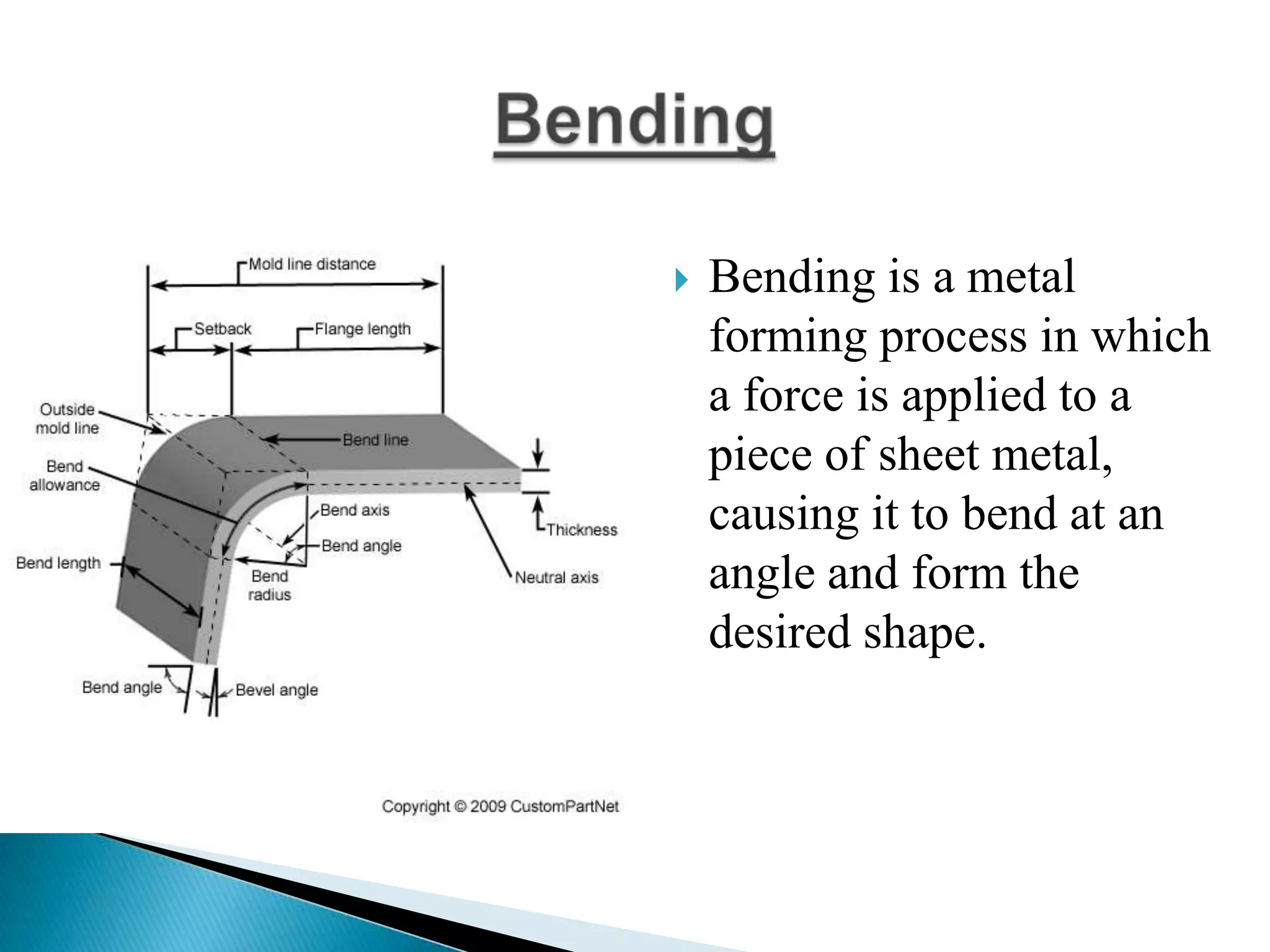
