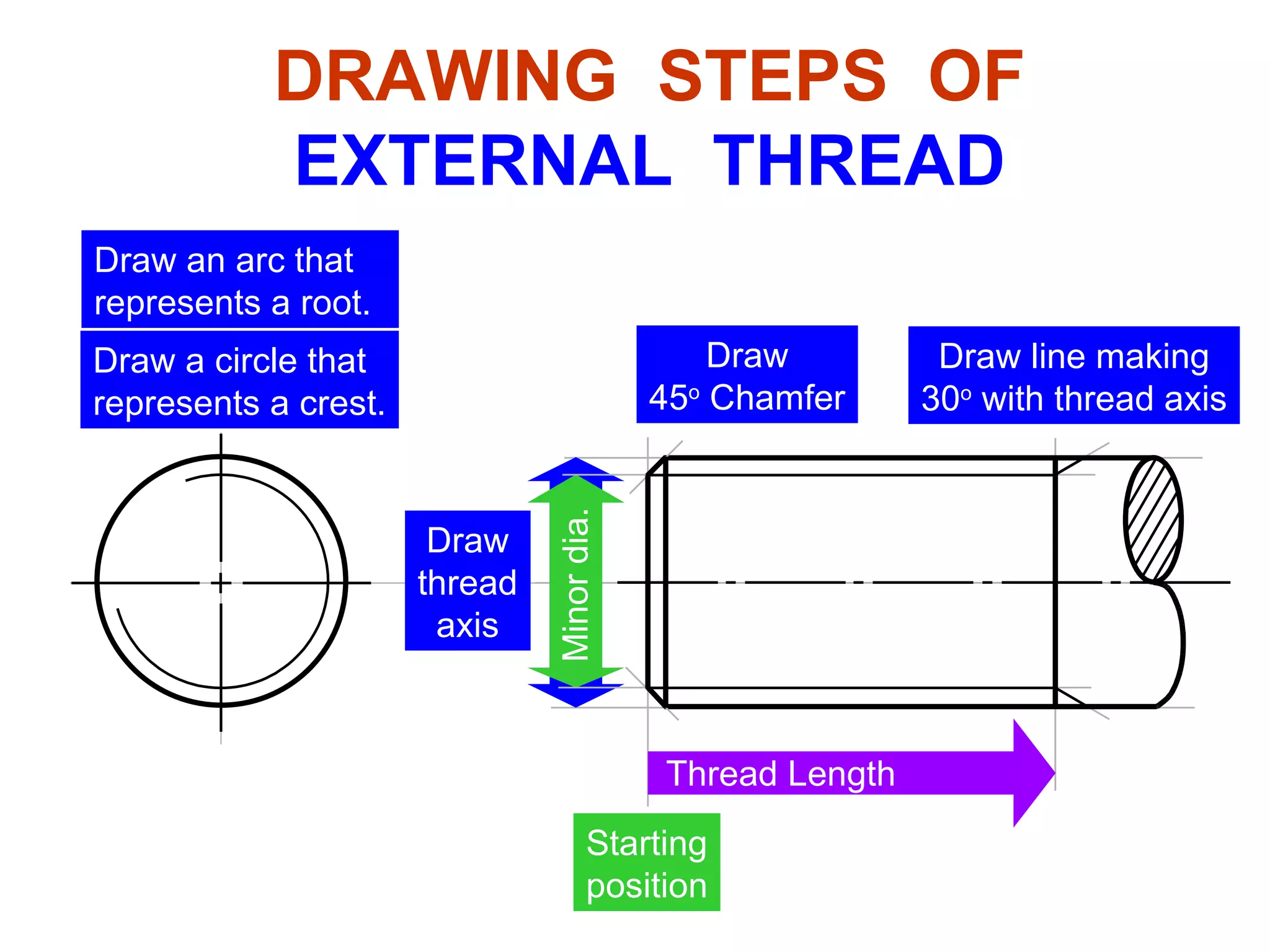
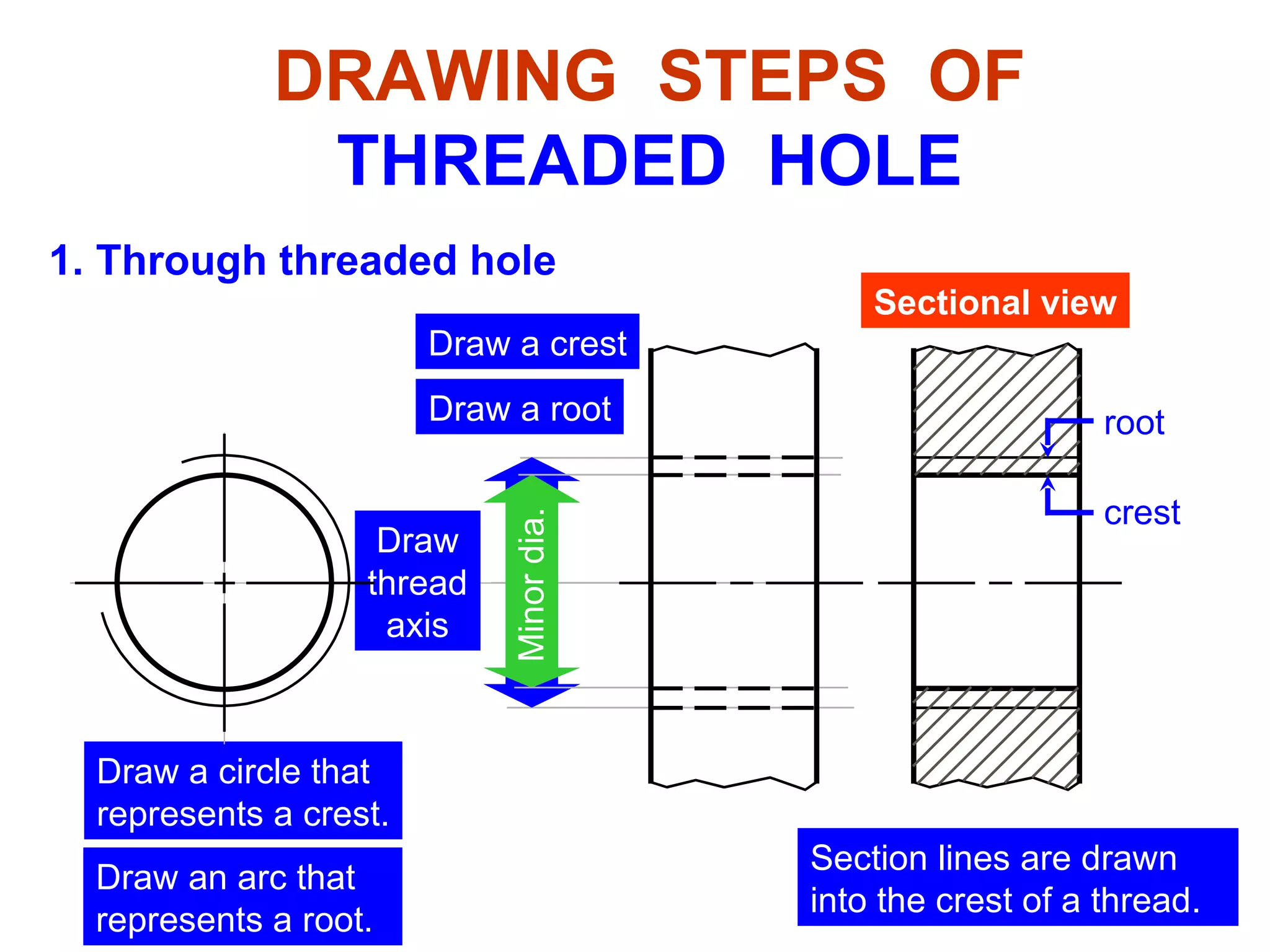
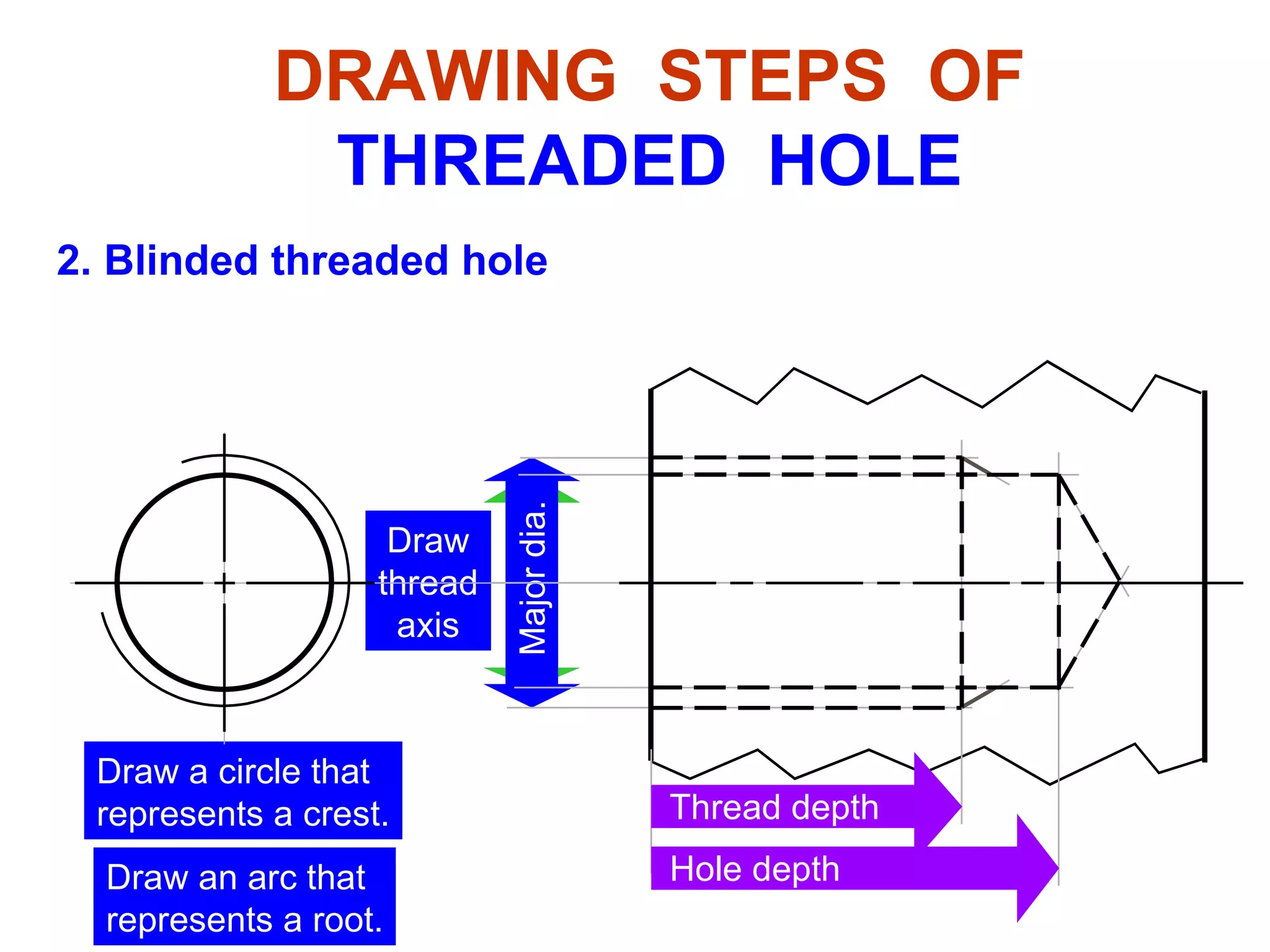
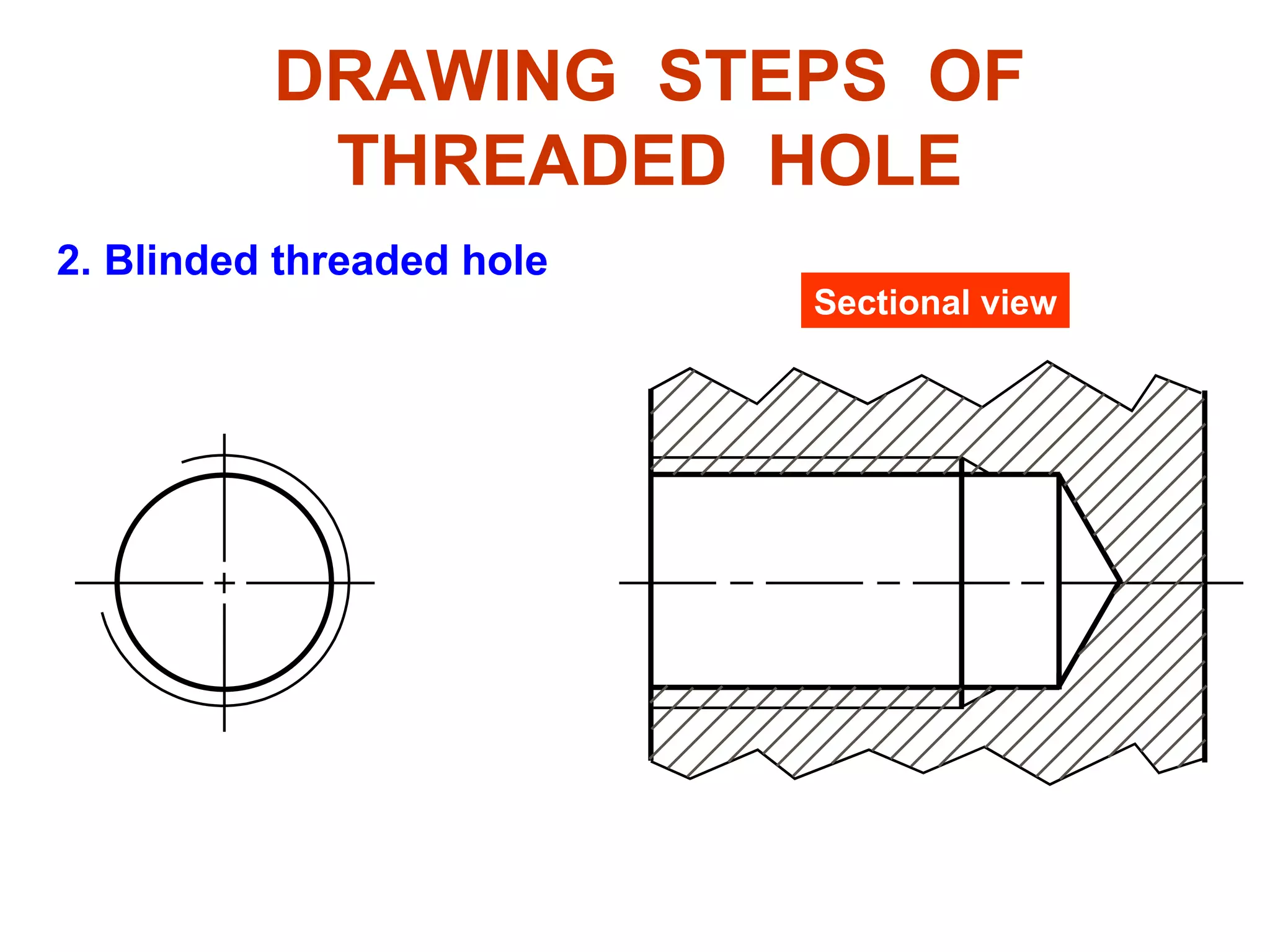
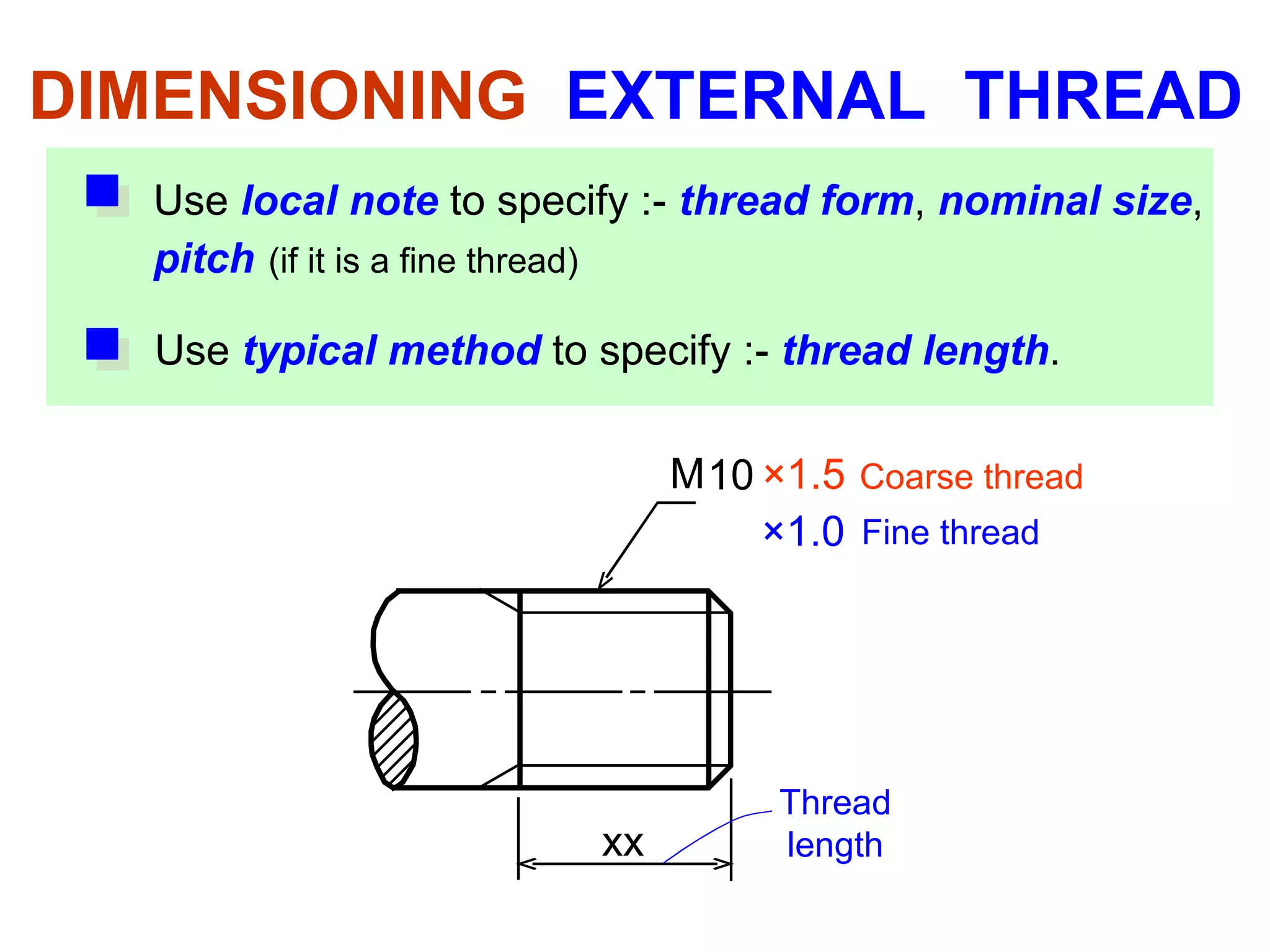
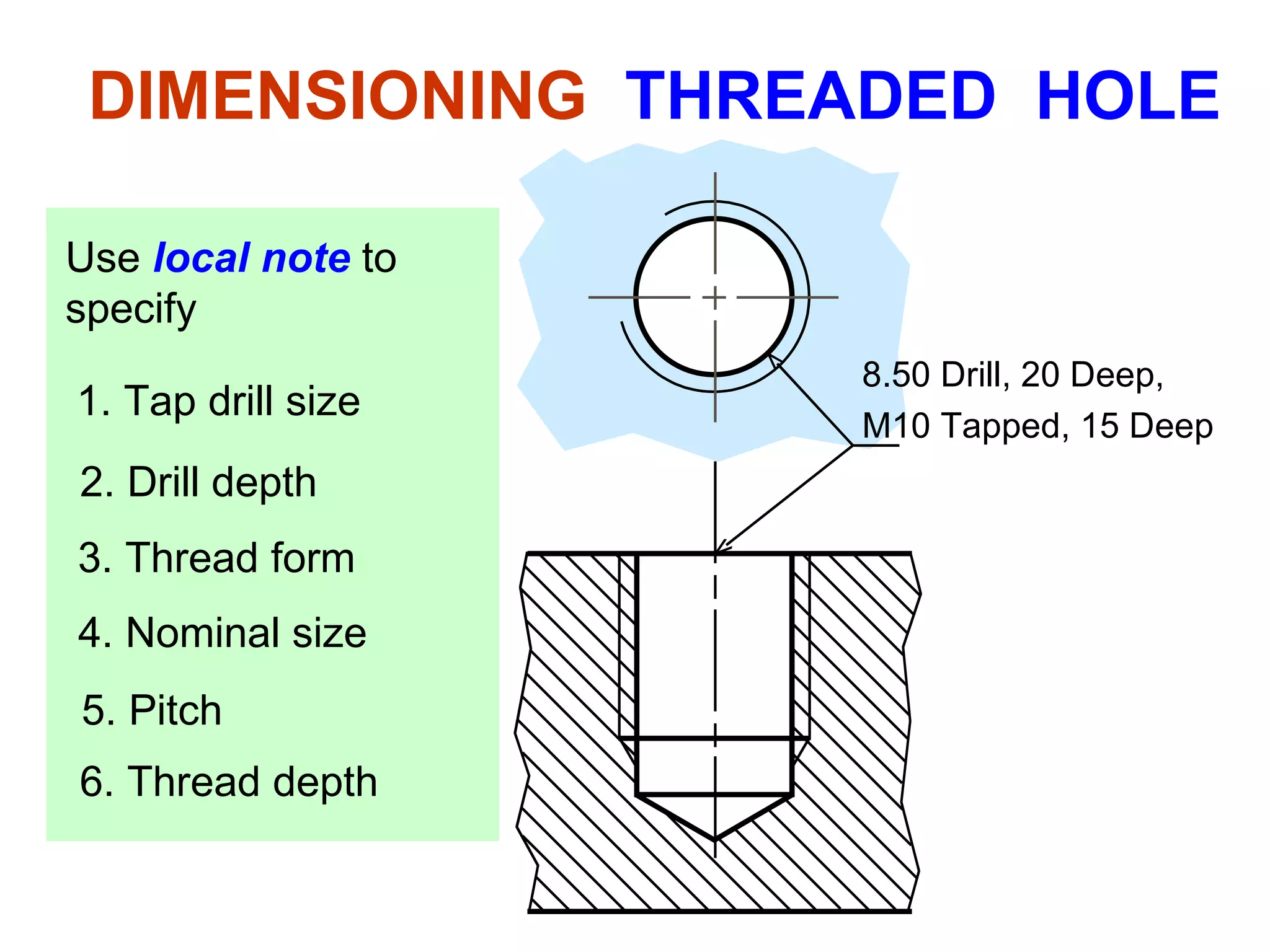
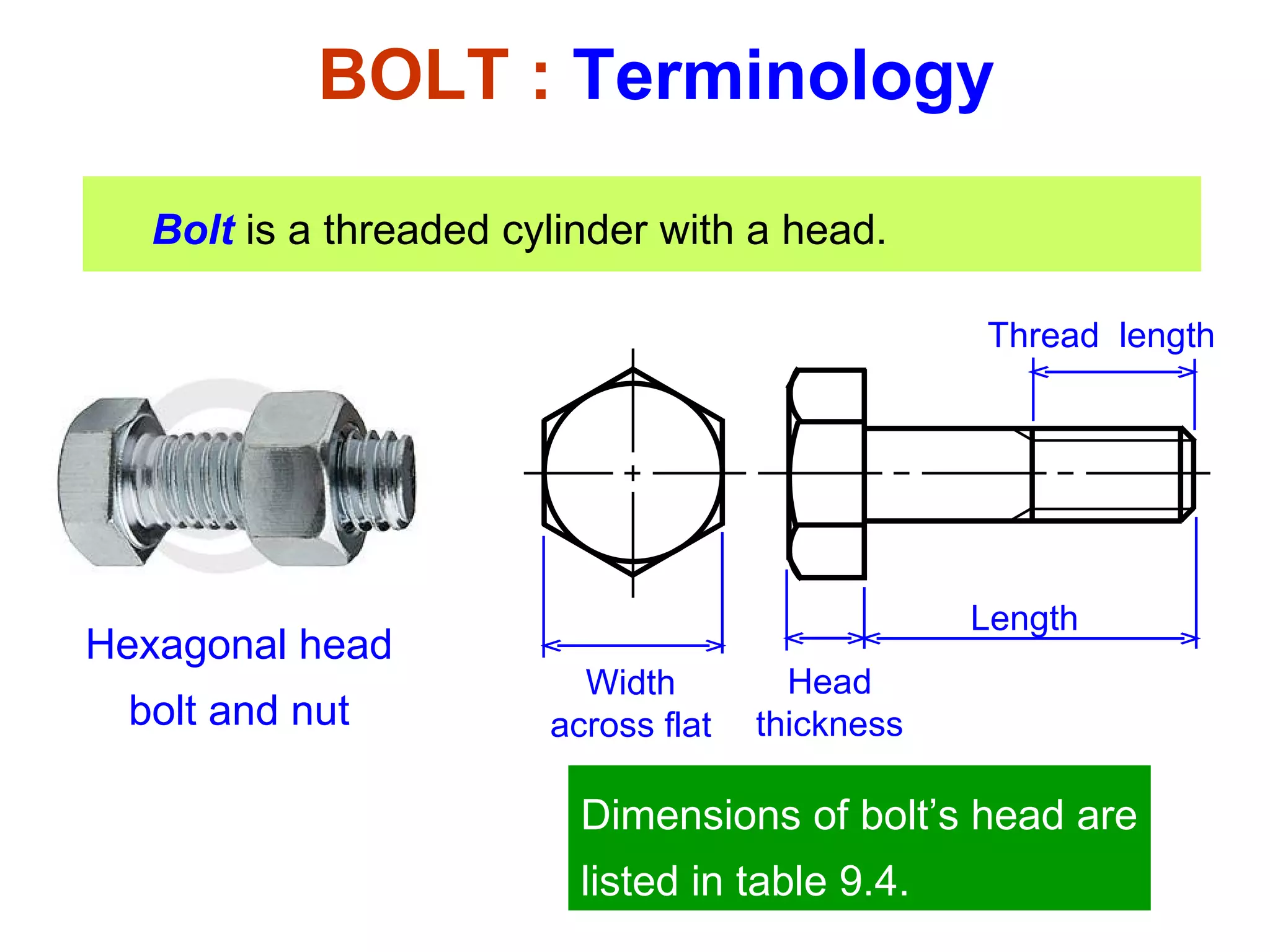
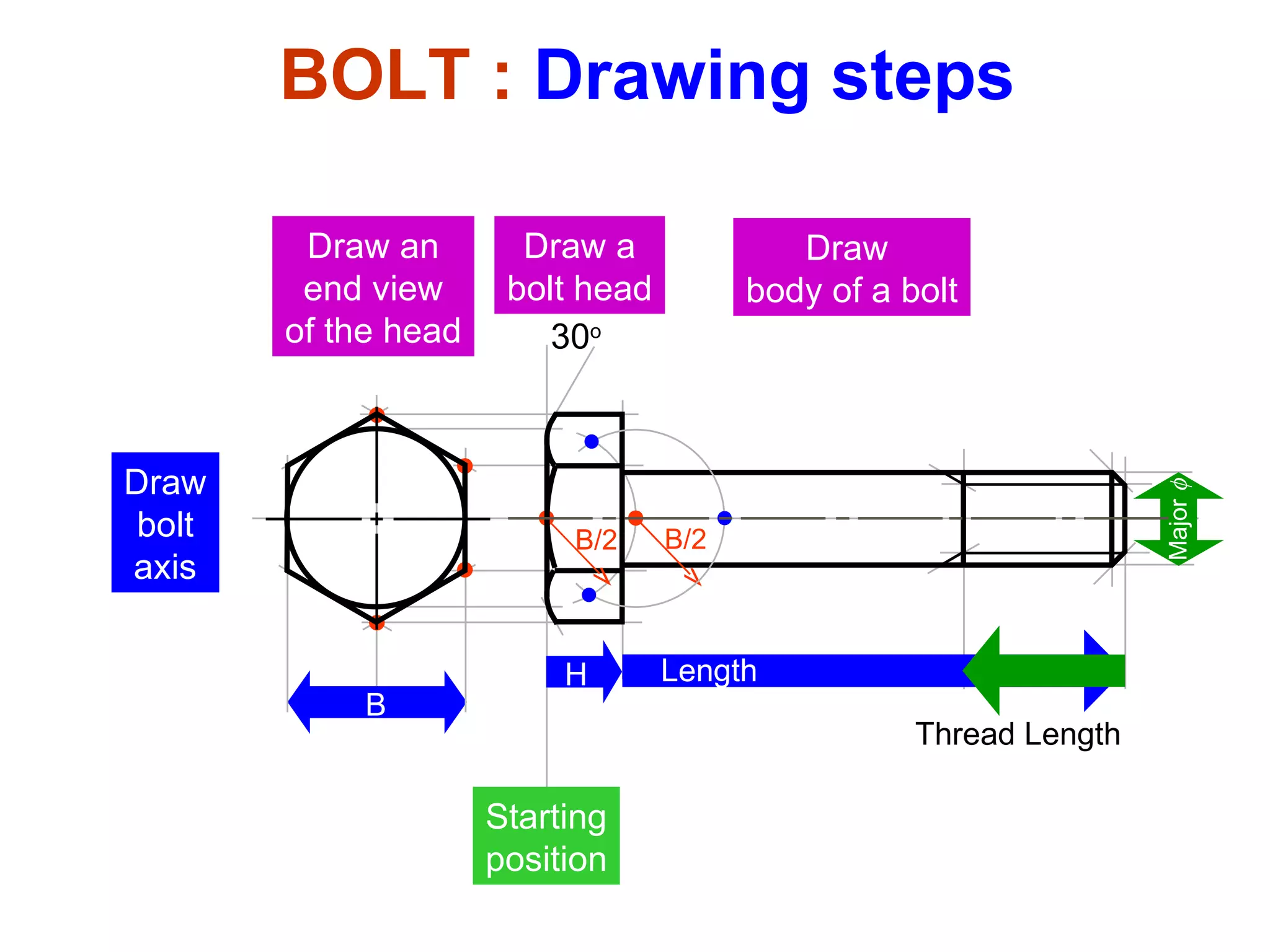
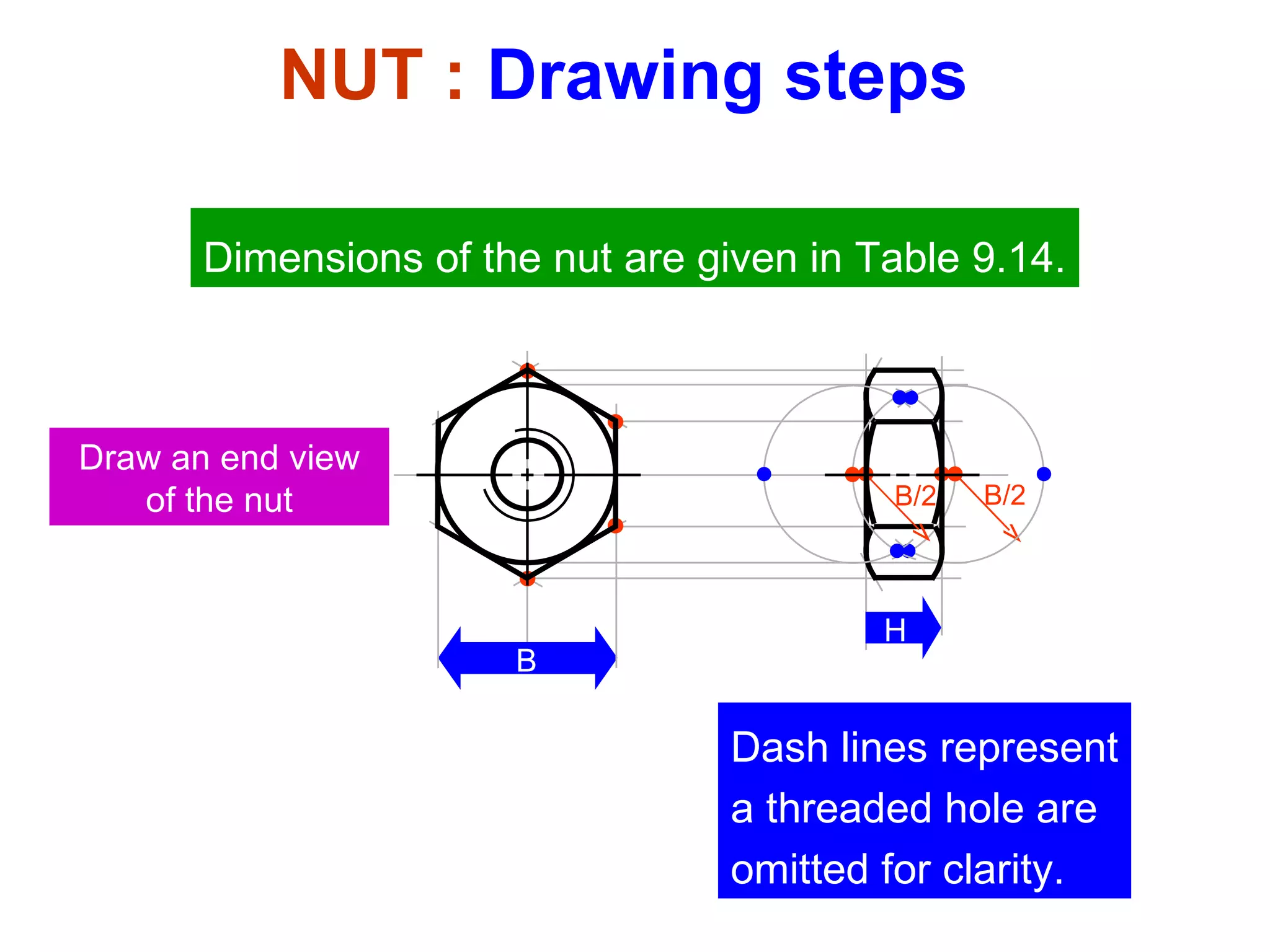
