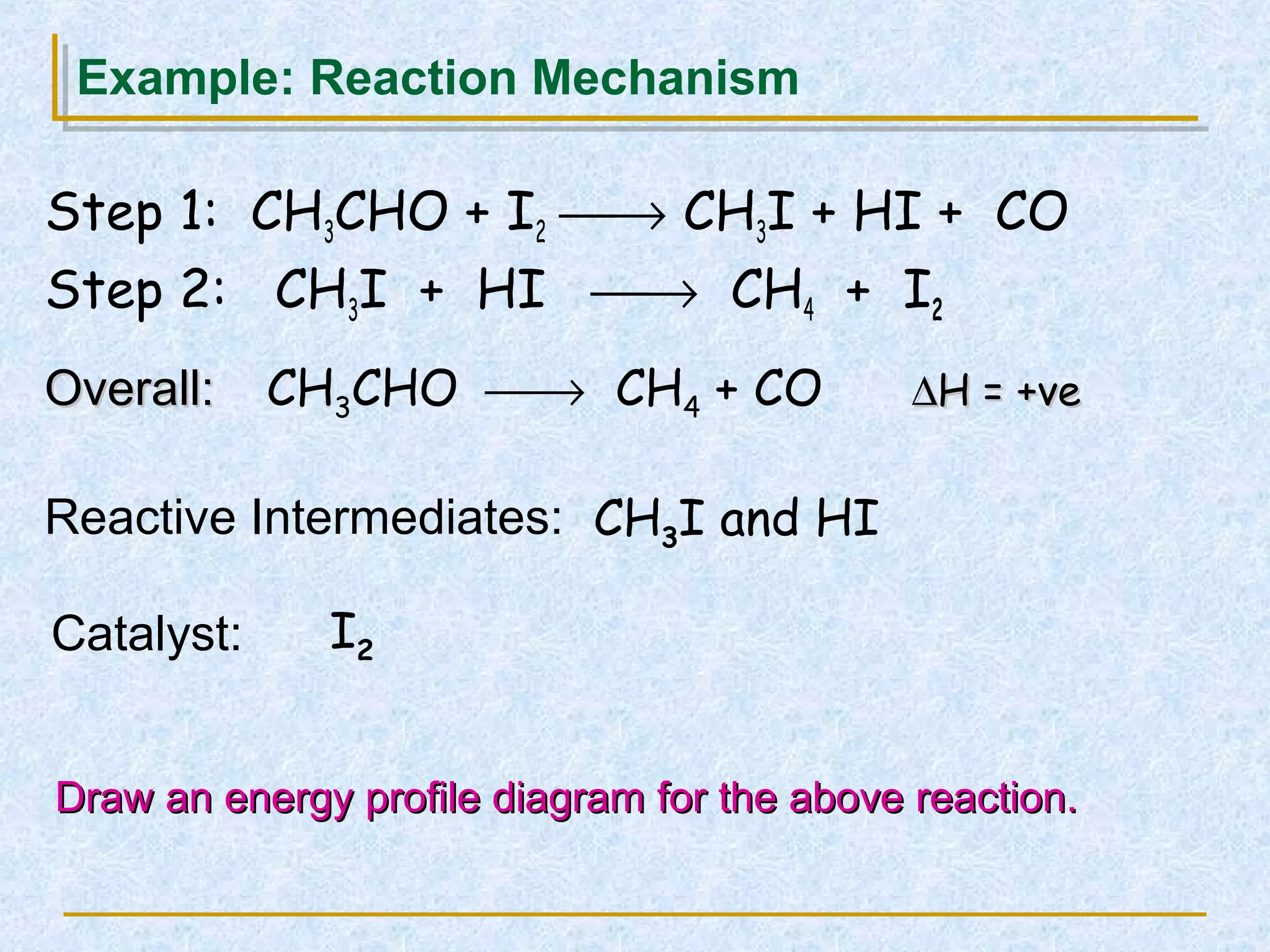
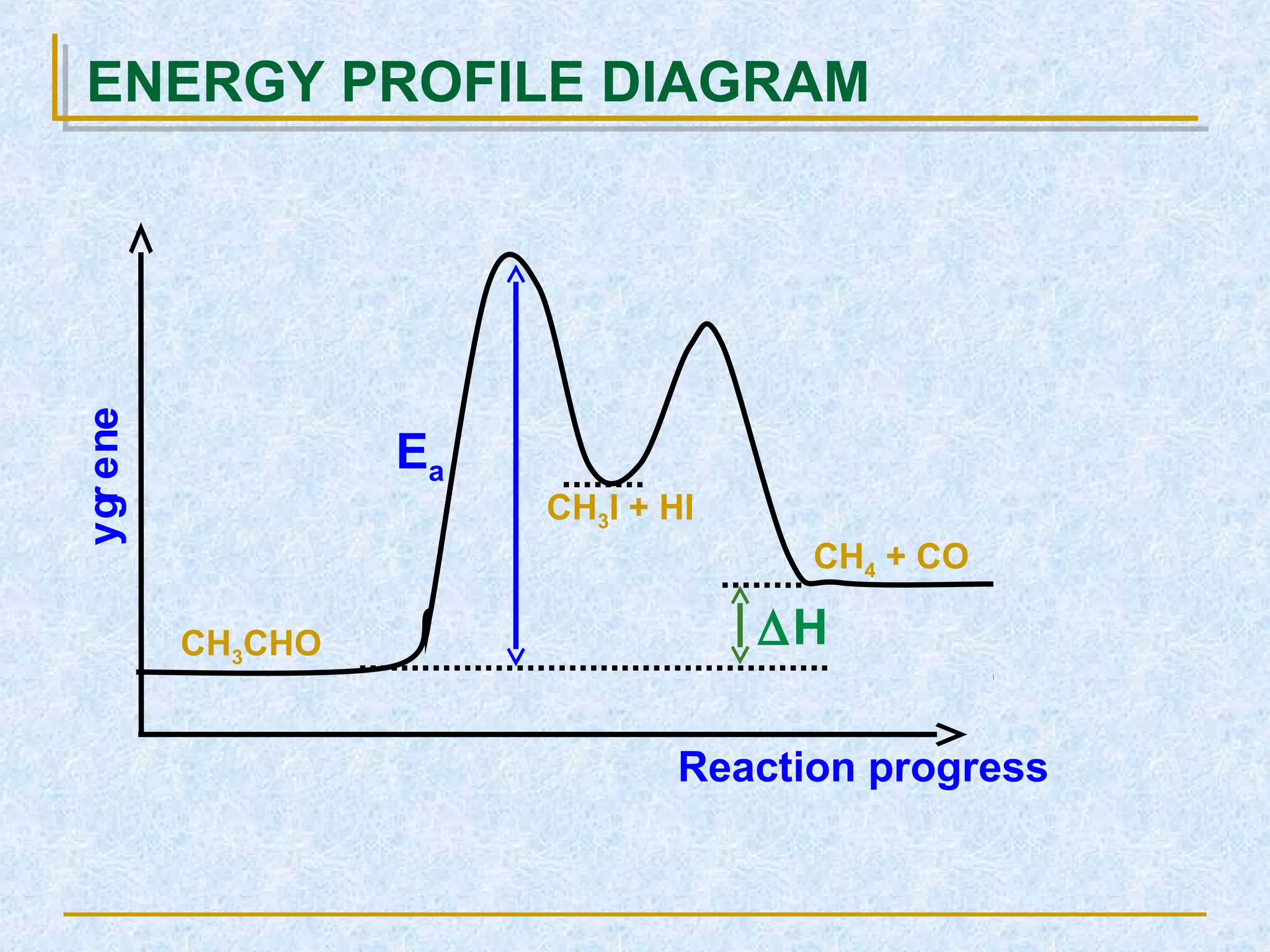
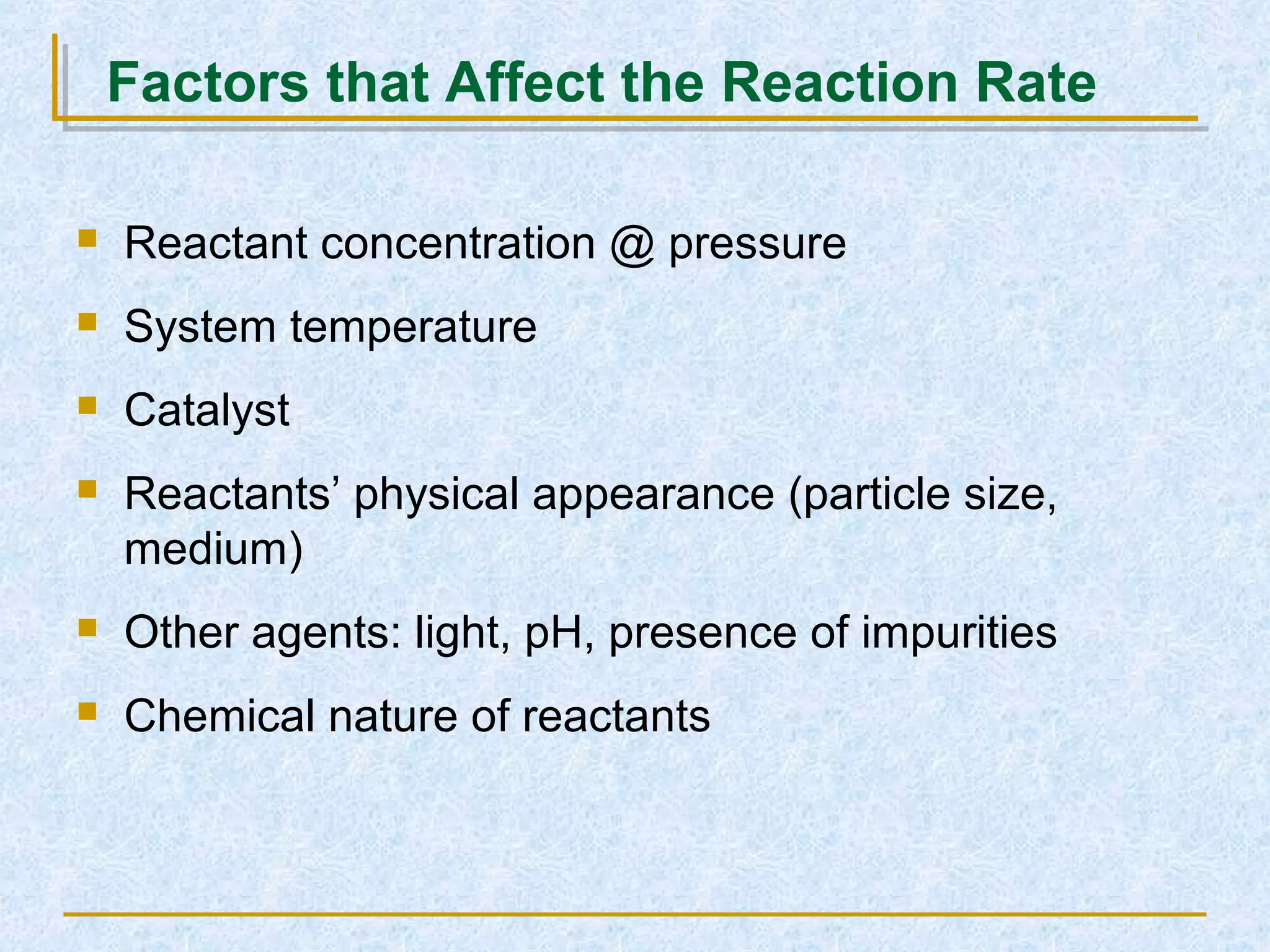
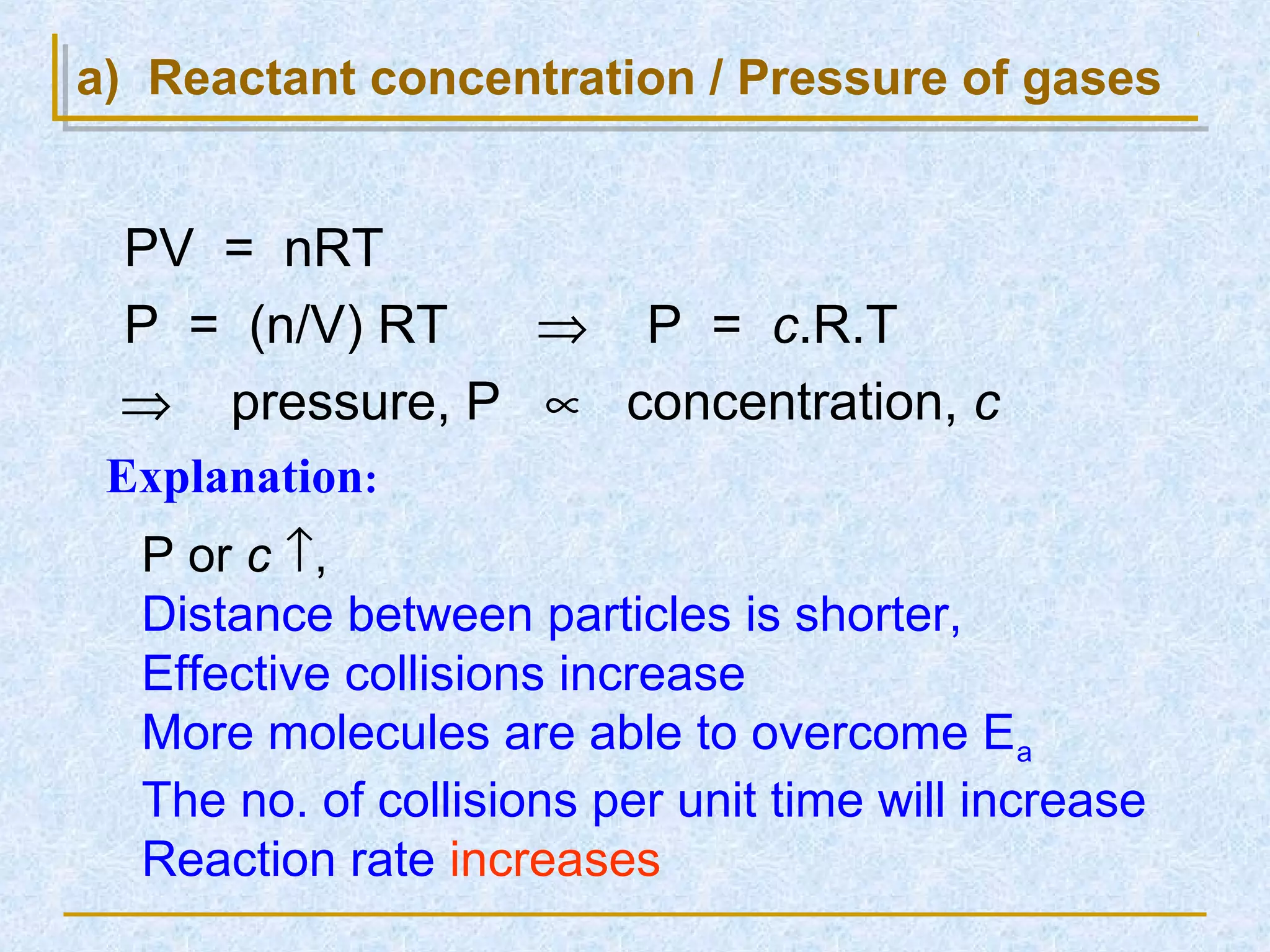