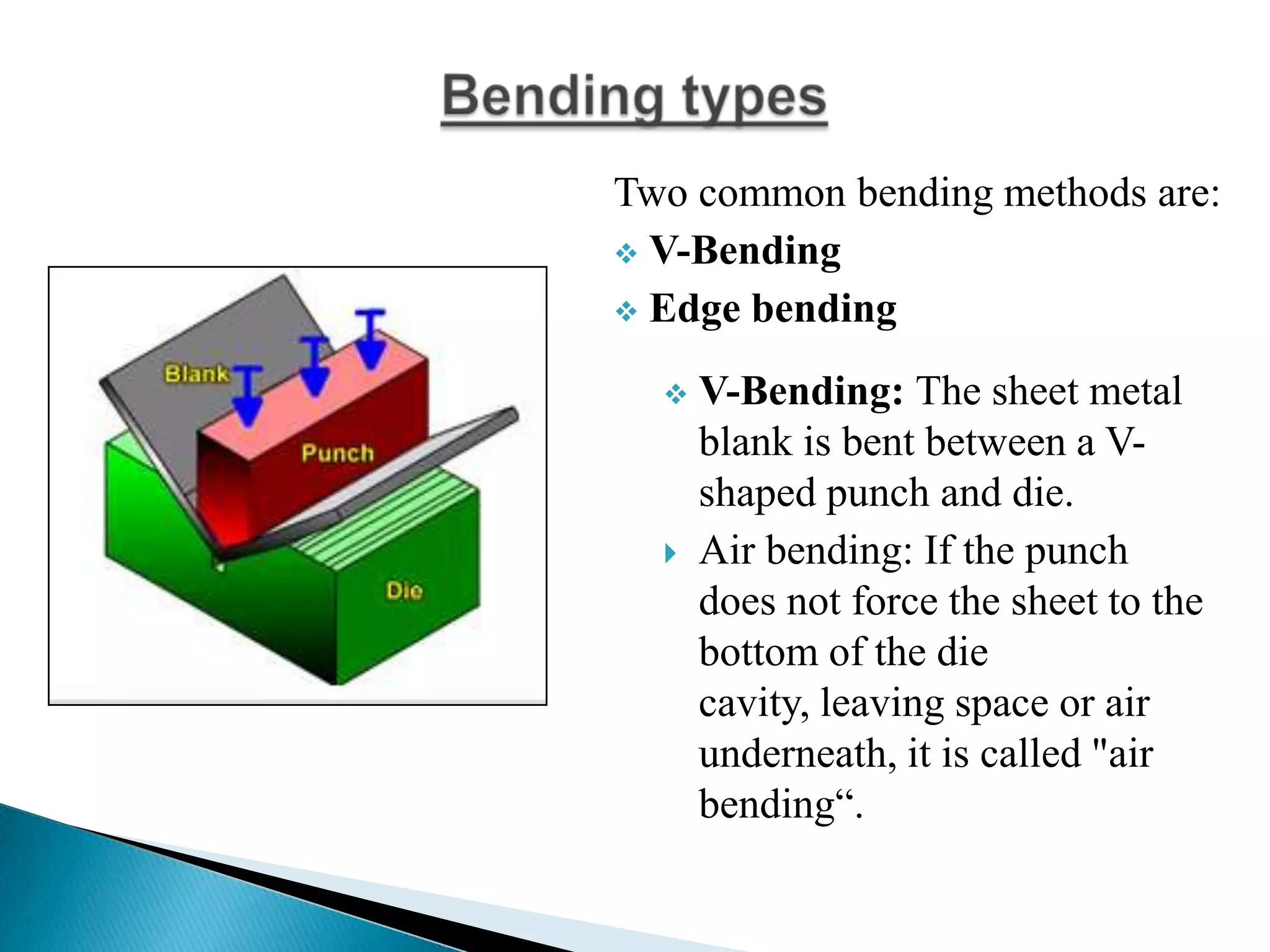