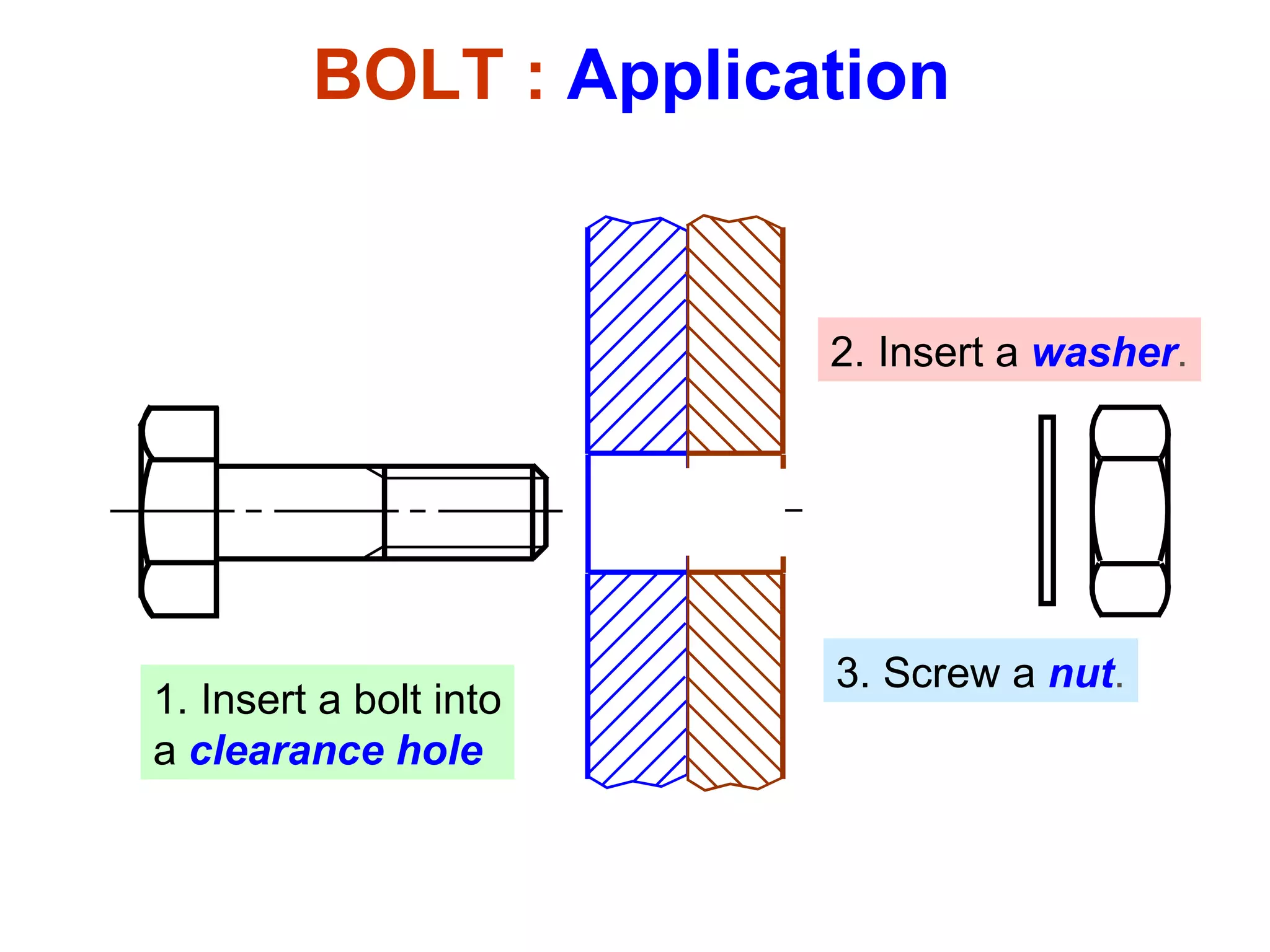
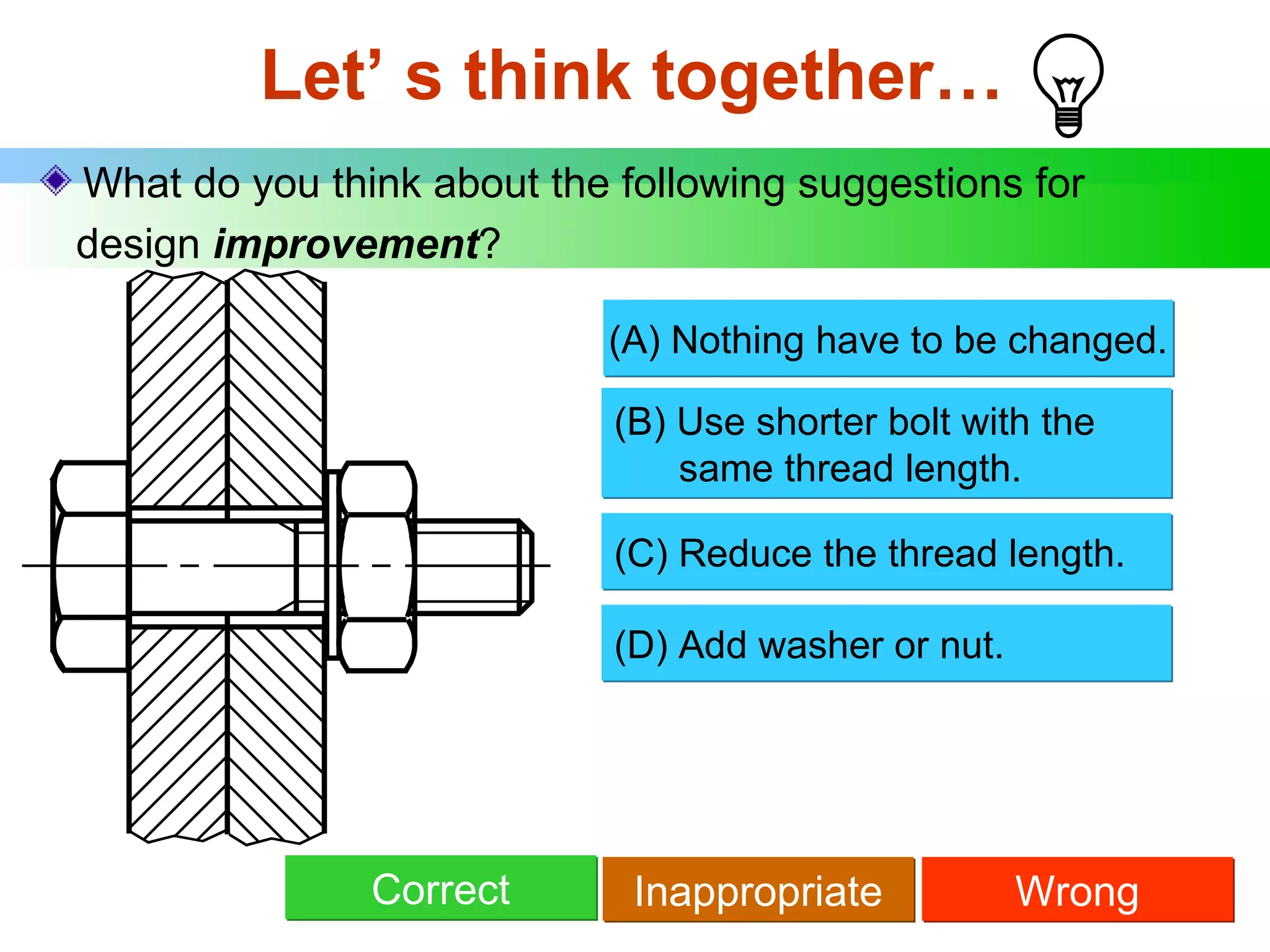
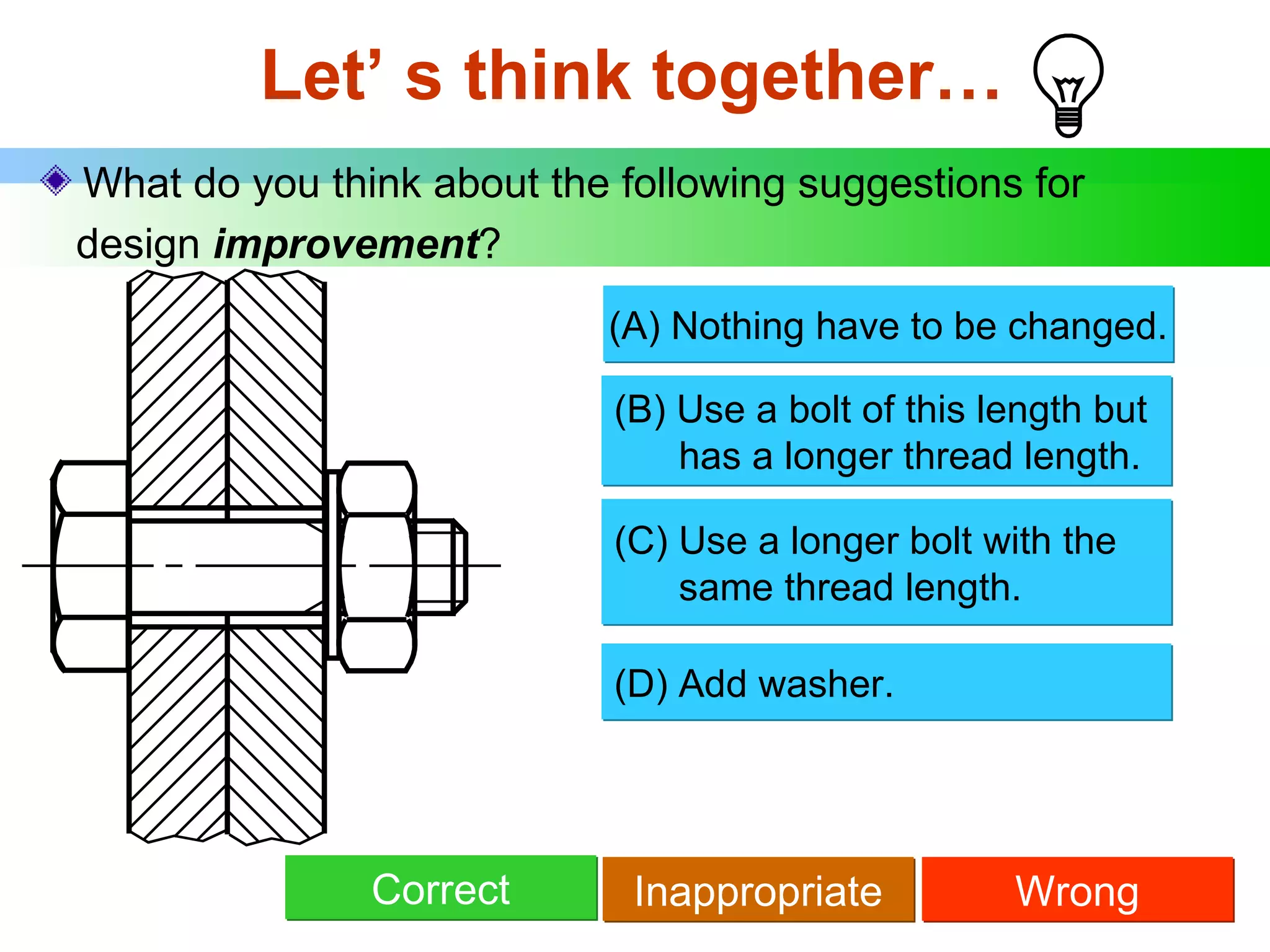
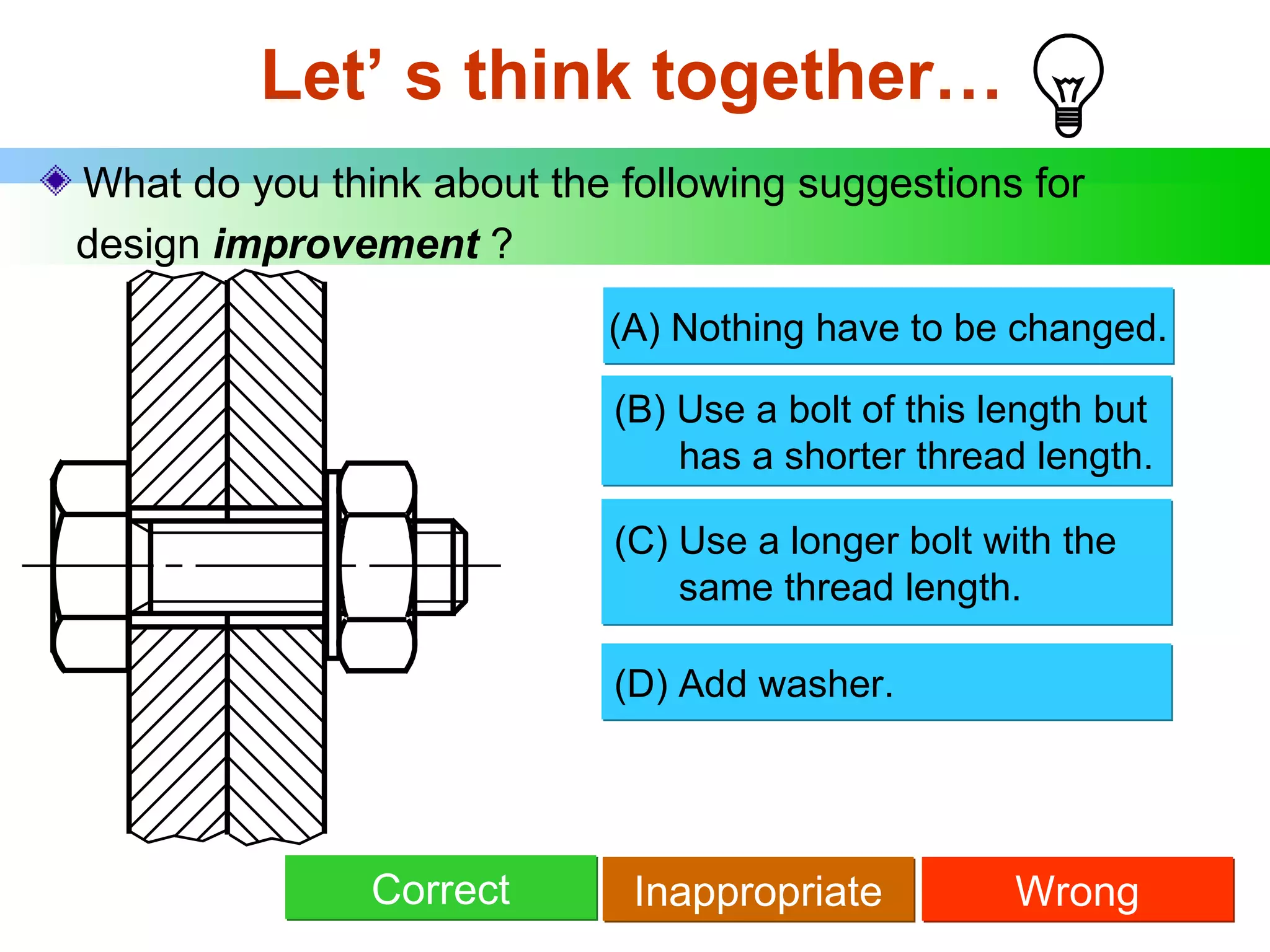
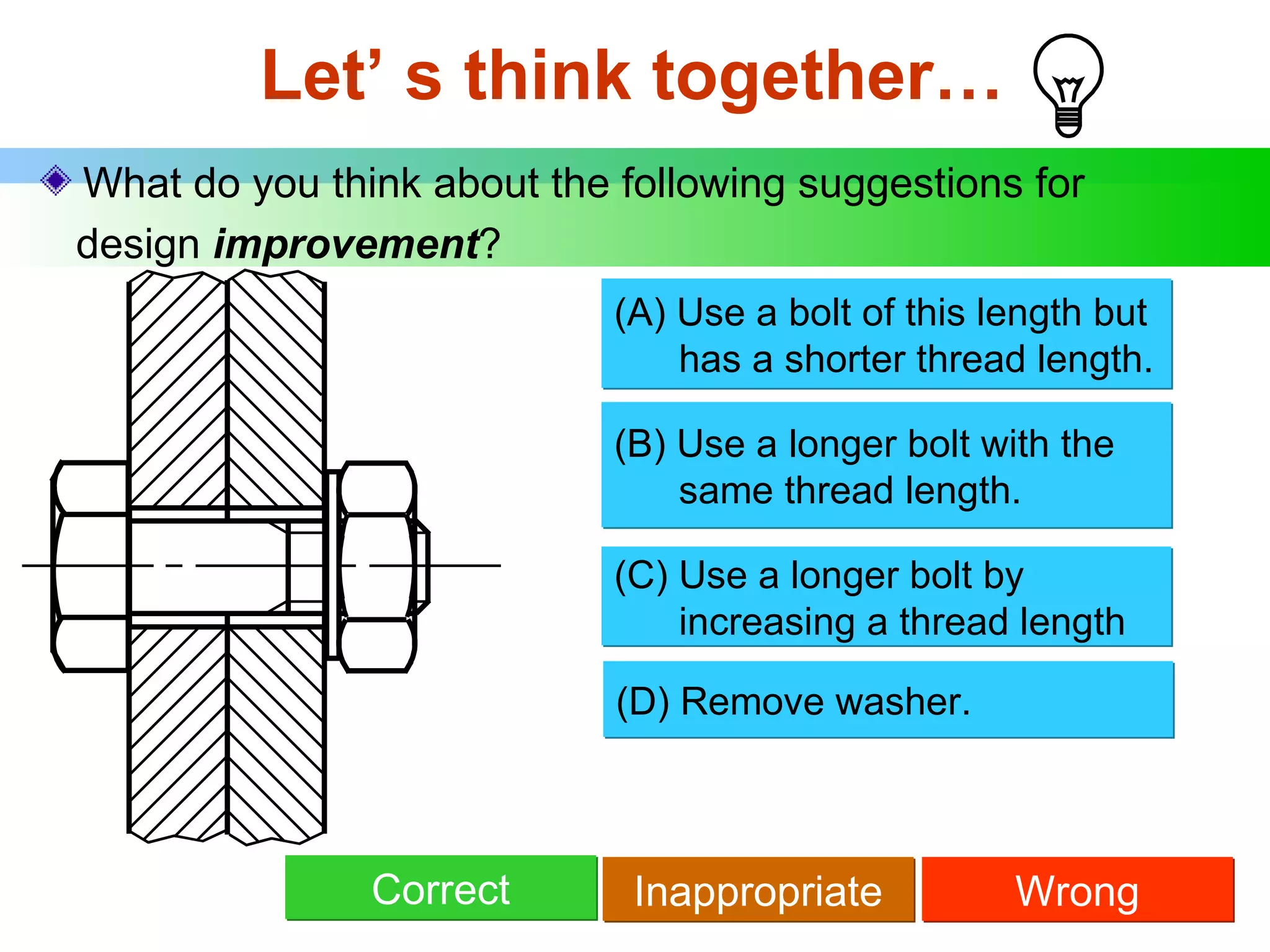
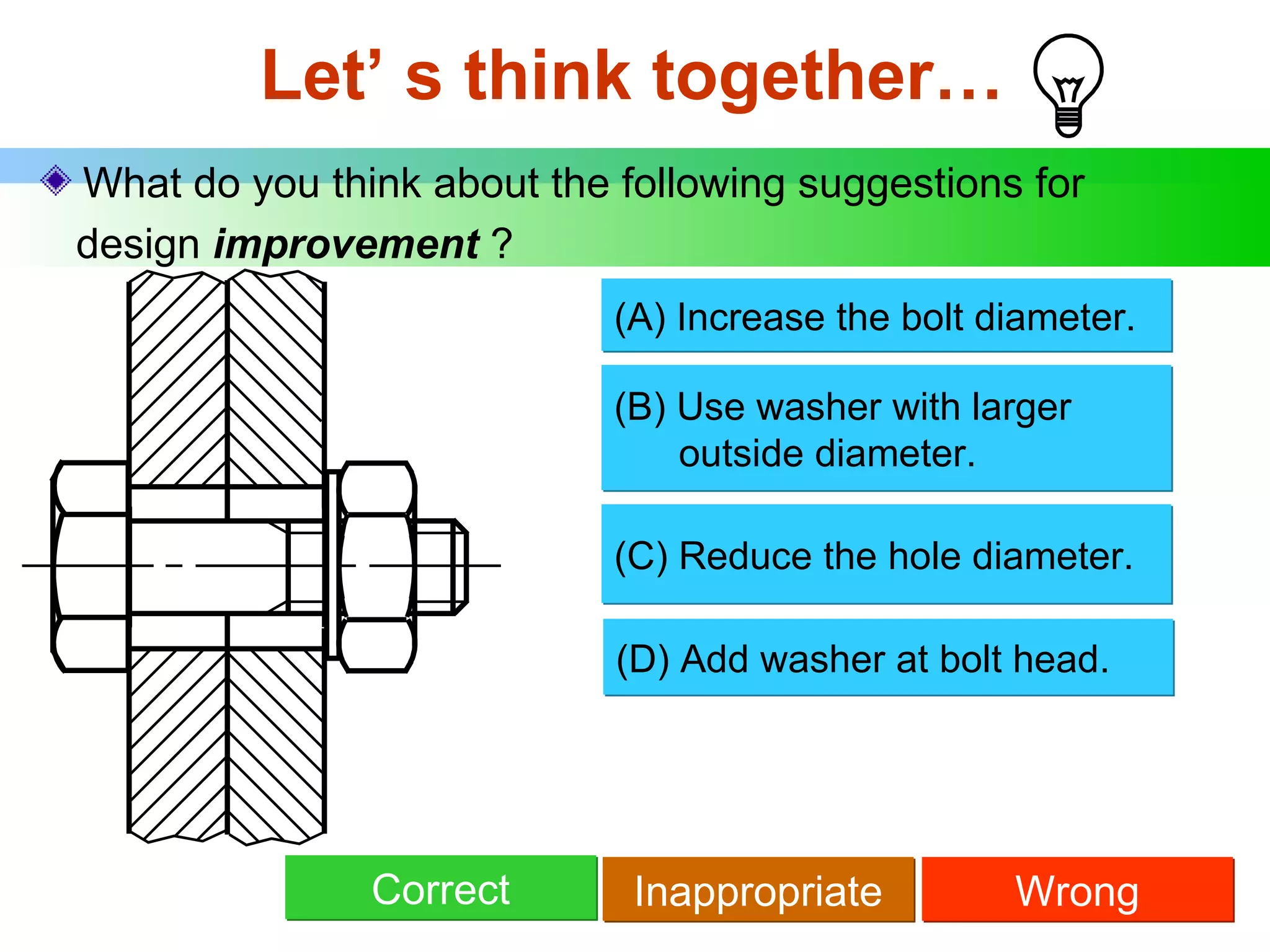
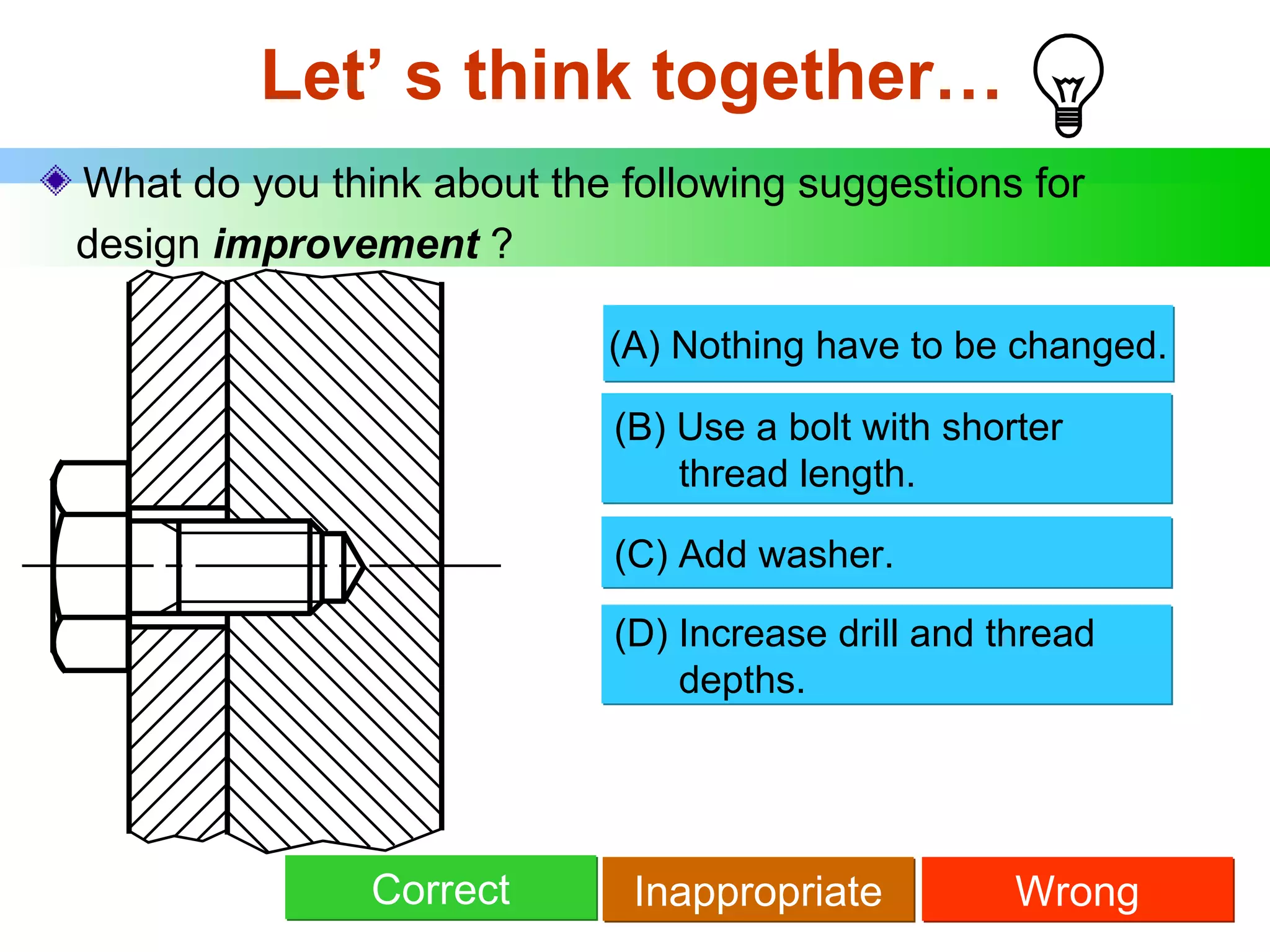
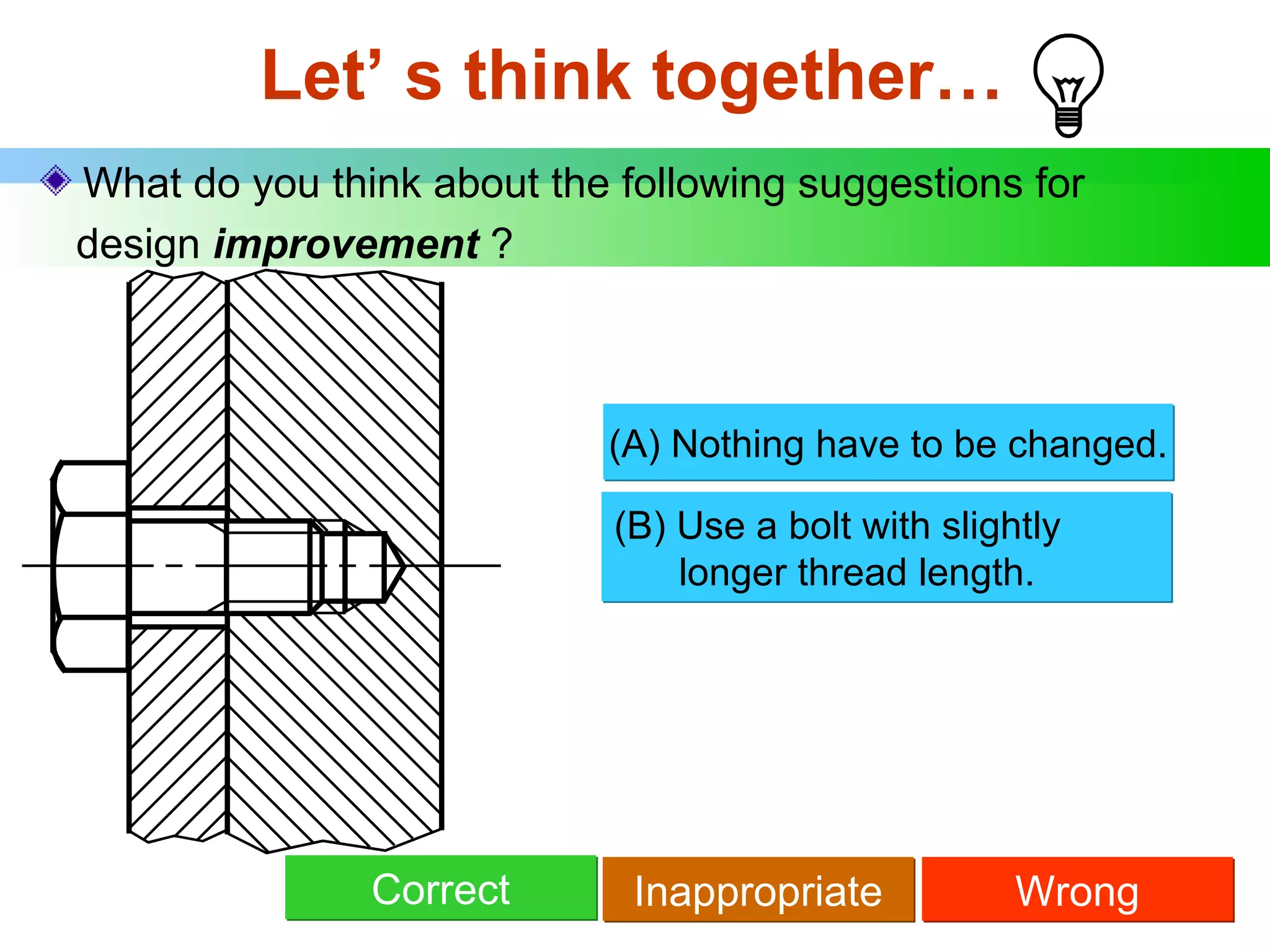
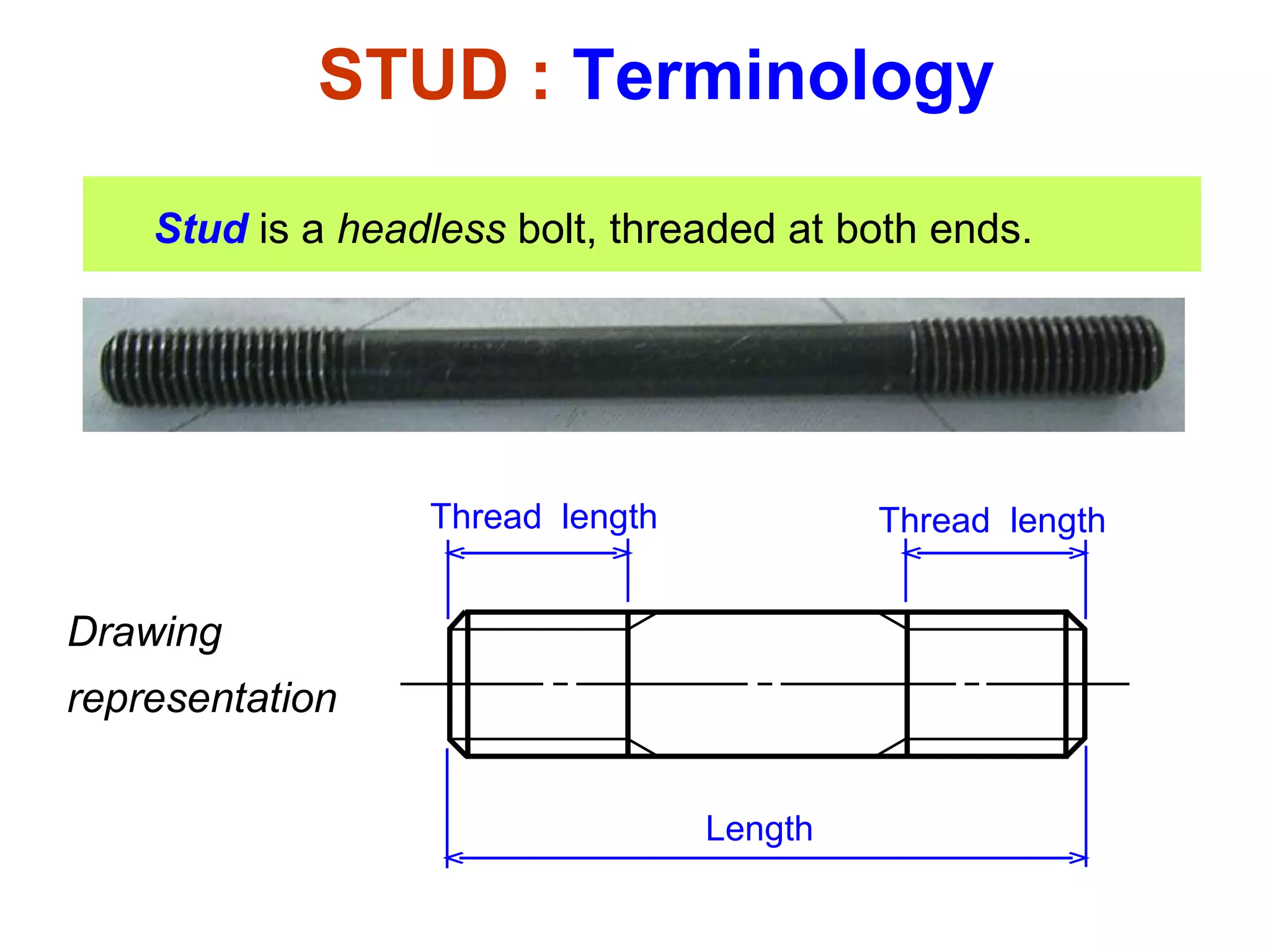