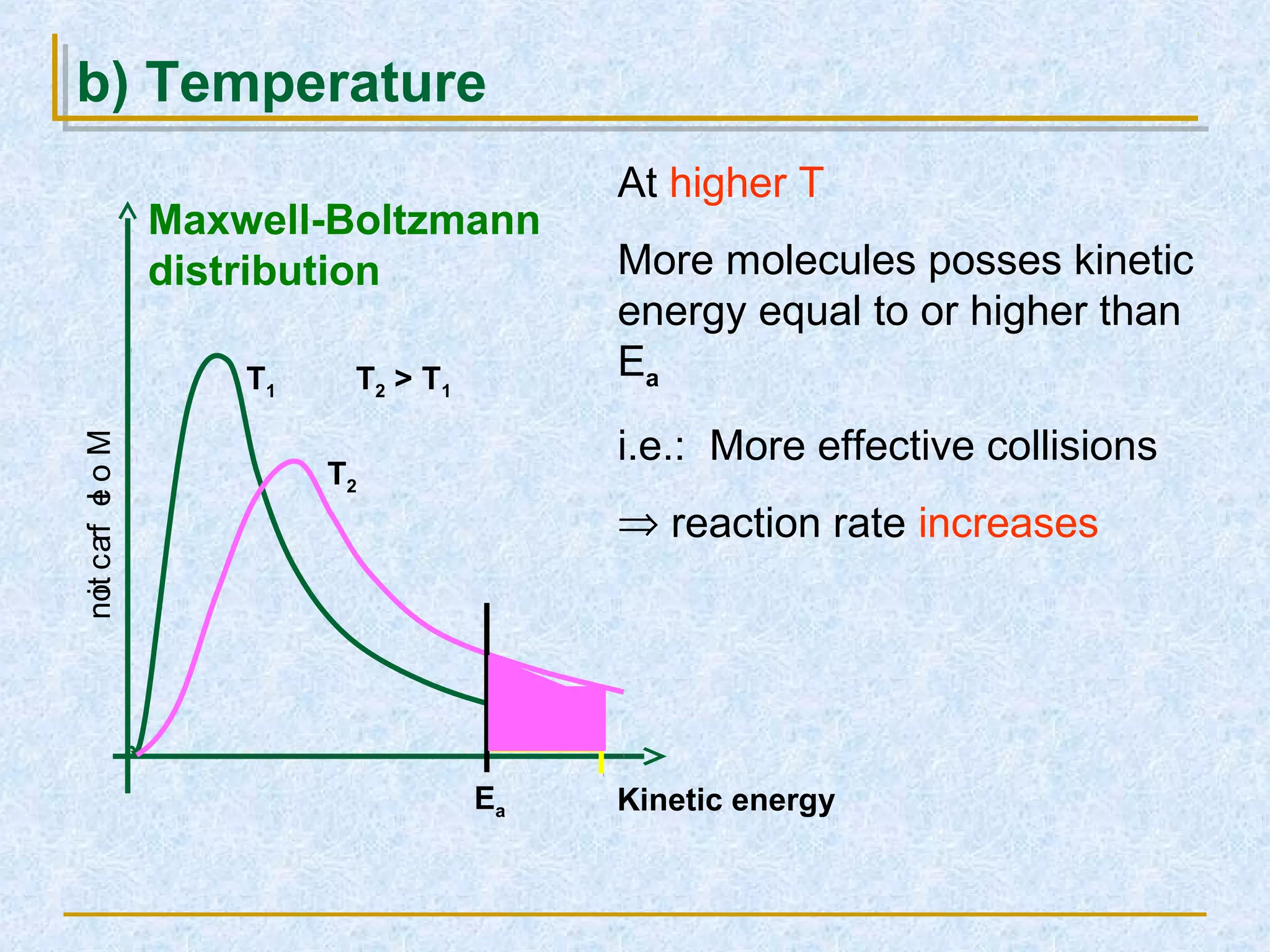
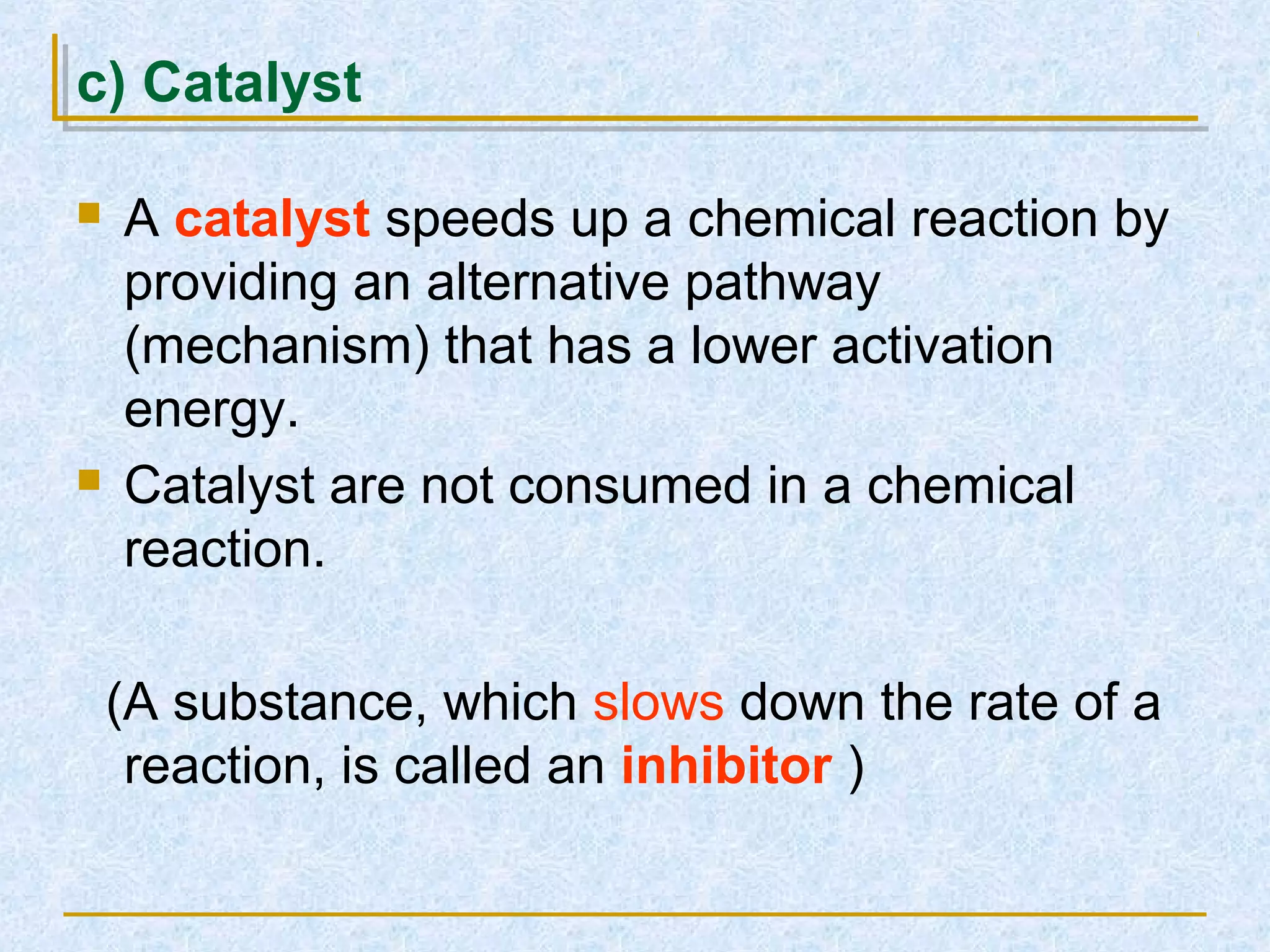
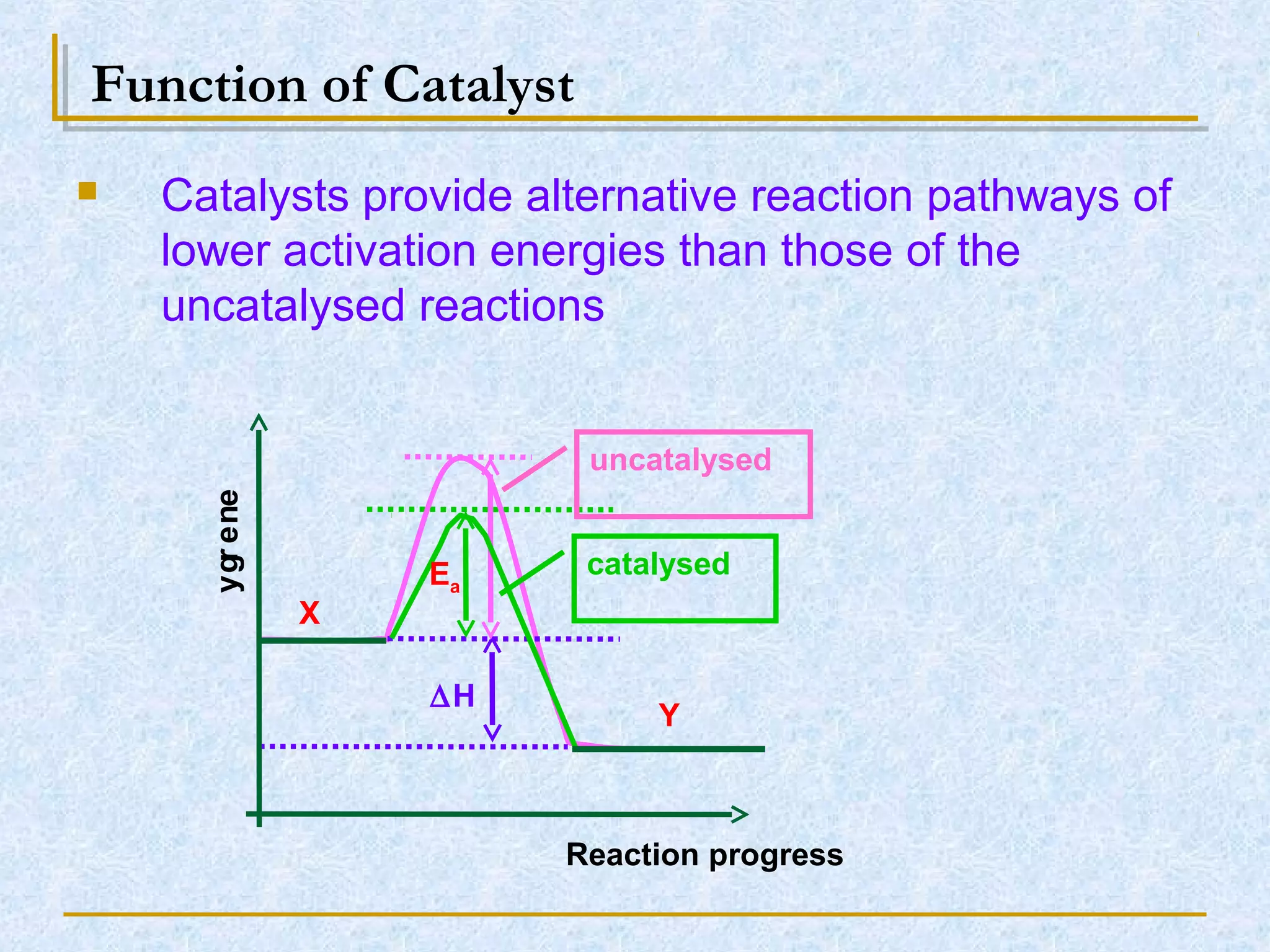
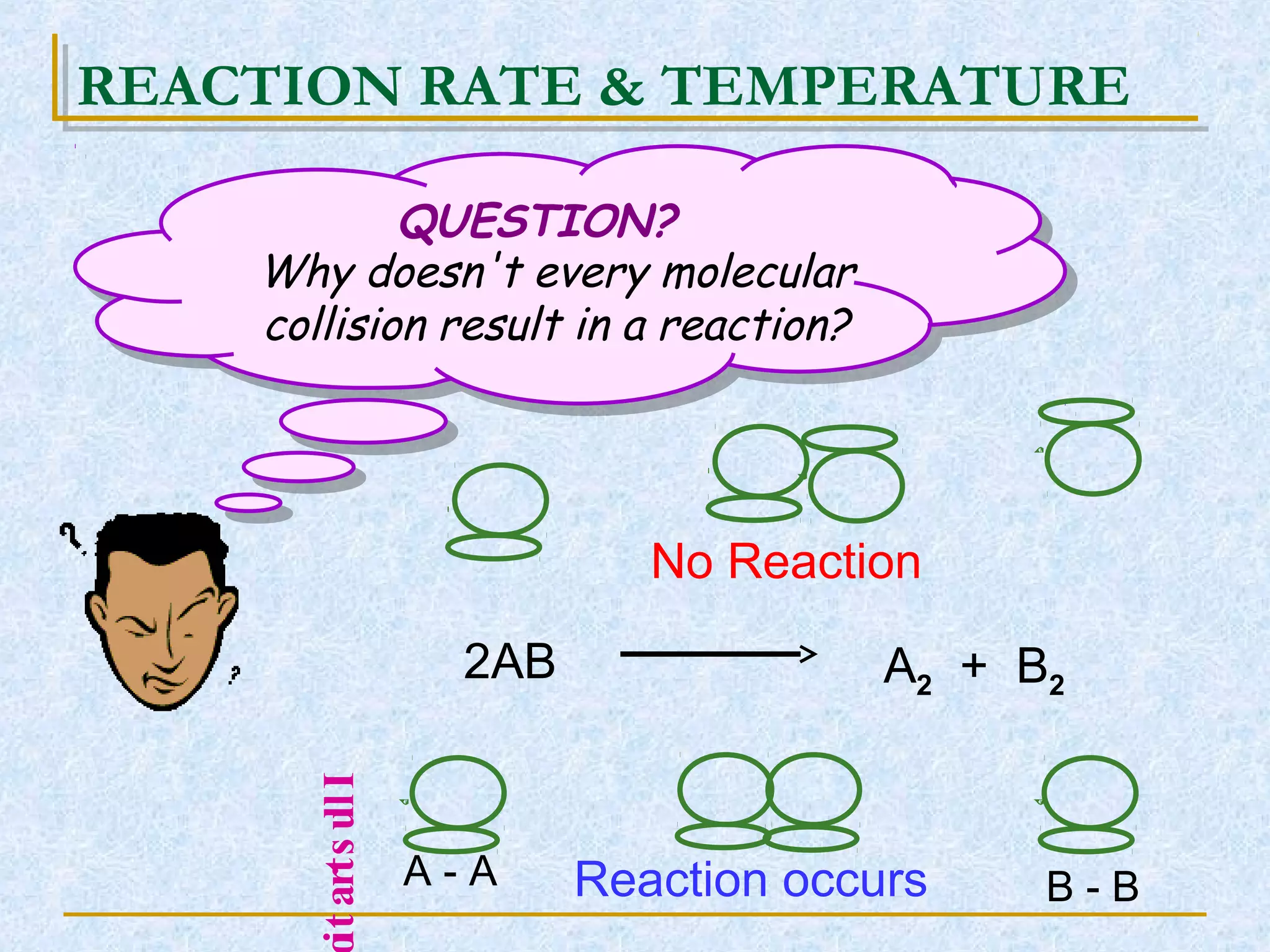