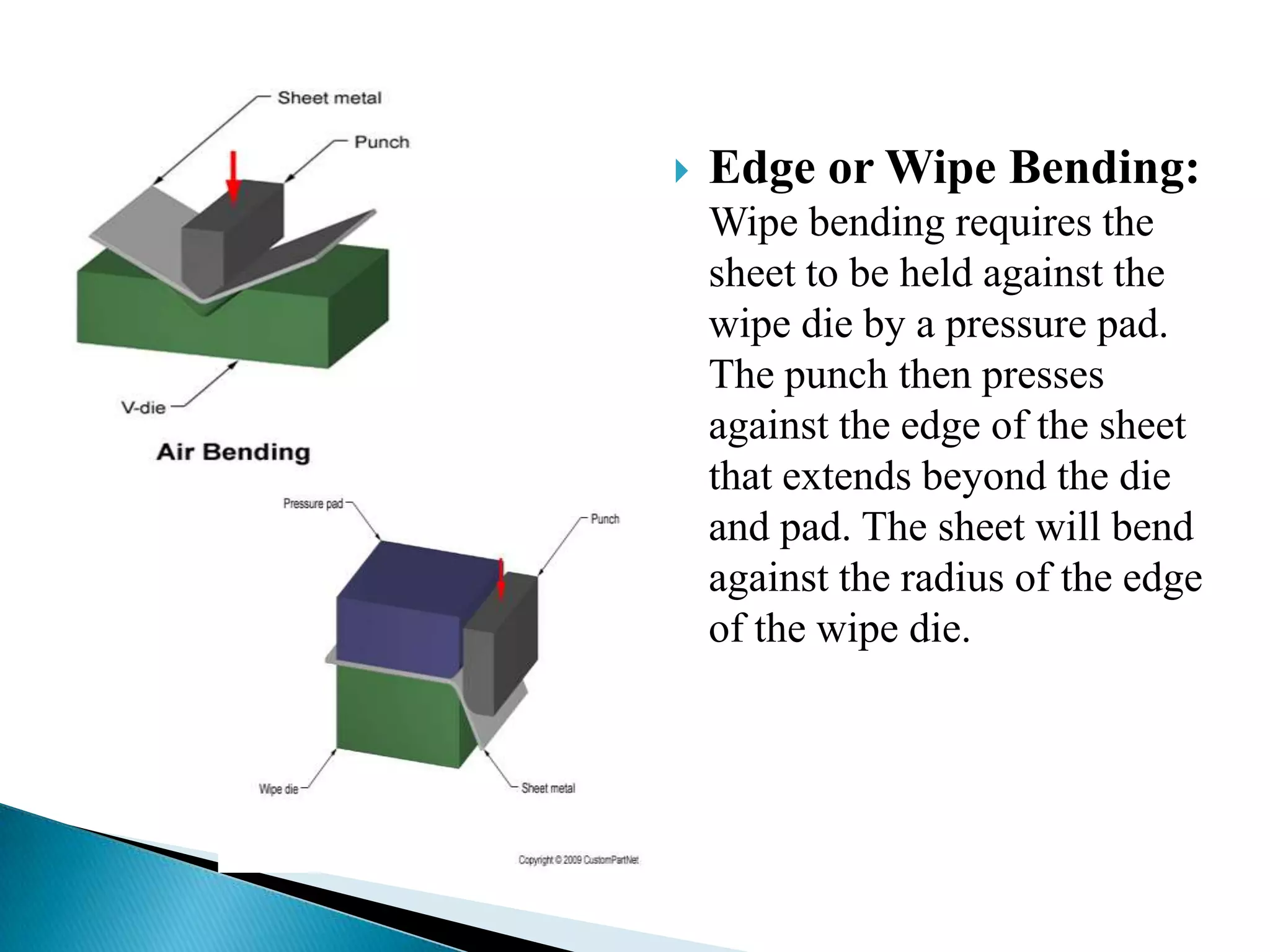