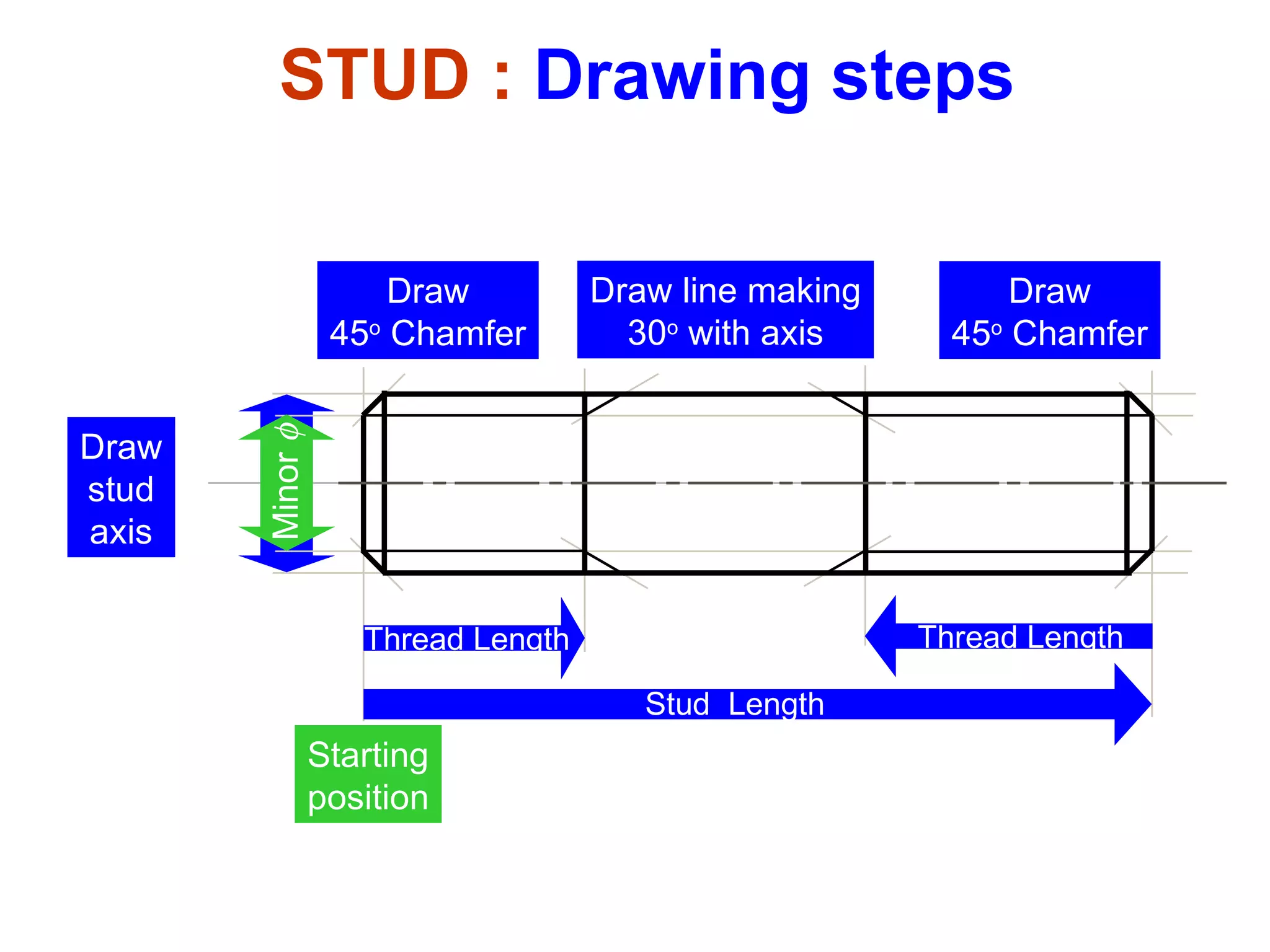
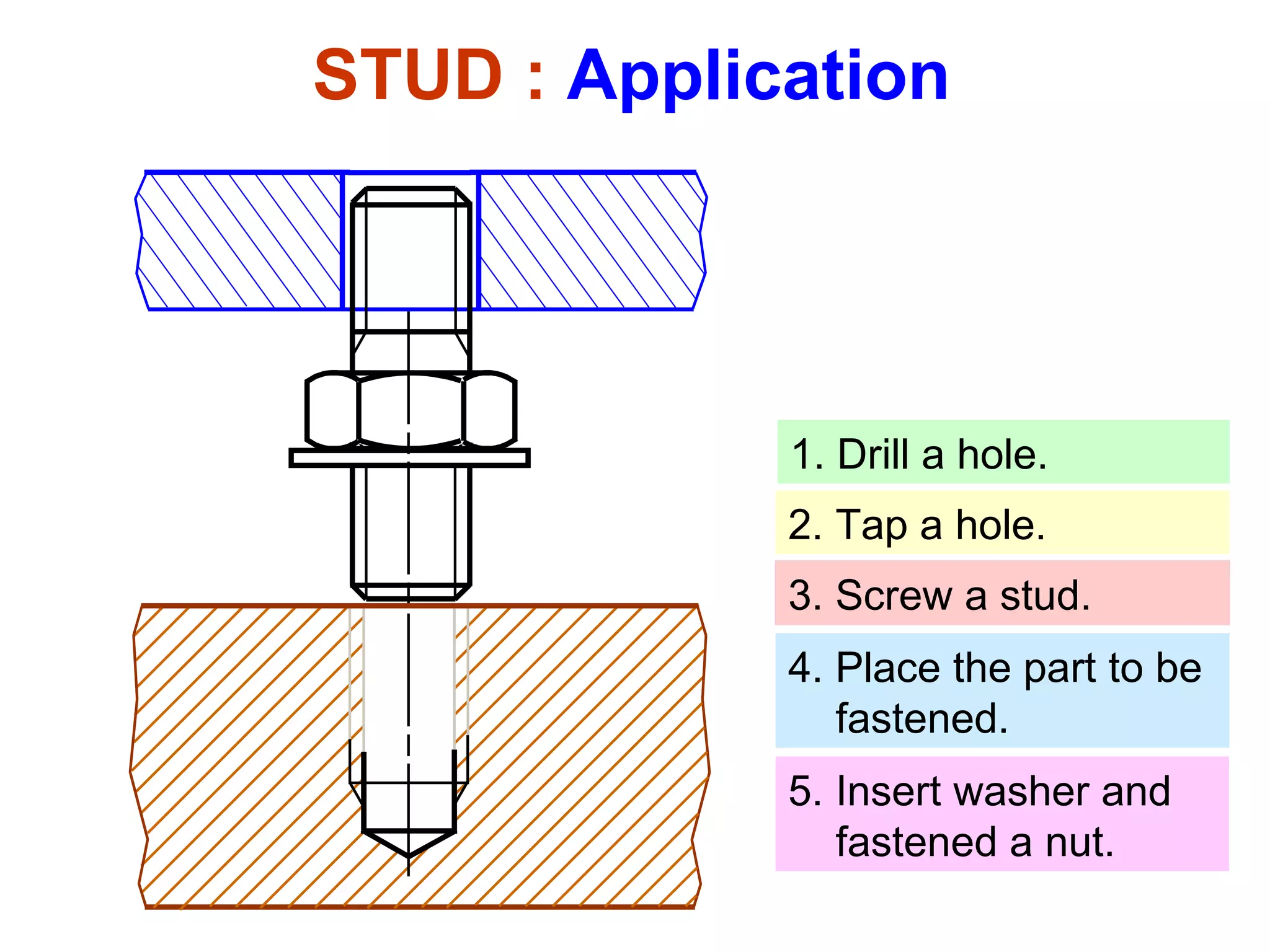
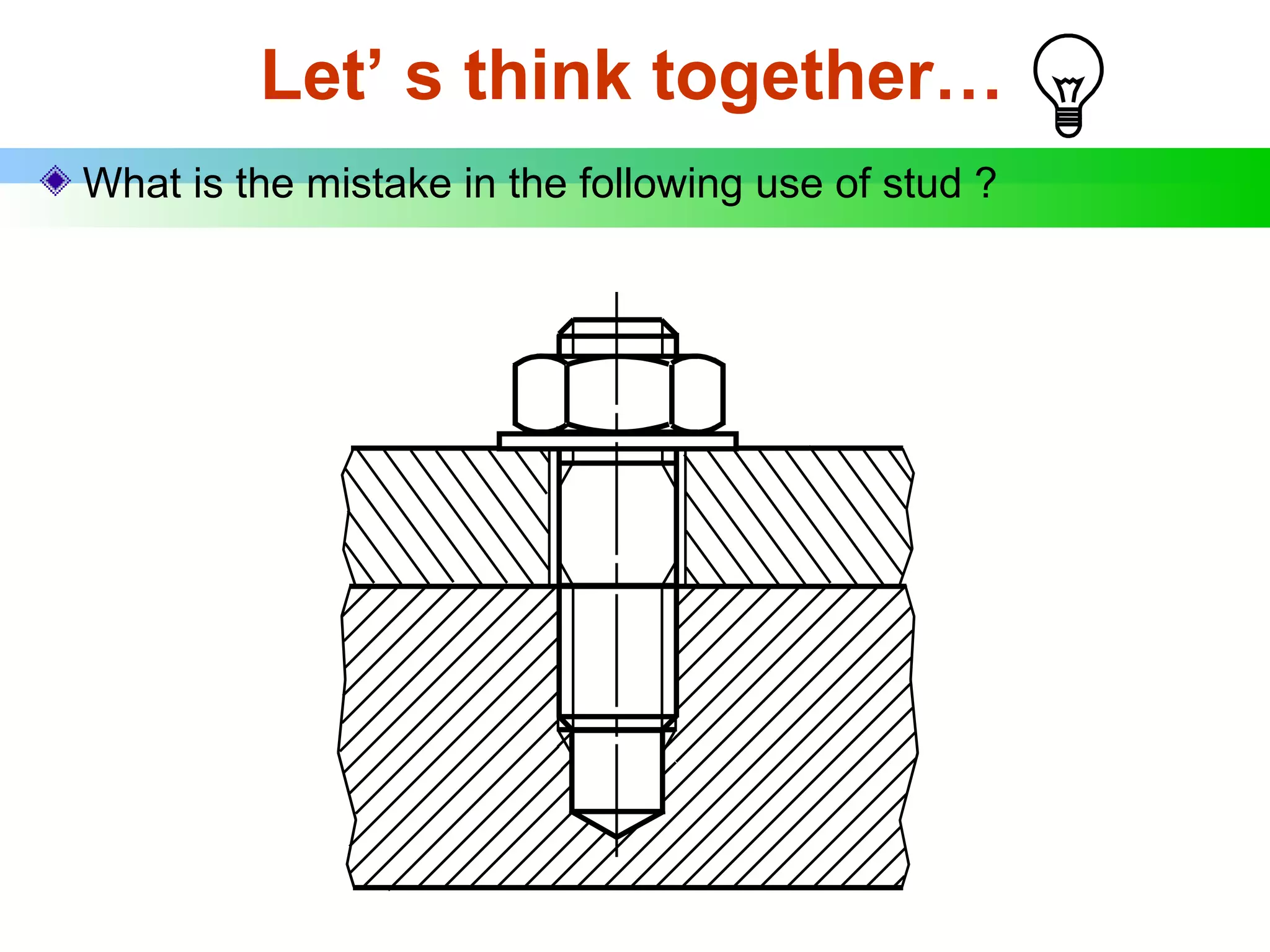
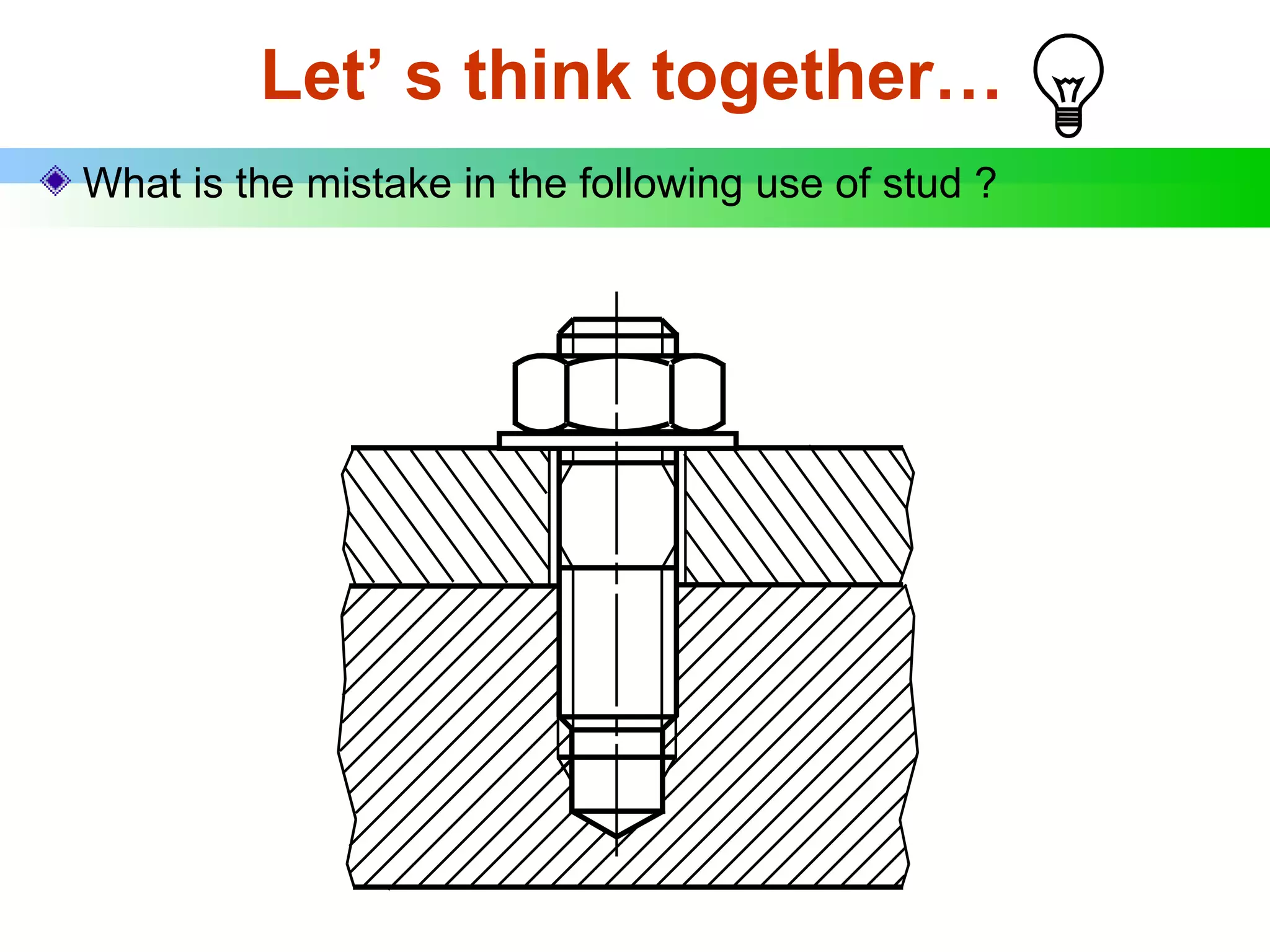
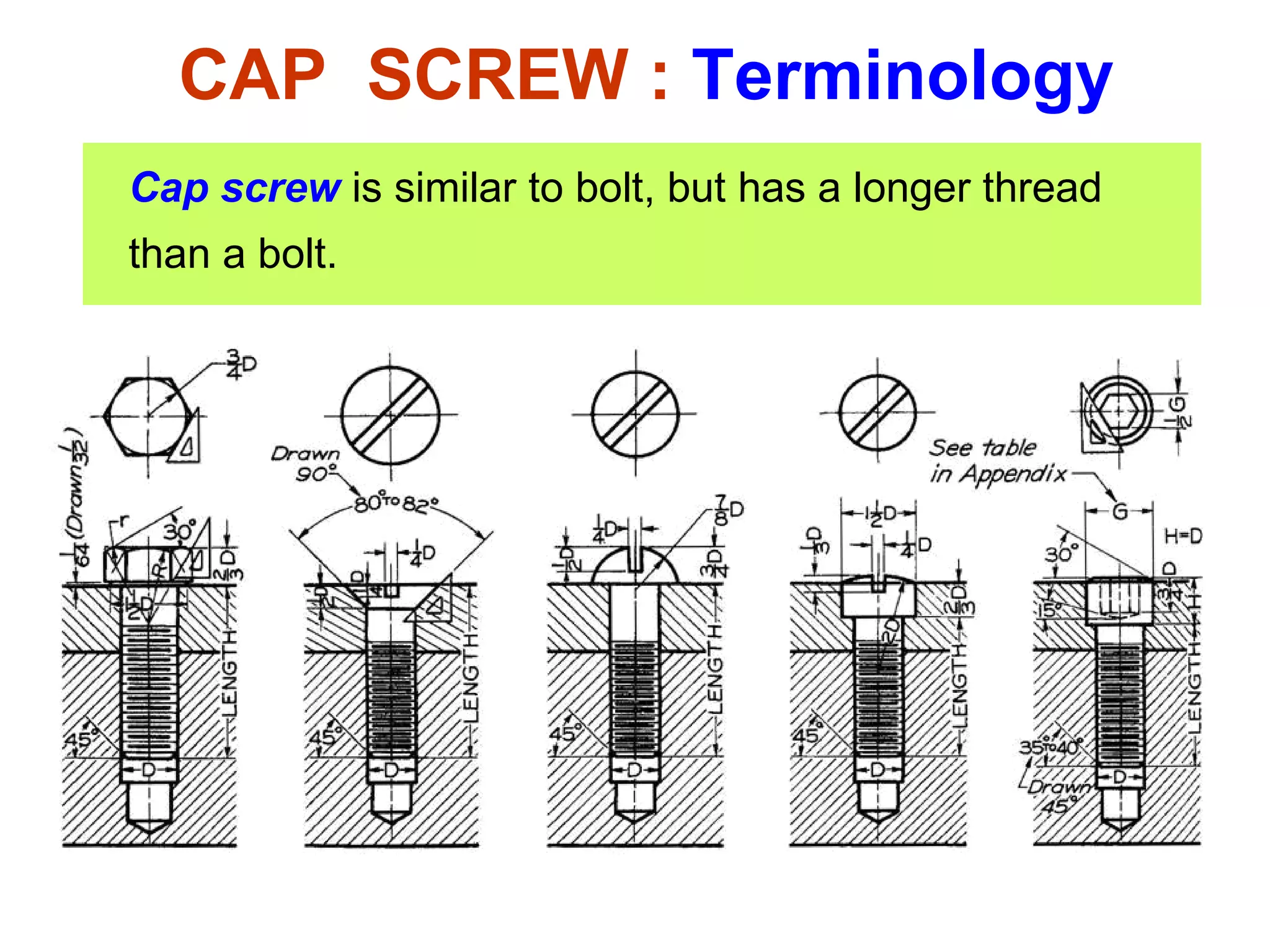
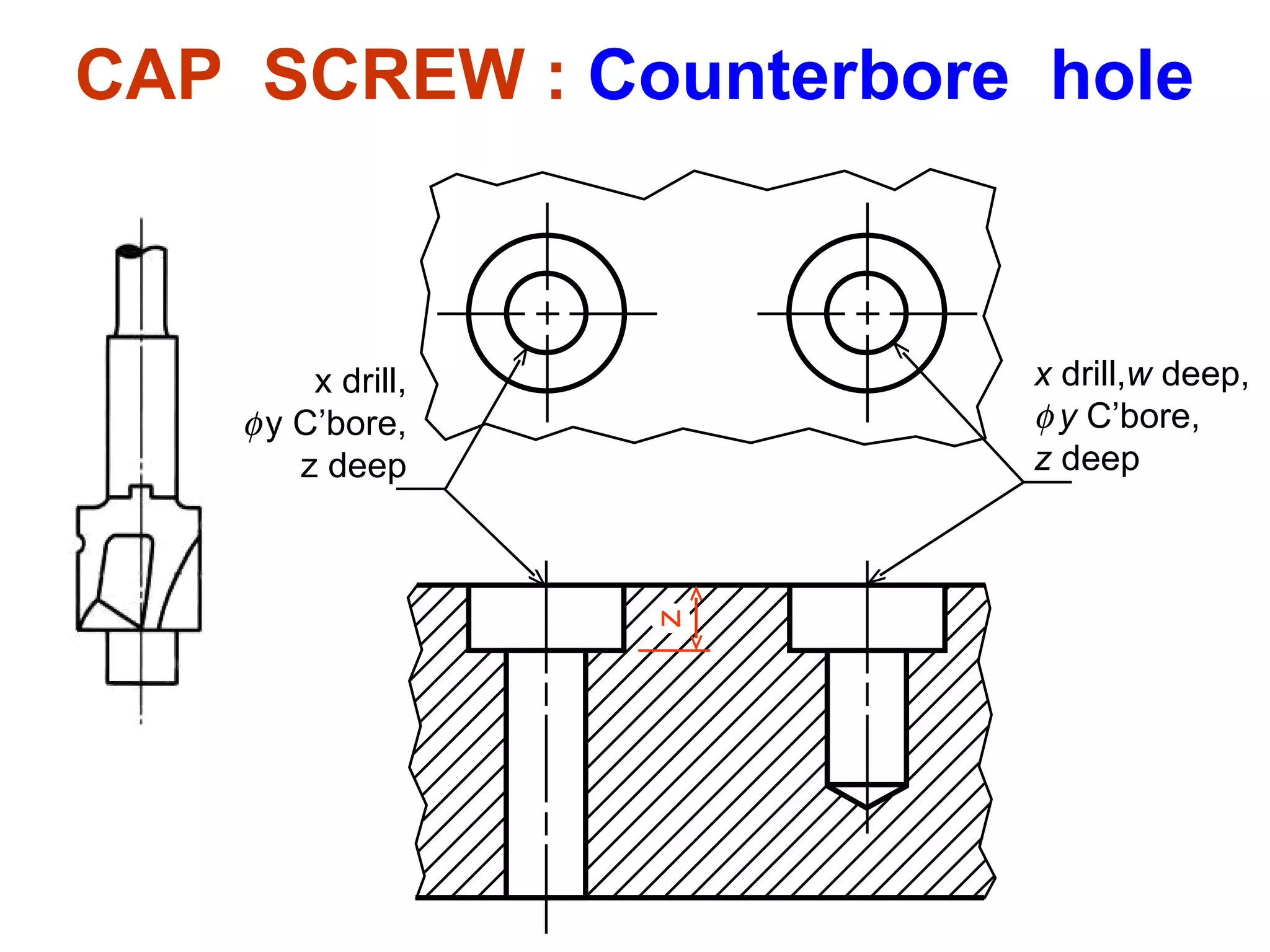
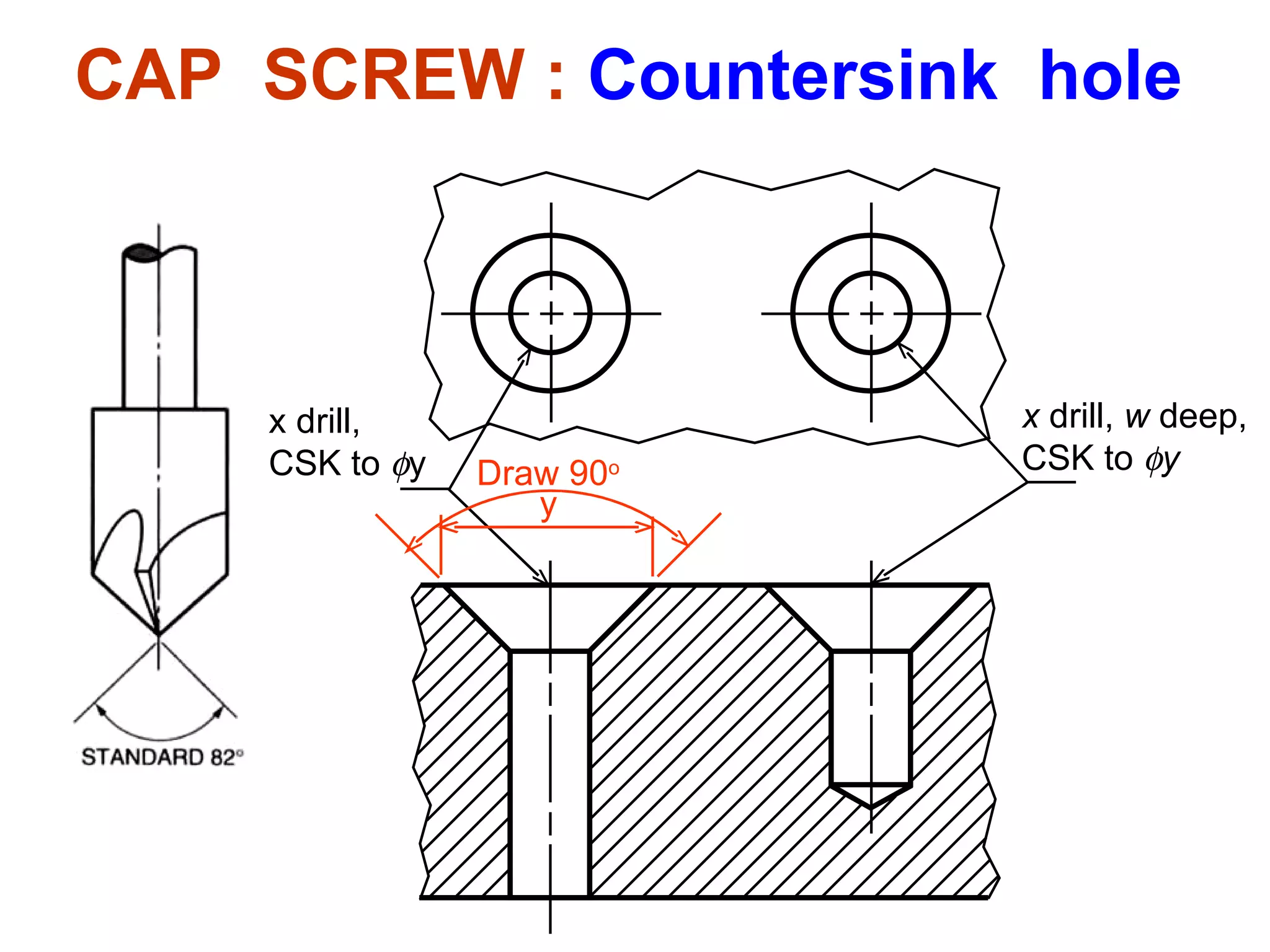
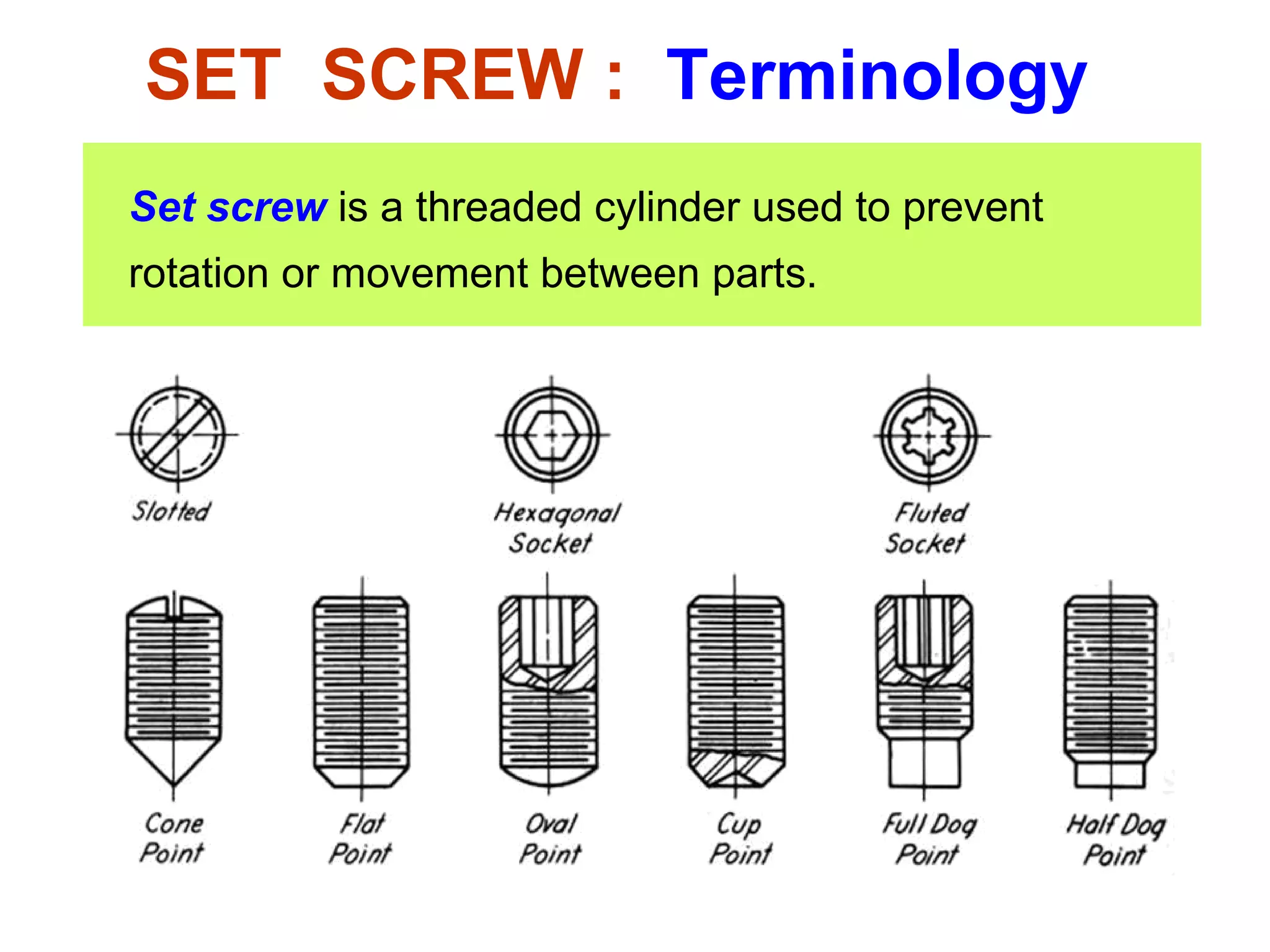
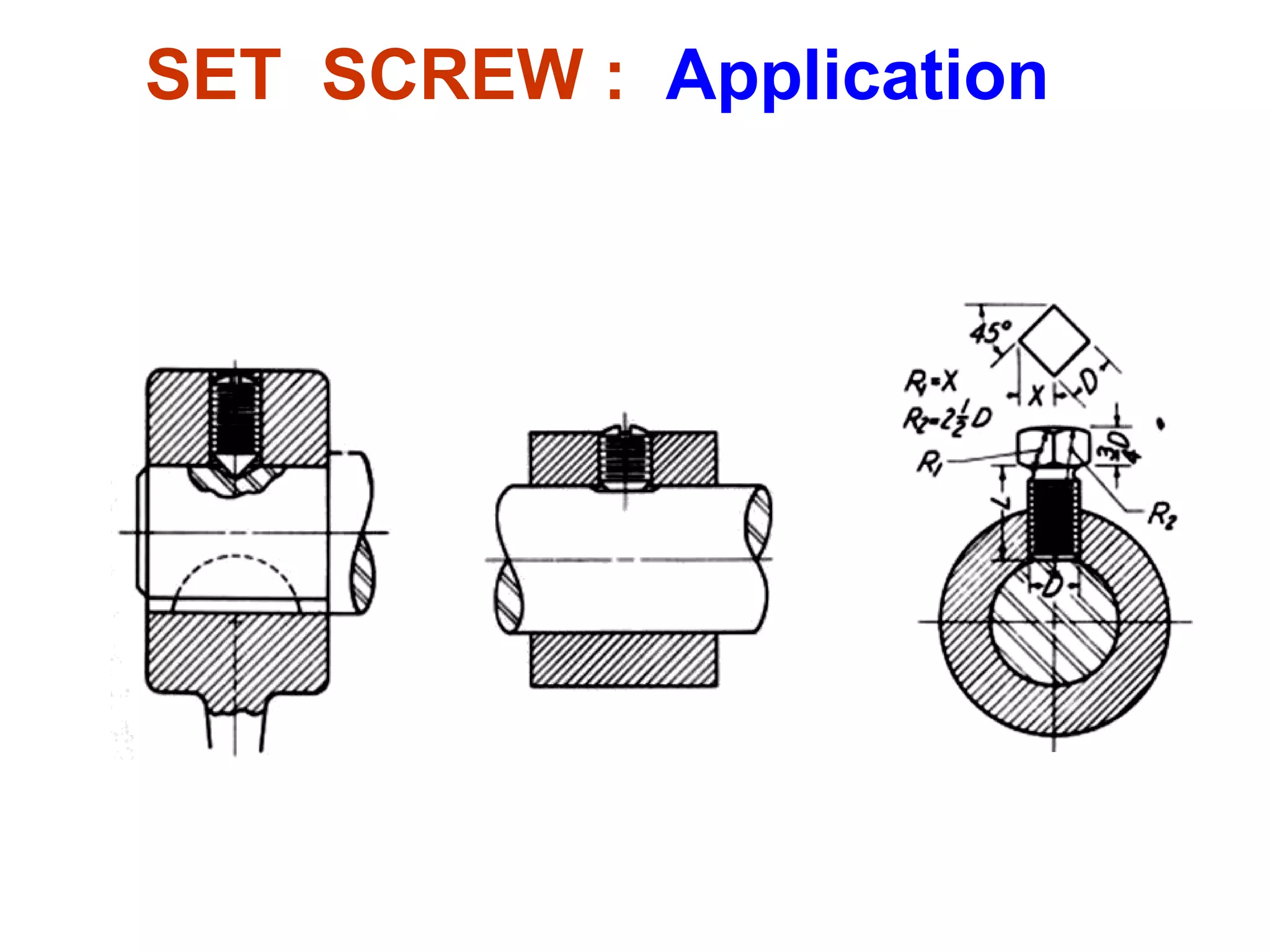