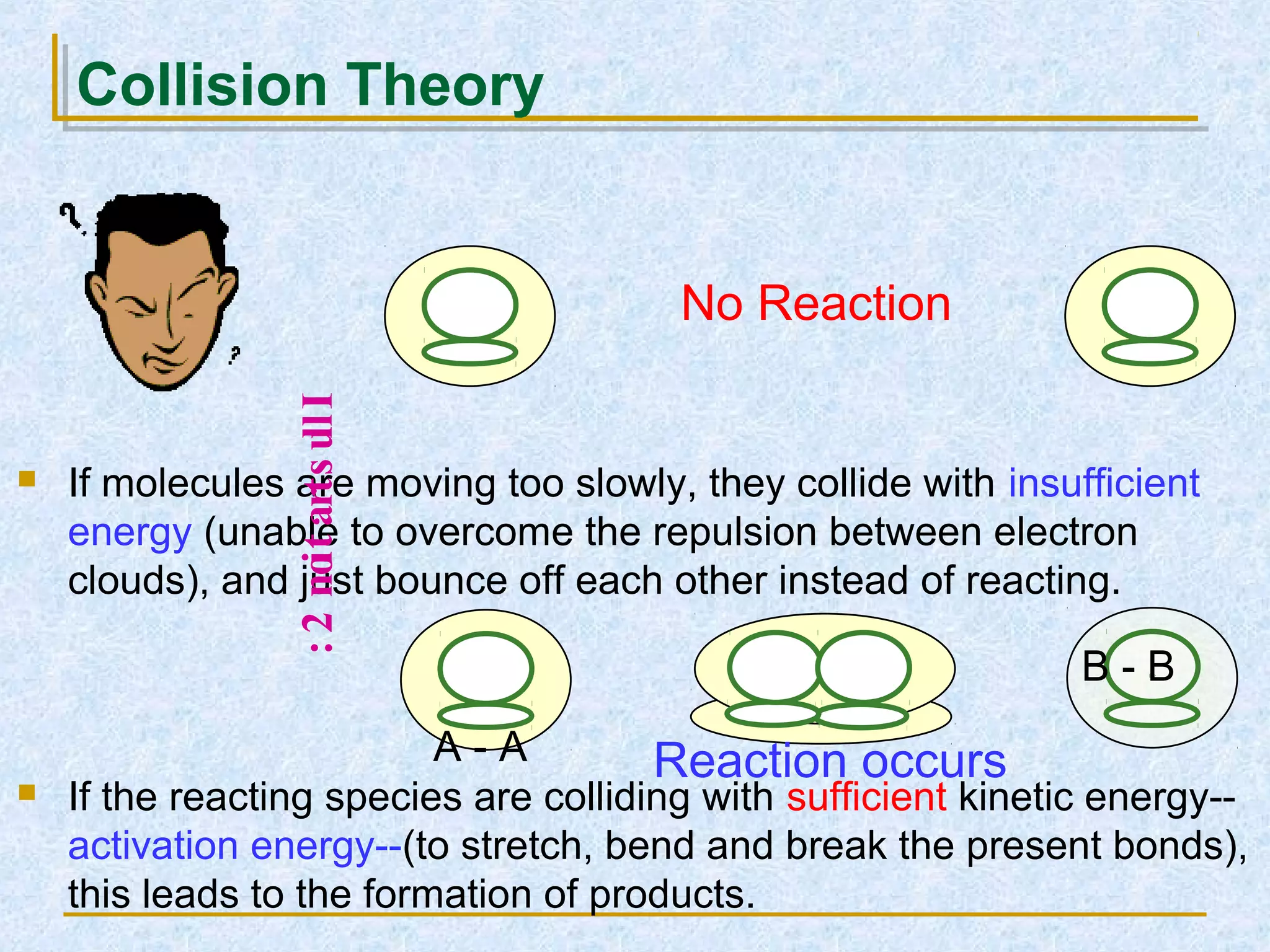
Only about 1 in 1013 molecular collisions results in a reaction. For a reaction to occur, colliding molecules must have sufficient kinetic energy to overcome the activation energy barrier. Insufficient energy results in the molecules bouncing off each other without reacting. The rate of reaction increases with higher temperature as more molecules then have enough energy to react. A catalyst also increases reaction rate by providing an alternative reaction pathway with lower activation energy. Increasing the concentration of reactants or the surface area of solids increases the number of collisions and reaction rate.


![Reaction Profile
Energy
Reaction Pathway
CH3• + HCl → [H3C---H---Cl]#
→ CH4 + Cl•
CH3• + HCl
[ H3C---H---Cl ]#
CH4 + Cl•
∆H
Ea1
Ea2
A) One Essential Step
or Energy Profile Diagram](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/collisiontheoryfactors-160110173502/75/reaction-kinetic-collision-theory-a-level-5-2048.jpg)