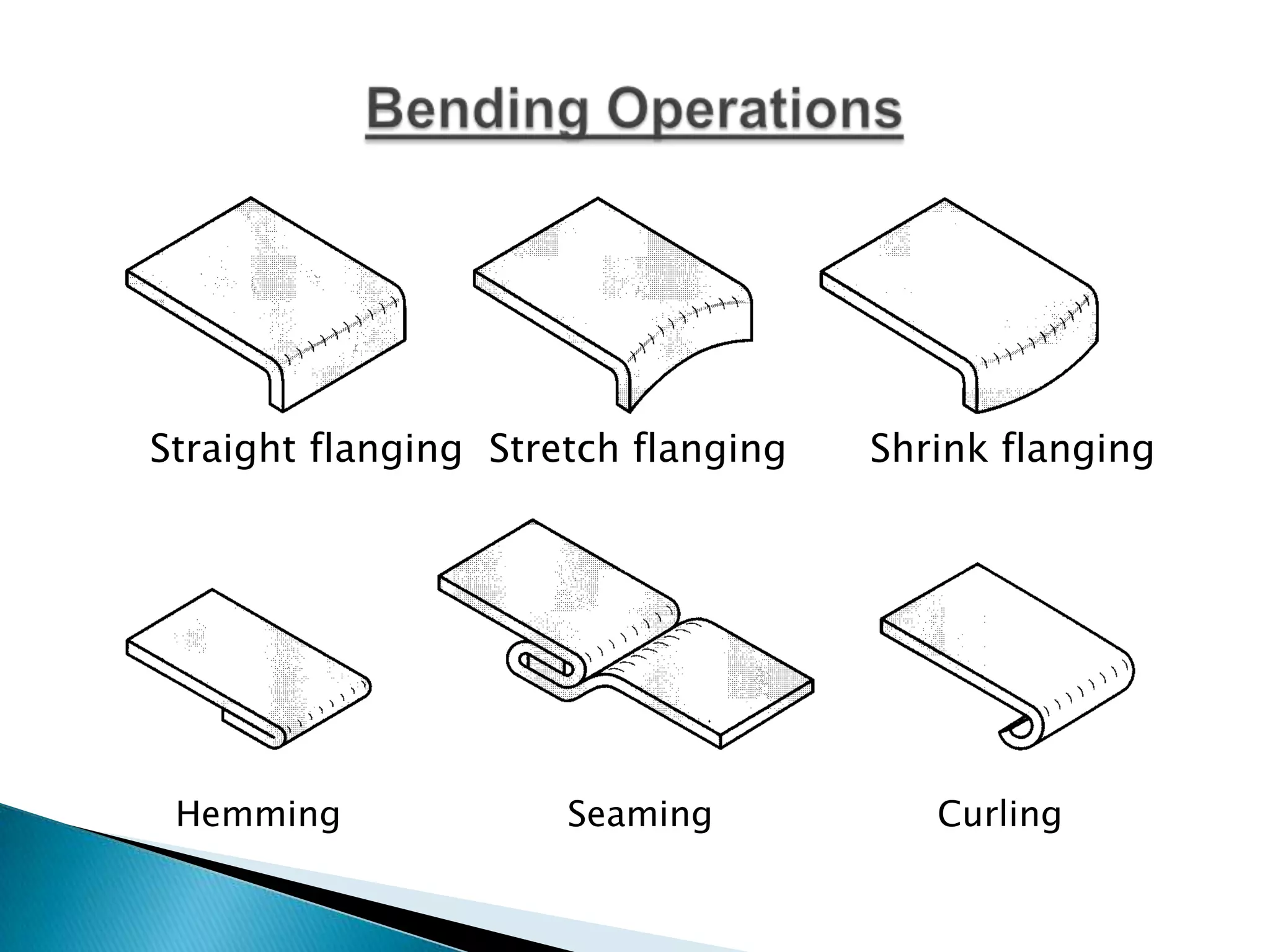
