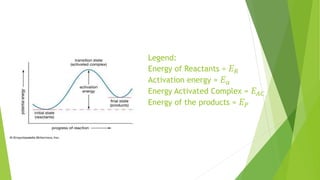
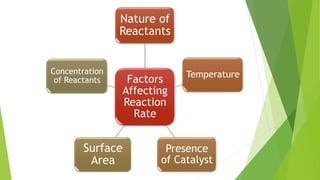
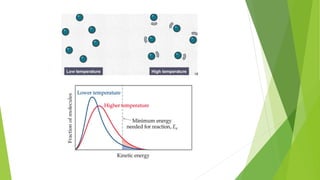
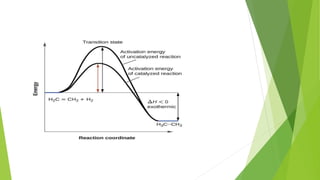
Chemical changes occur when substances combine to form new substances and are not reversible without further chemical reactions. The rate of a chemical reaction depends on factors like the nature of reactants, temperature, concentration, surface area, and presence of catalysts. A catalyst lowers the activation energy needed for molecules to collide and react, accelerating the reaction rate without being consumed in the process.