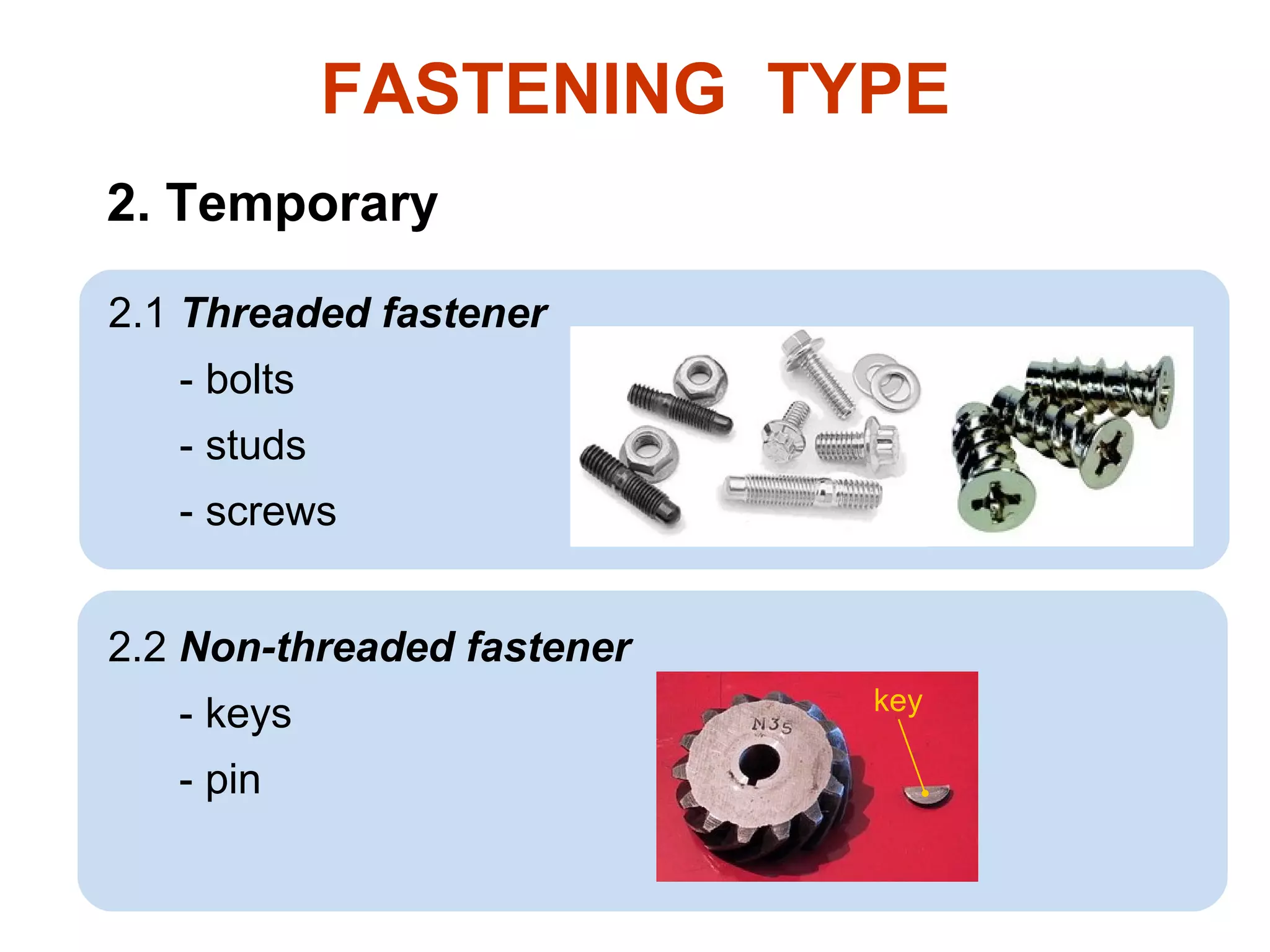
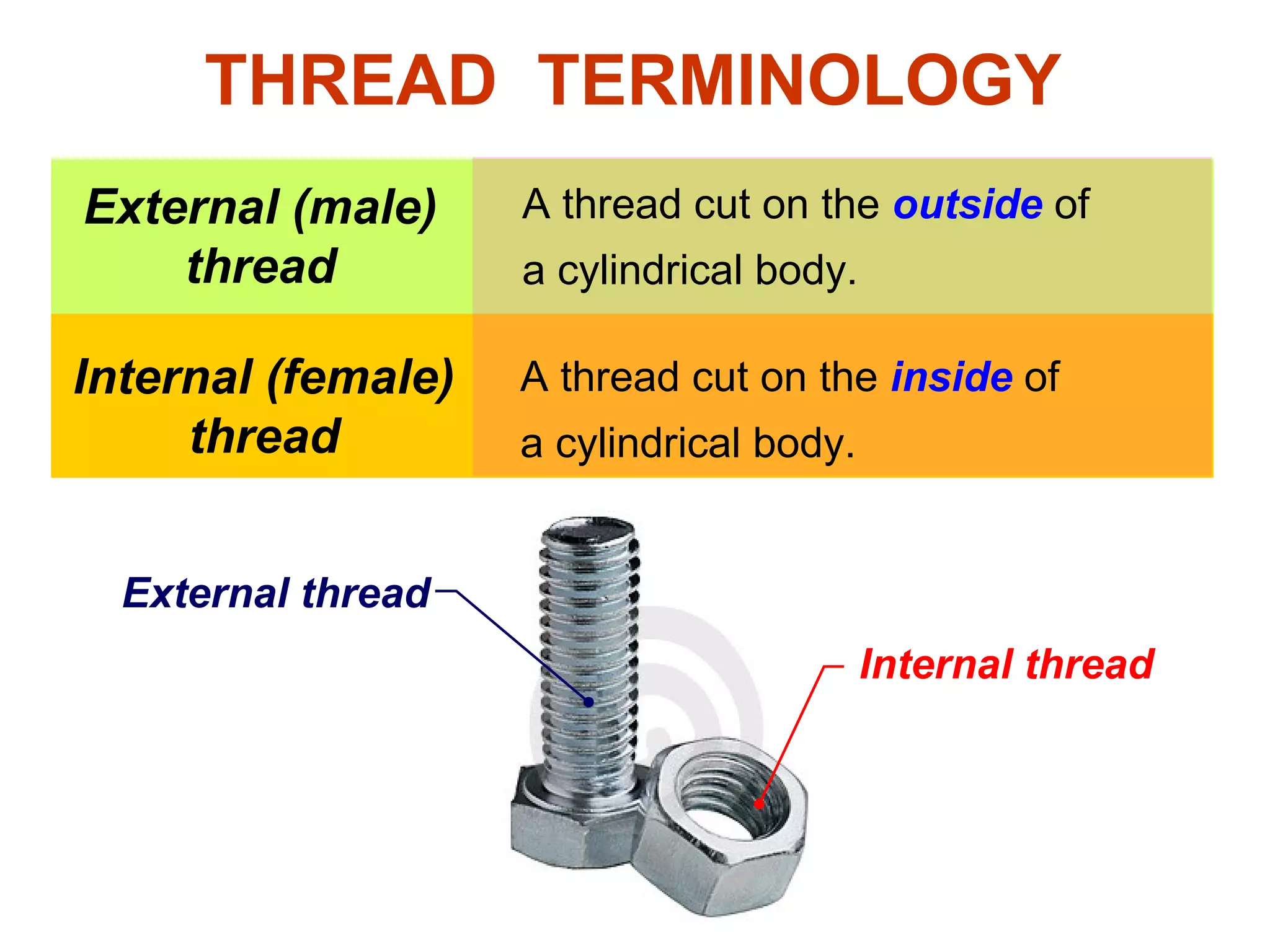
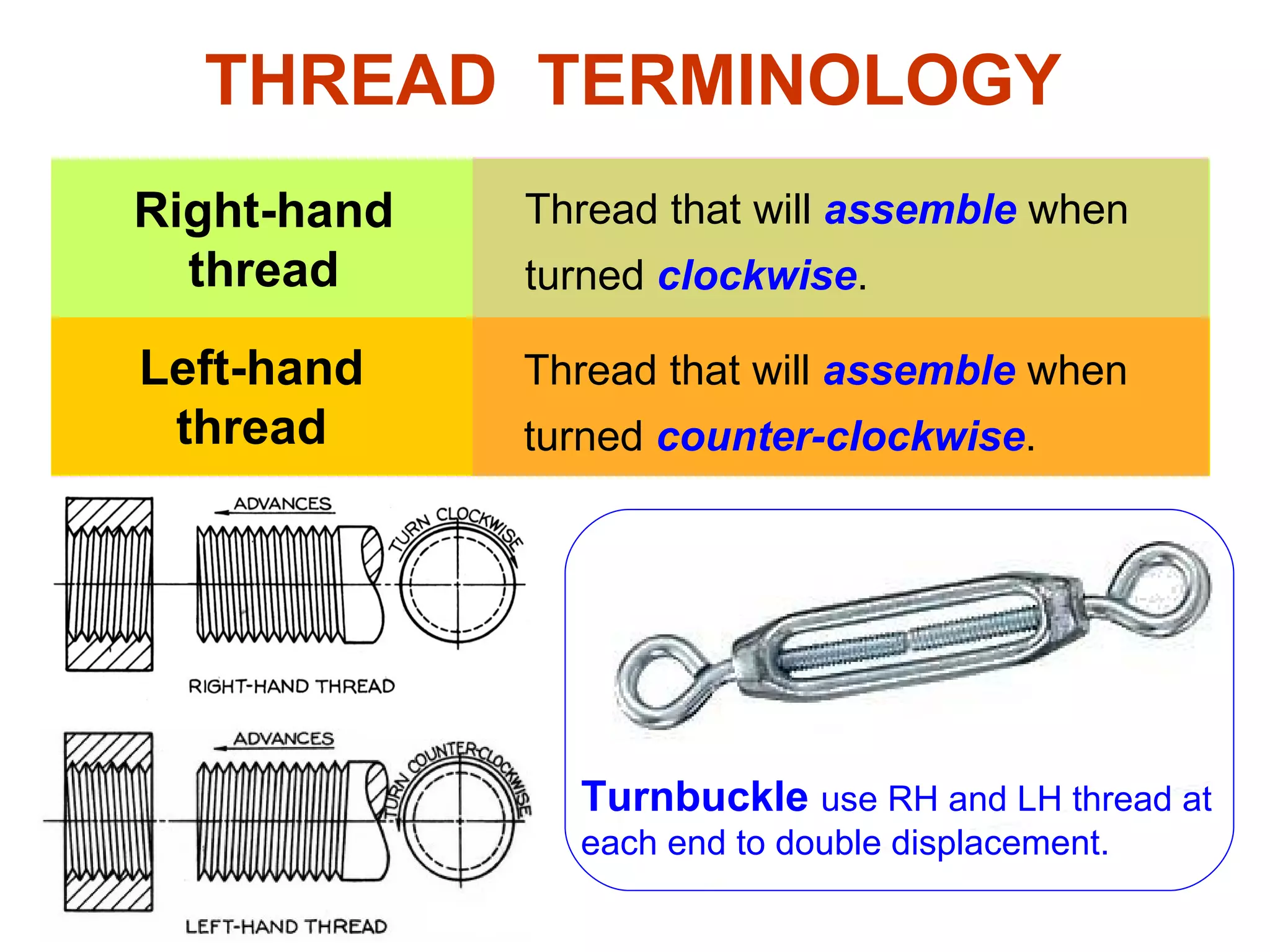
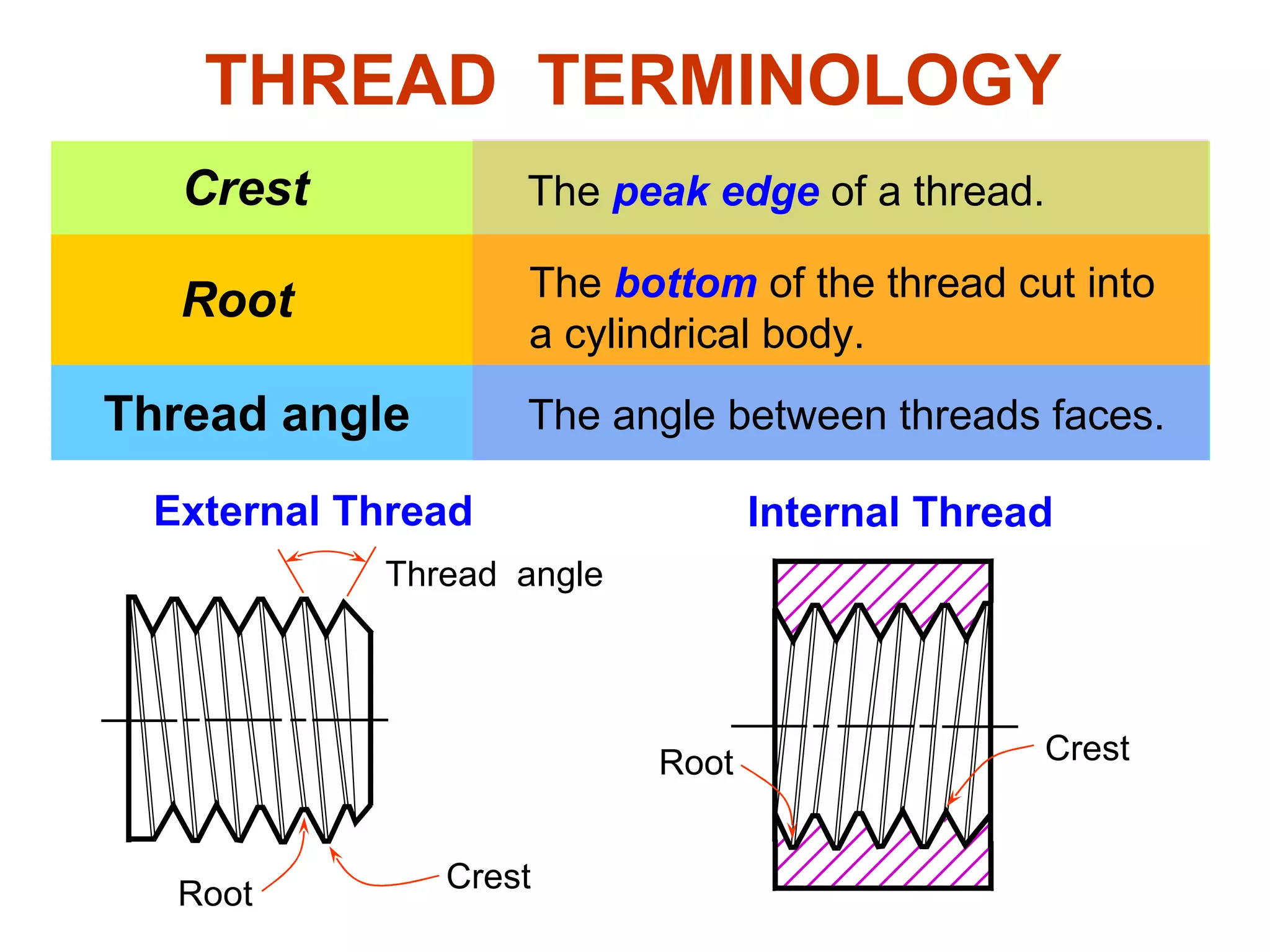
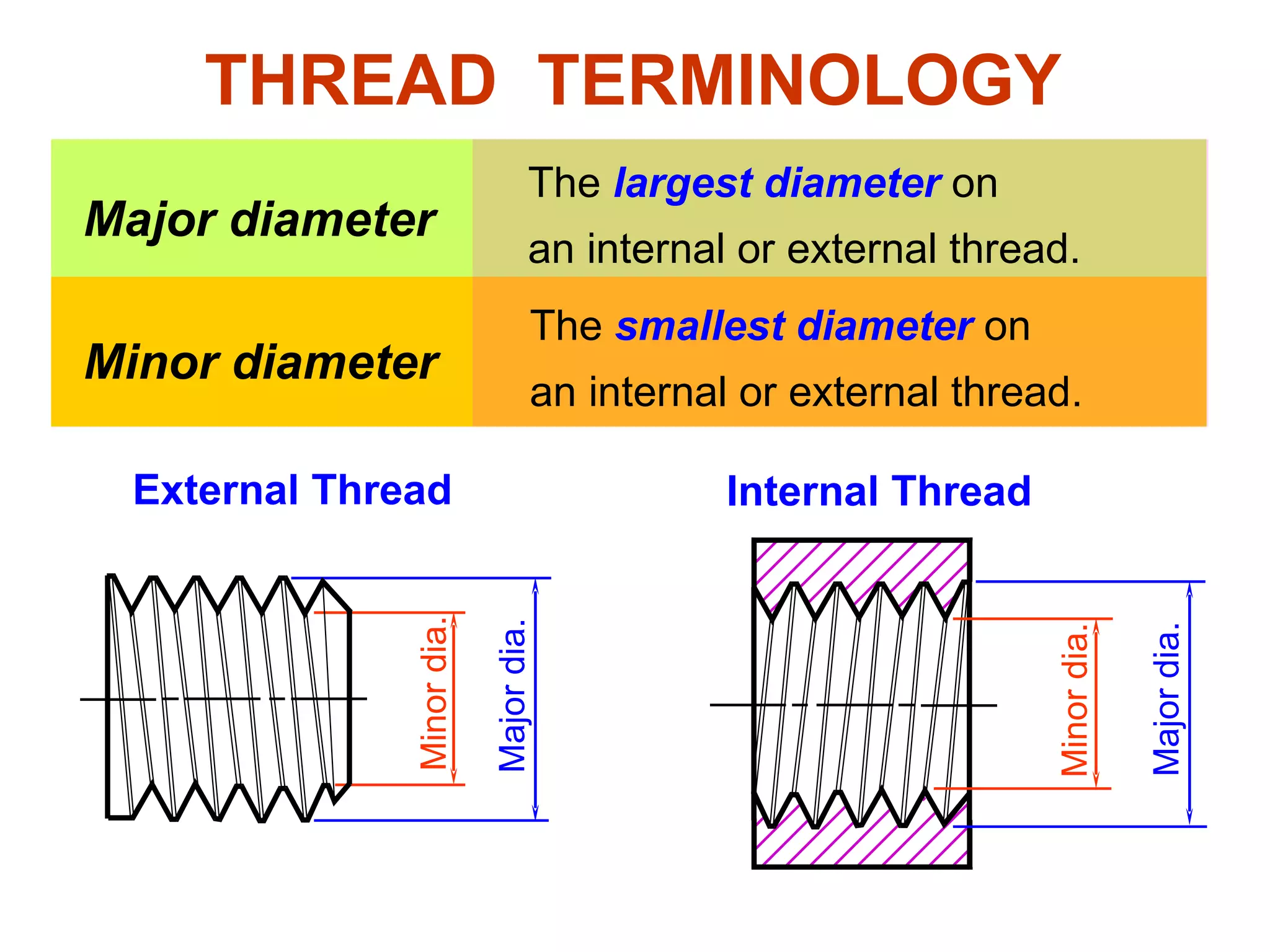
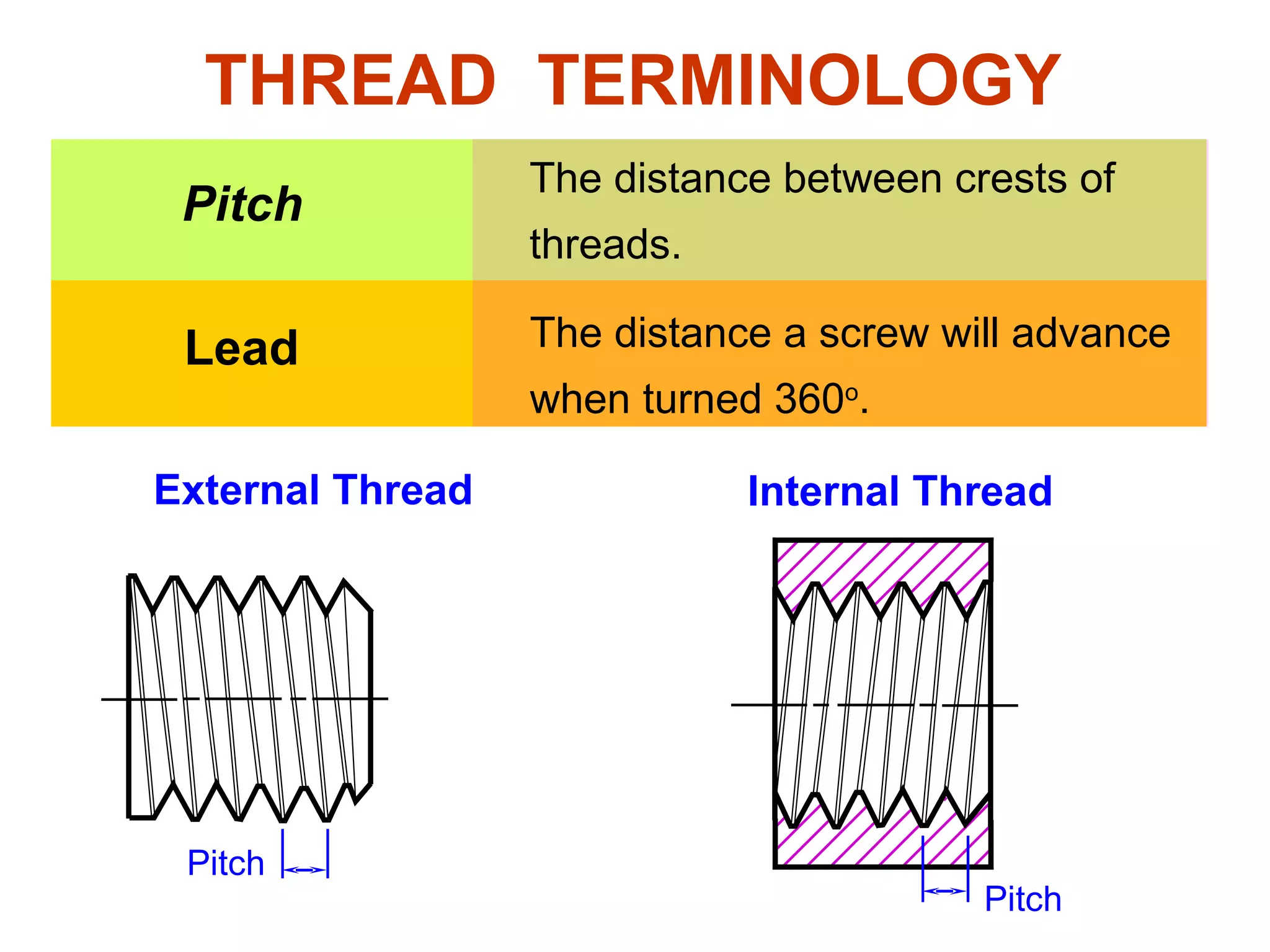
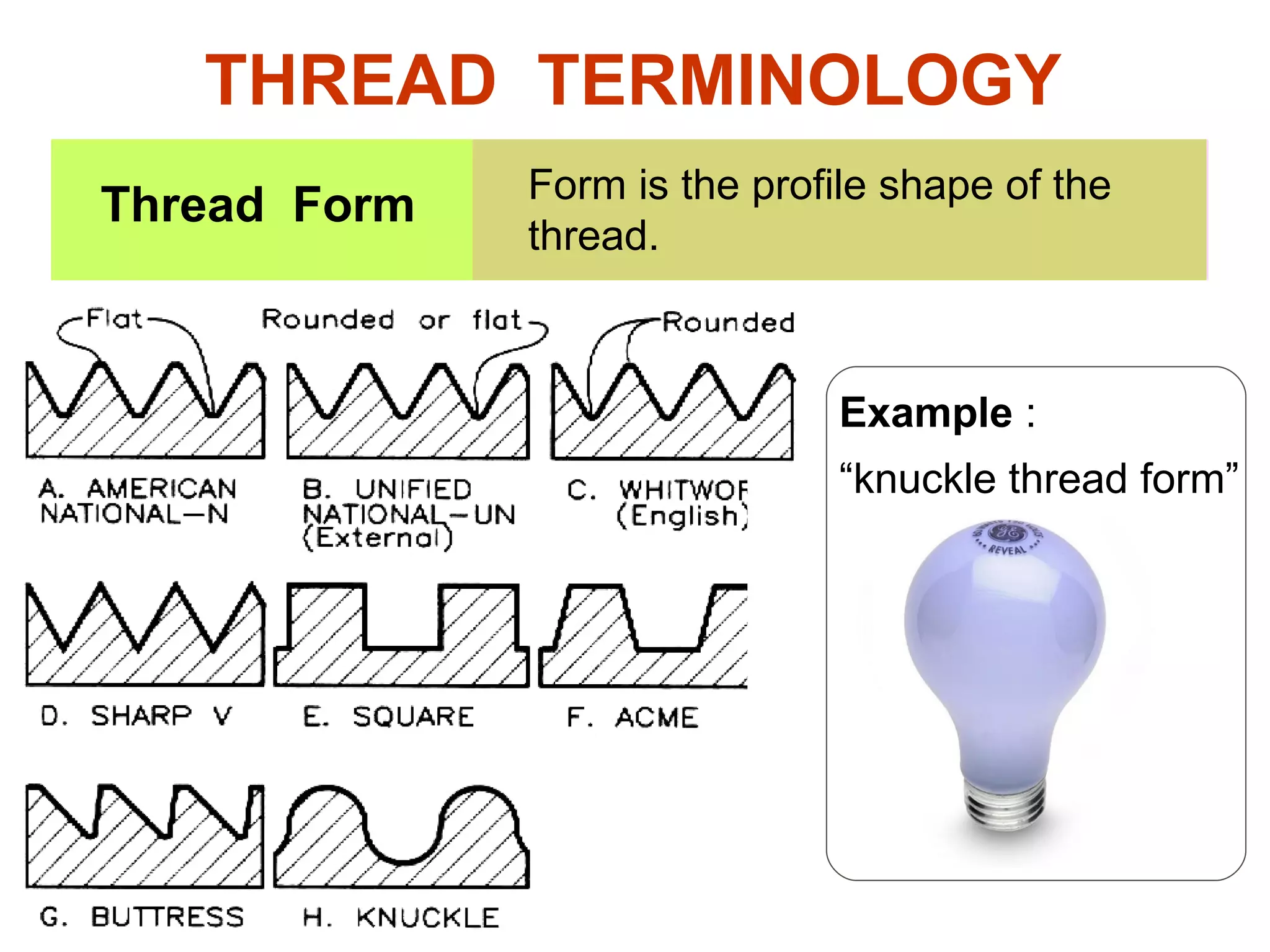
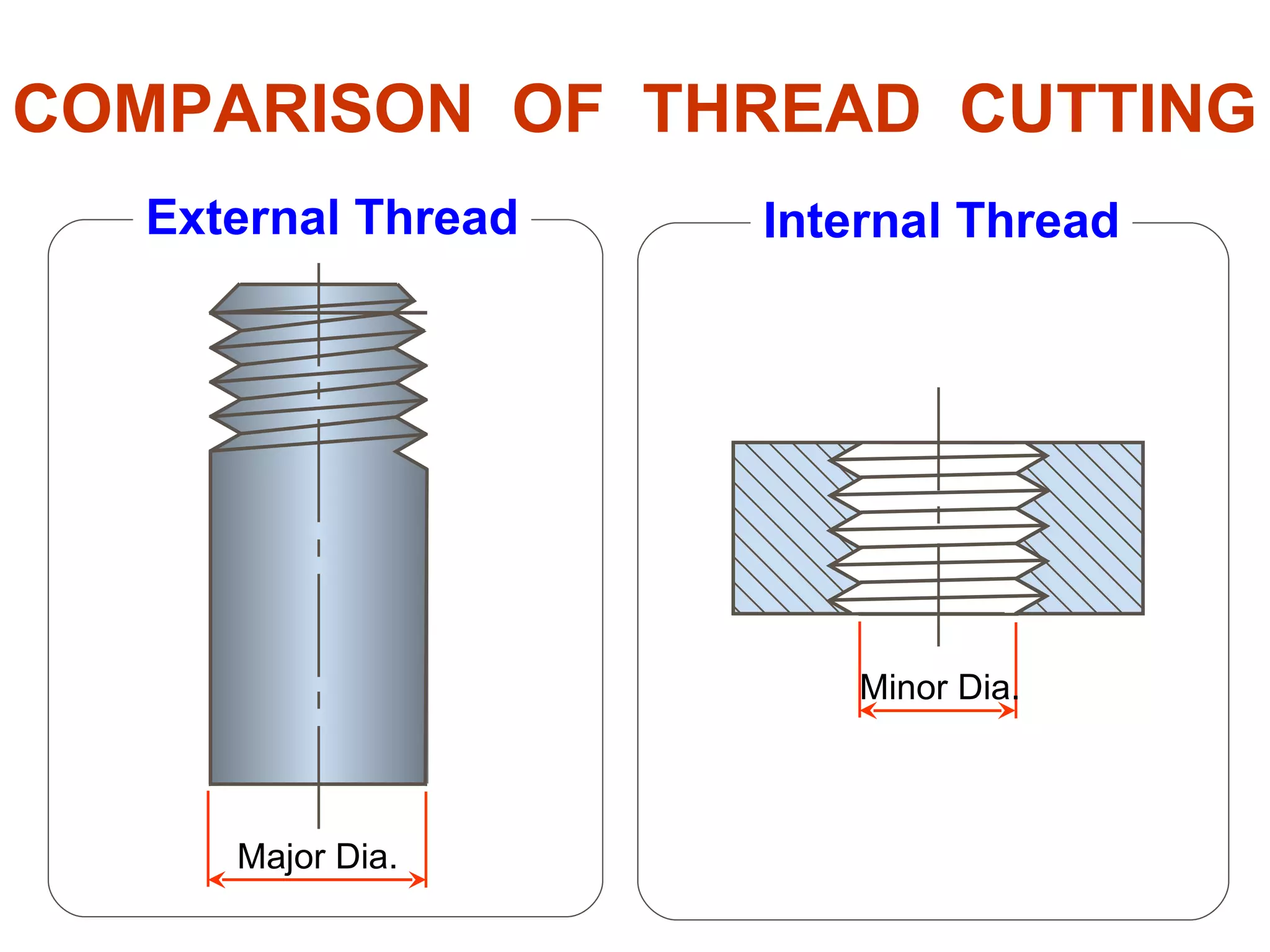
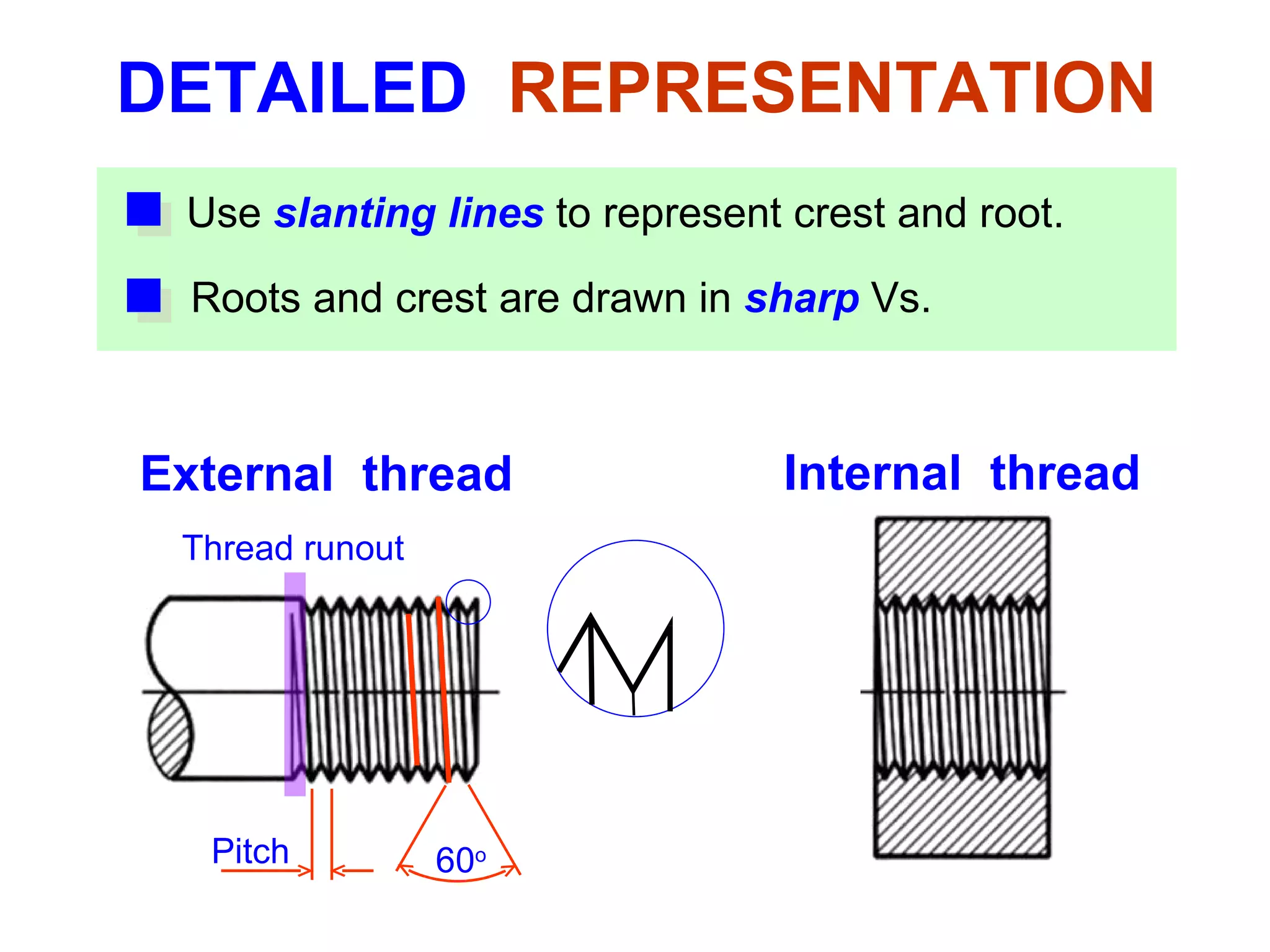