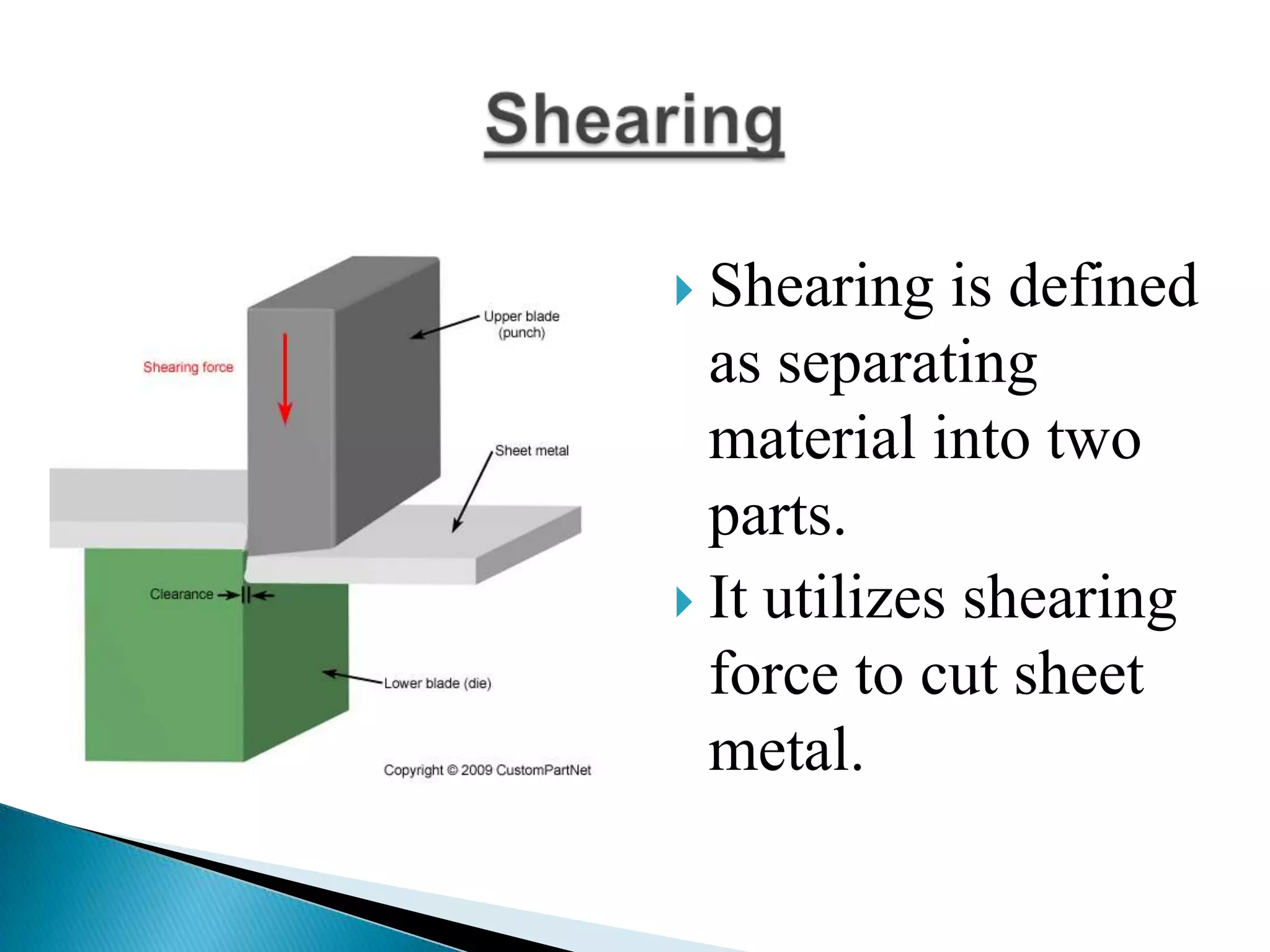
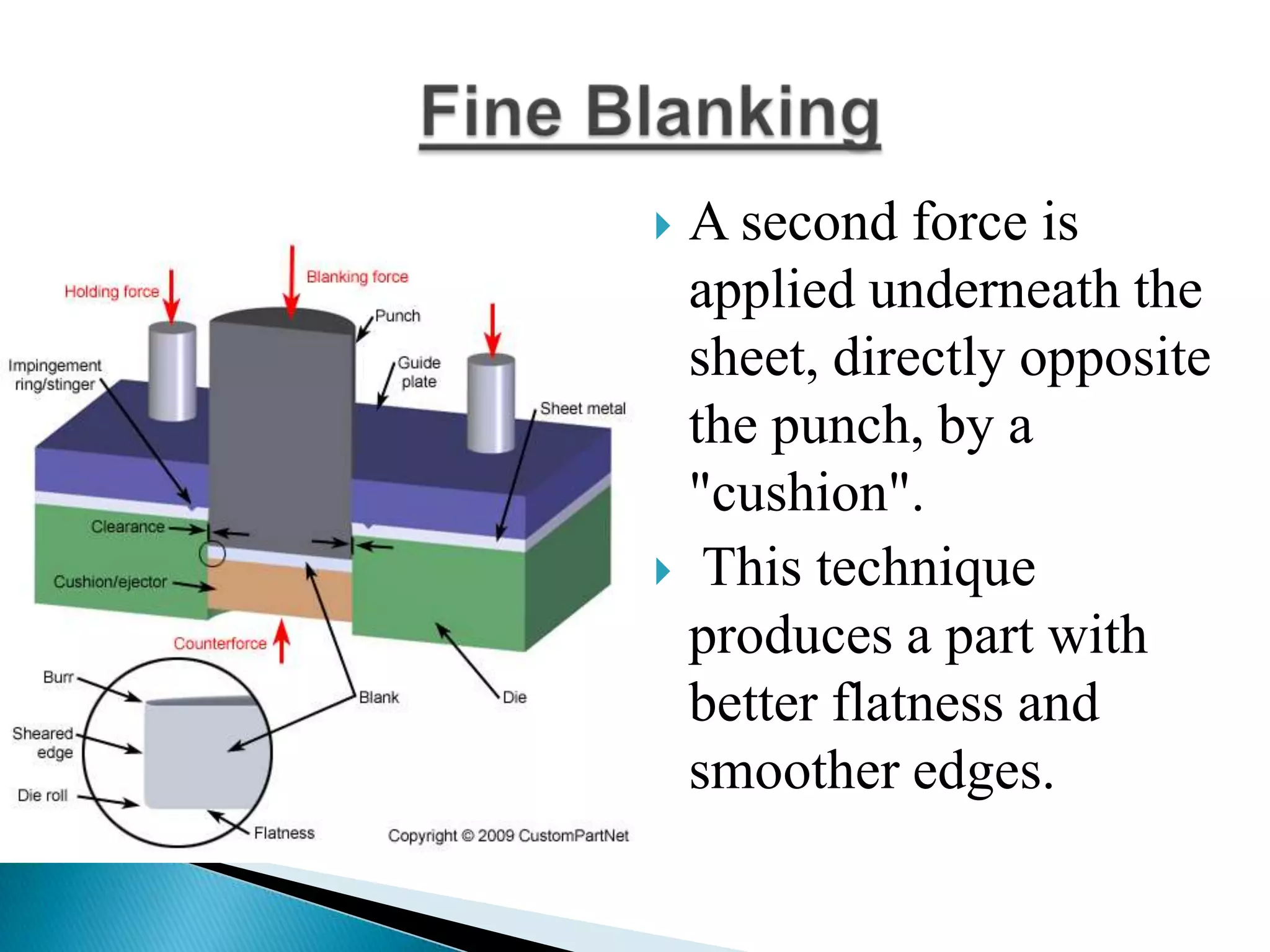
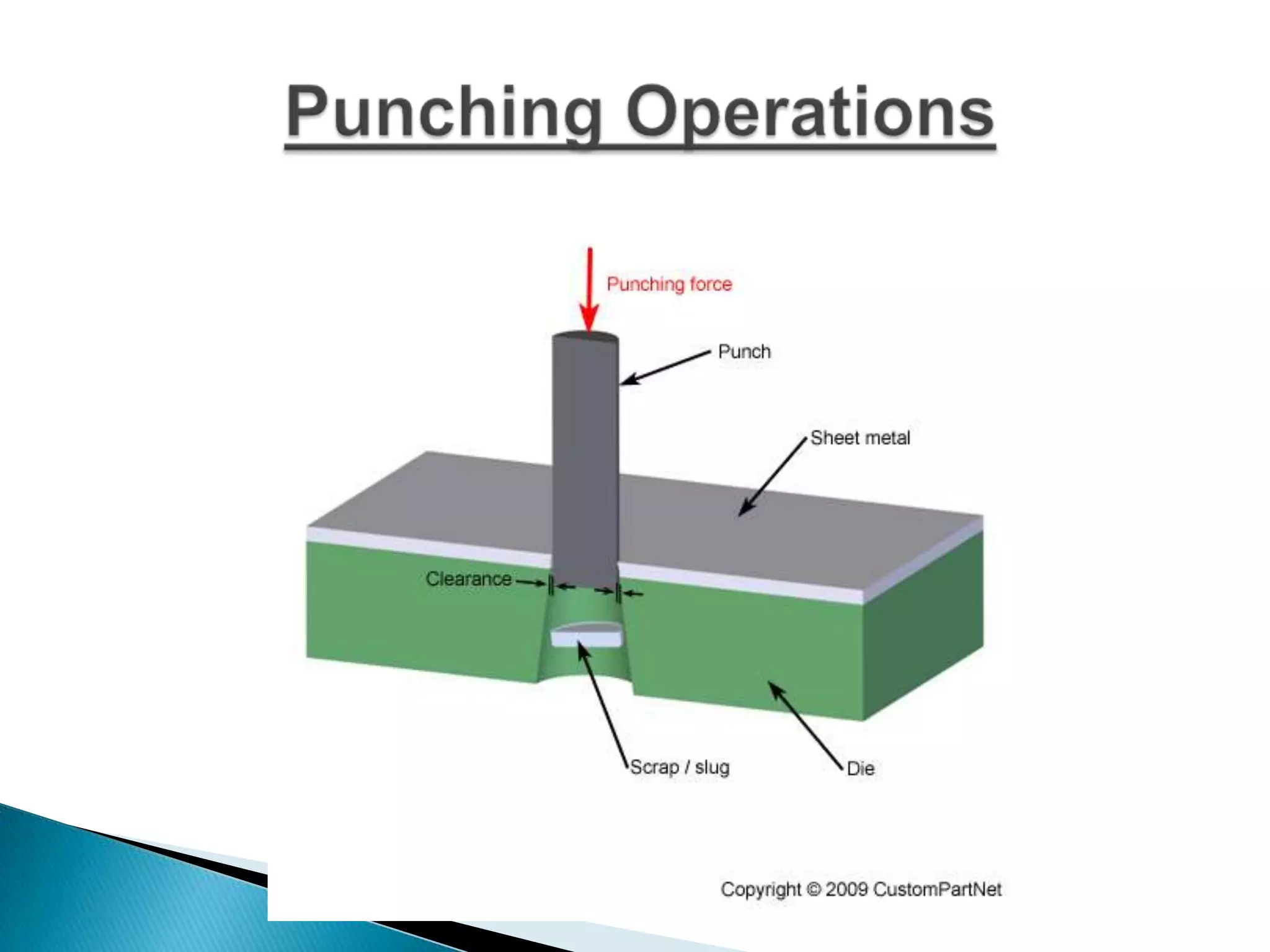