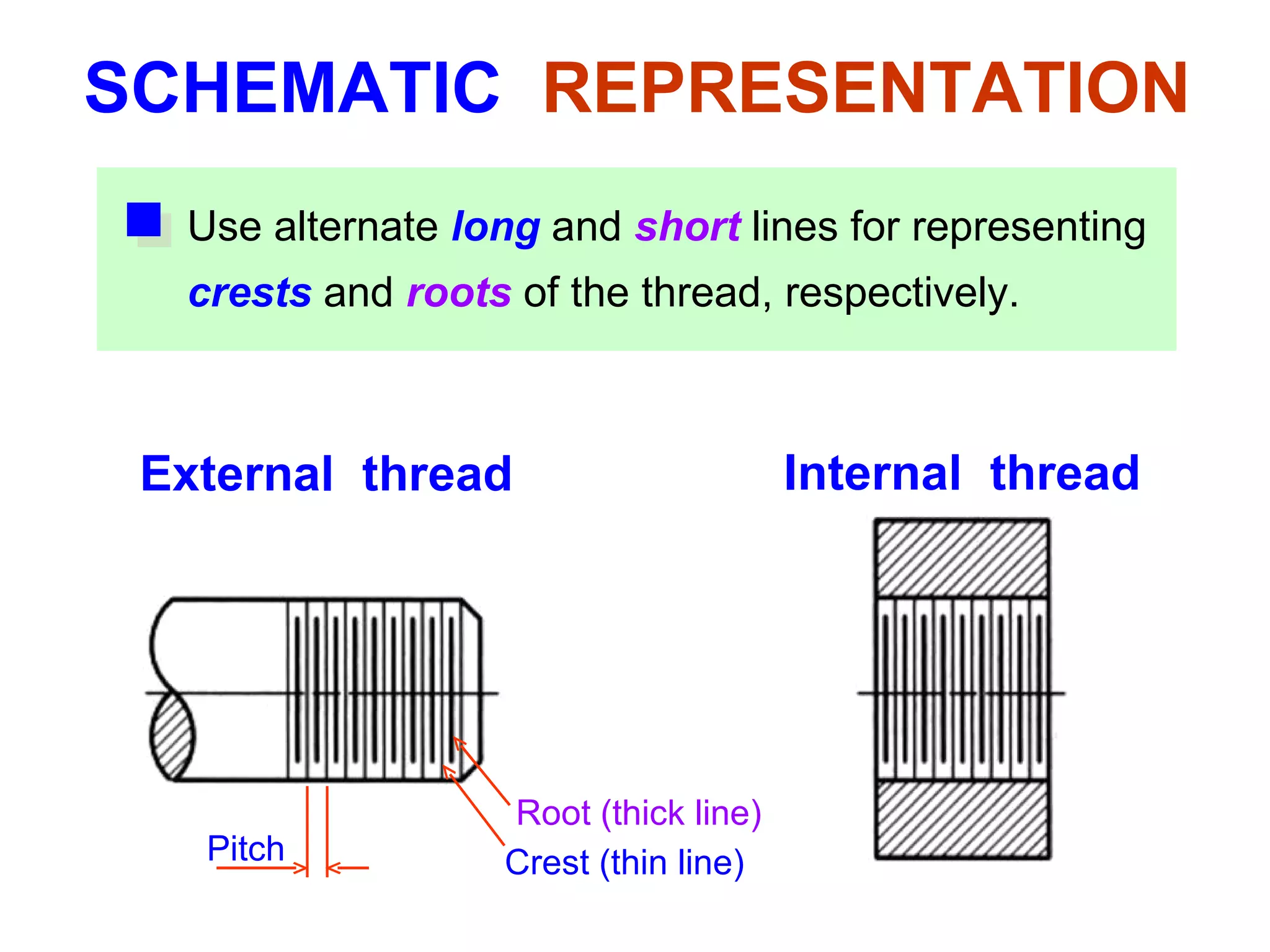
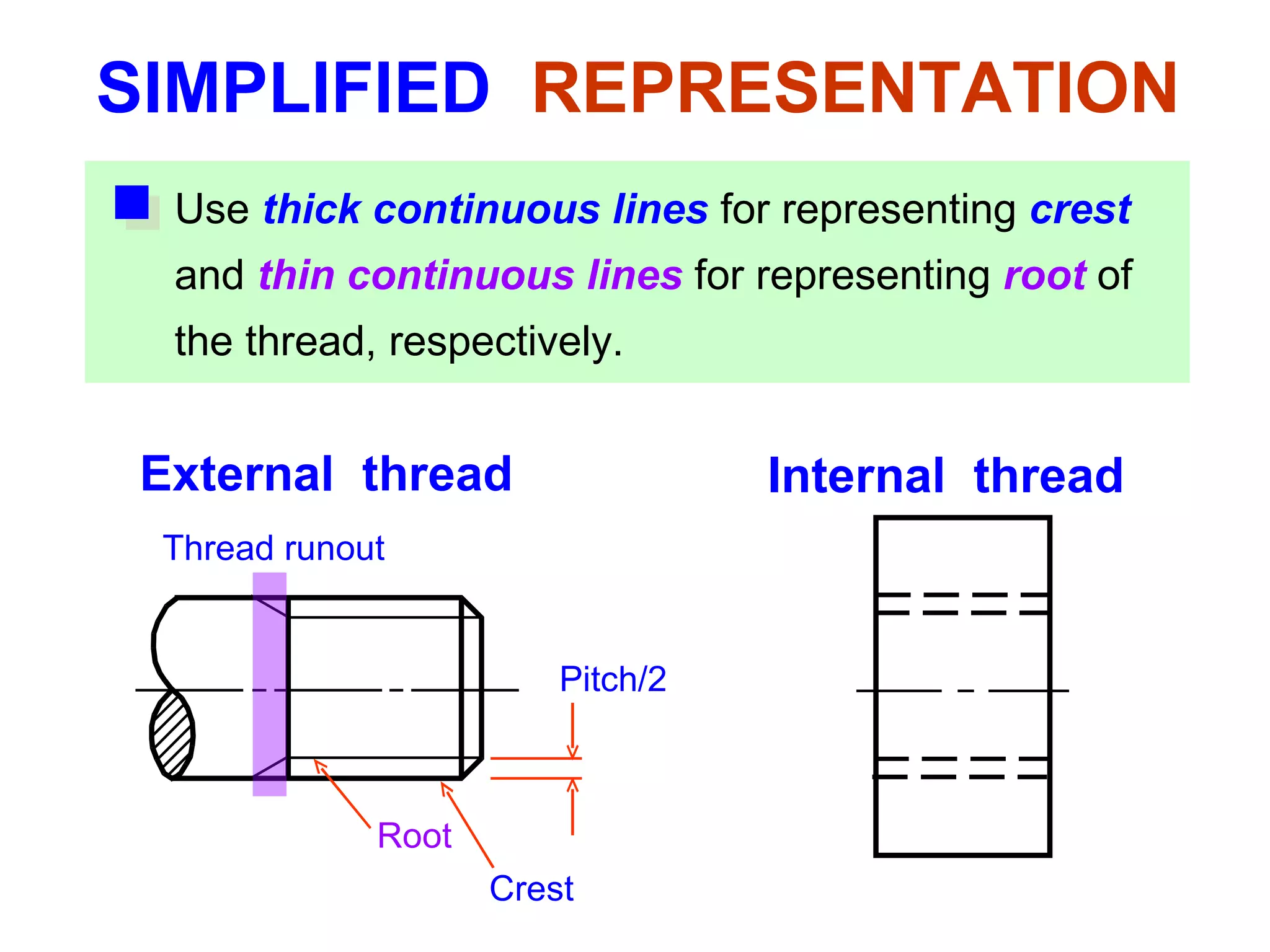
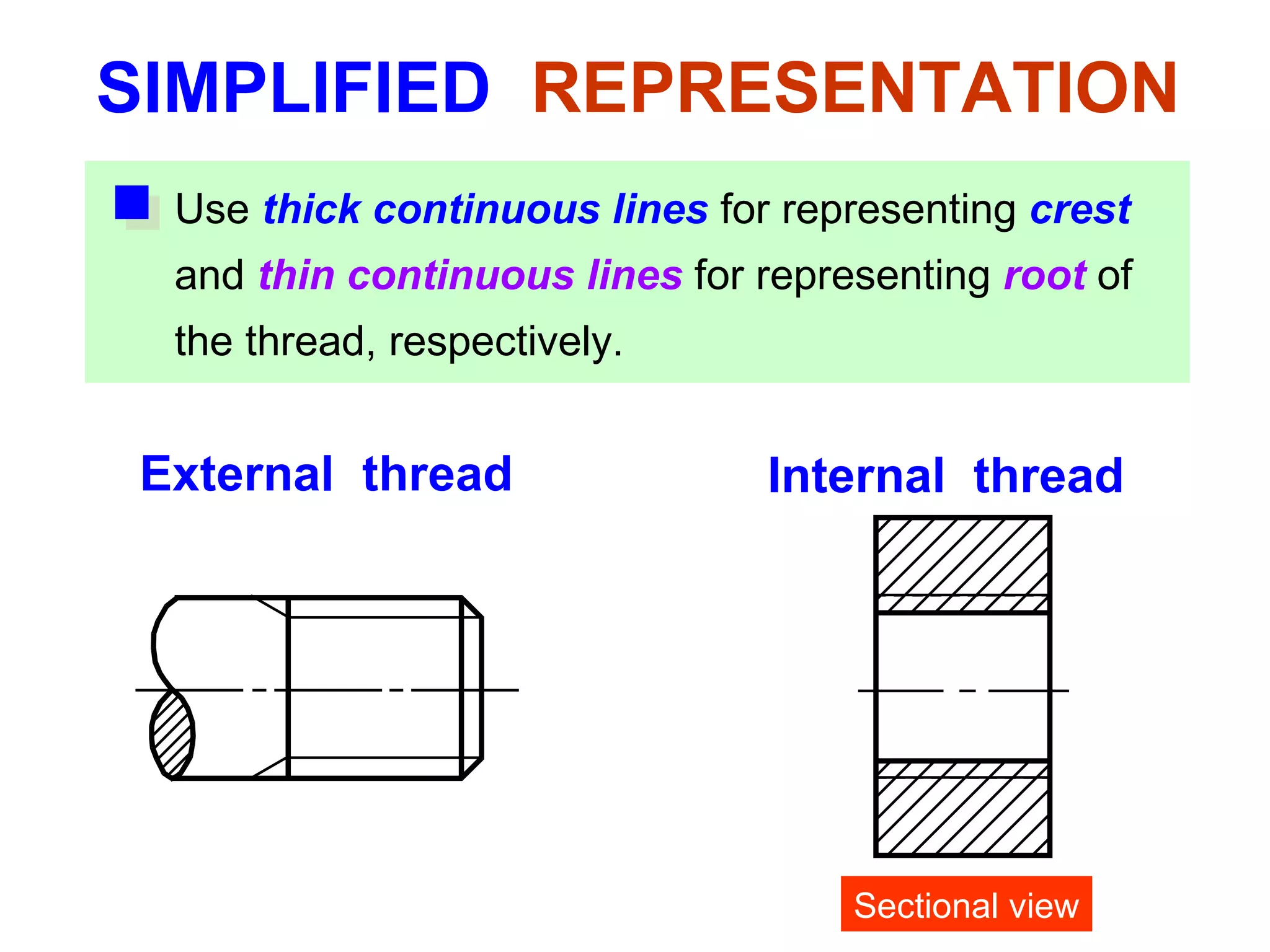
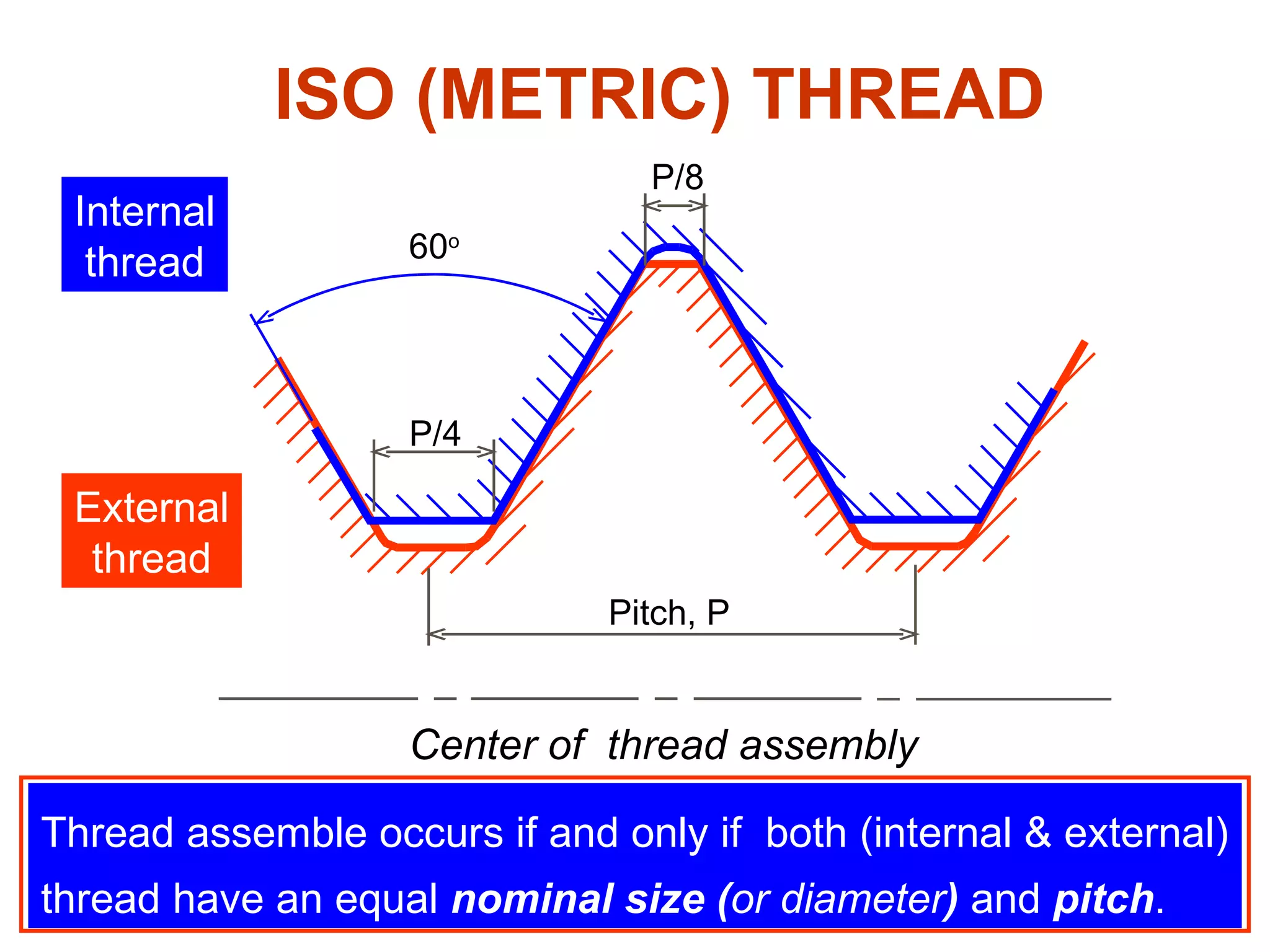
The document discusses different types of threaded fasteners including bolts, studs, screws, and set screws. It defines threaded fastener terminology such as external and internal threads, major and minor diameters, pitch, and thread forms. It also provides steps for drawing representations of various threaded fasteners and holes.









![METRIC COARSE THREAD Minor diameter = Major diameter – Pitch Minor diameter ≈ Tap drill size [Table 9.1] Metric thread In thread drawing , the following relationship is used. 10.00 10.11 1.75 12.00 M12 8.50 8.38 1.50 10.00 M10 6.75 6.65 1.25 8.00 M8 5.00 4.92 1.00 6.00 M6 Tap drill size Minor diameter Pitch Major diameter Nominal size](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter11threadfastener-110727065553-phpapp01/75/Engineering-Drawing-Chapter-11-thread-fastener-25-2048.jpg)
![METRIC FINE THREAD [Table 9.2] Minor diameter = Major diameter – Pitch Minor diameter ≈ Tap drill size In thread drawing , the following relationship is used. 9.00 8.917 1.00 9.25 9.188 0.75 10.00 M10 8.75 8.647 1.25 7.00 6.917 1.00 7.25 7.188 0.75 8.00 M8 Tap drill size Minor diameter Pitch Major diameter Nominal size](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter11threadfastener-110727065553-phpapp01/75/Engineering-Drawing-Chapter-11-thread-fastener-26-2048.jpg)