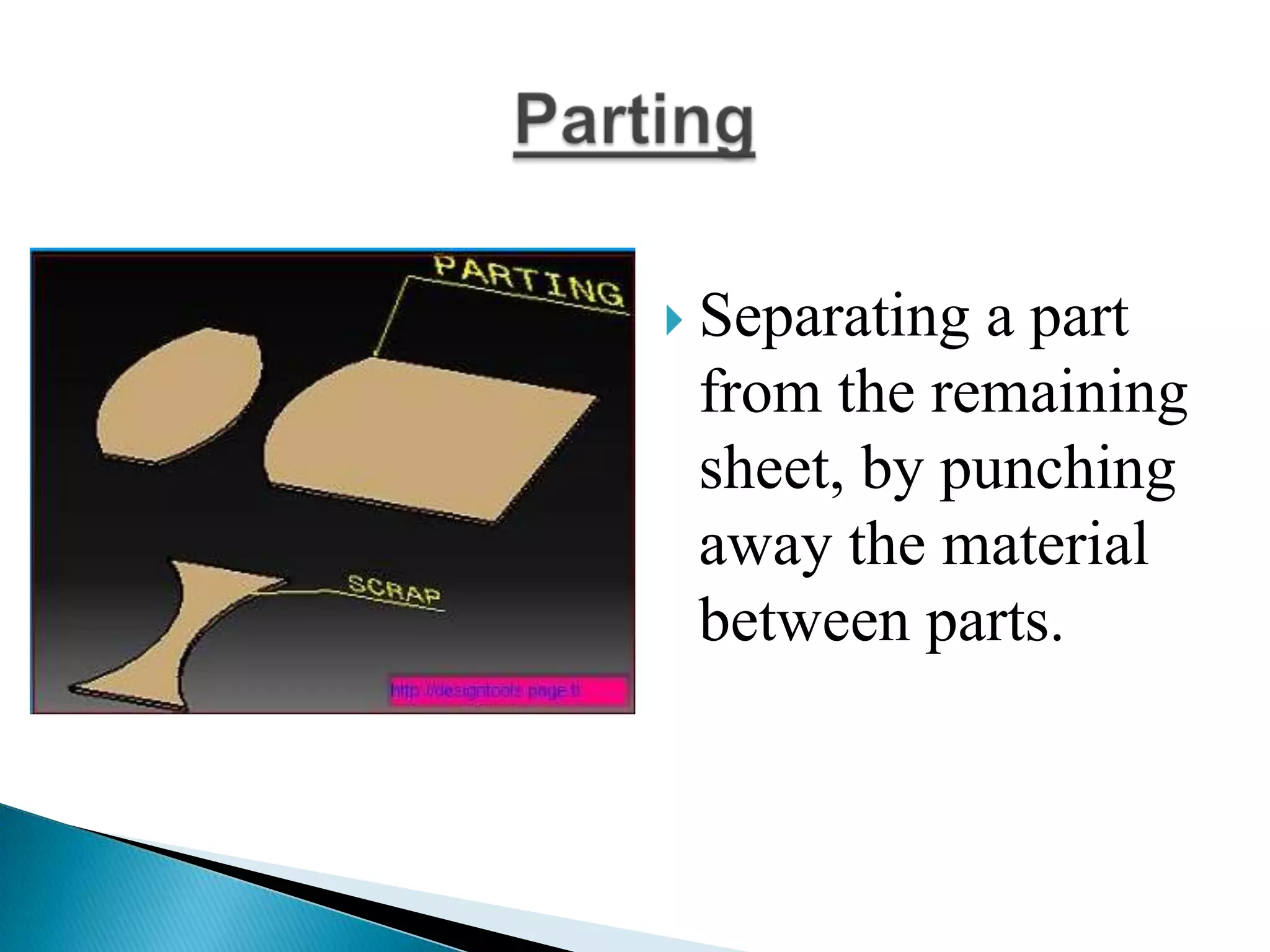
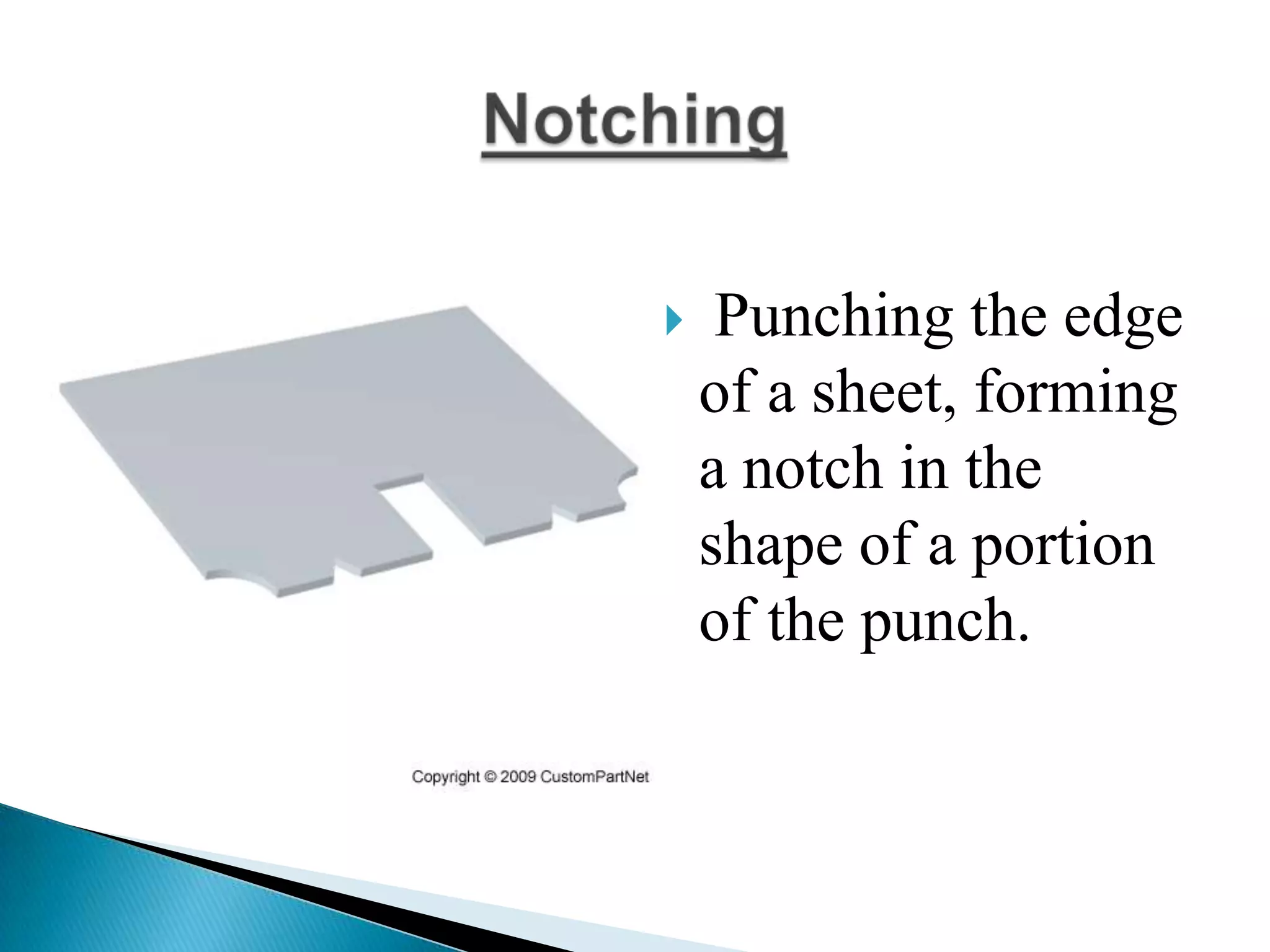
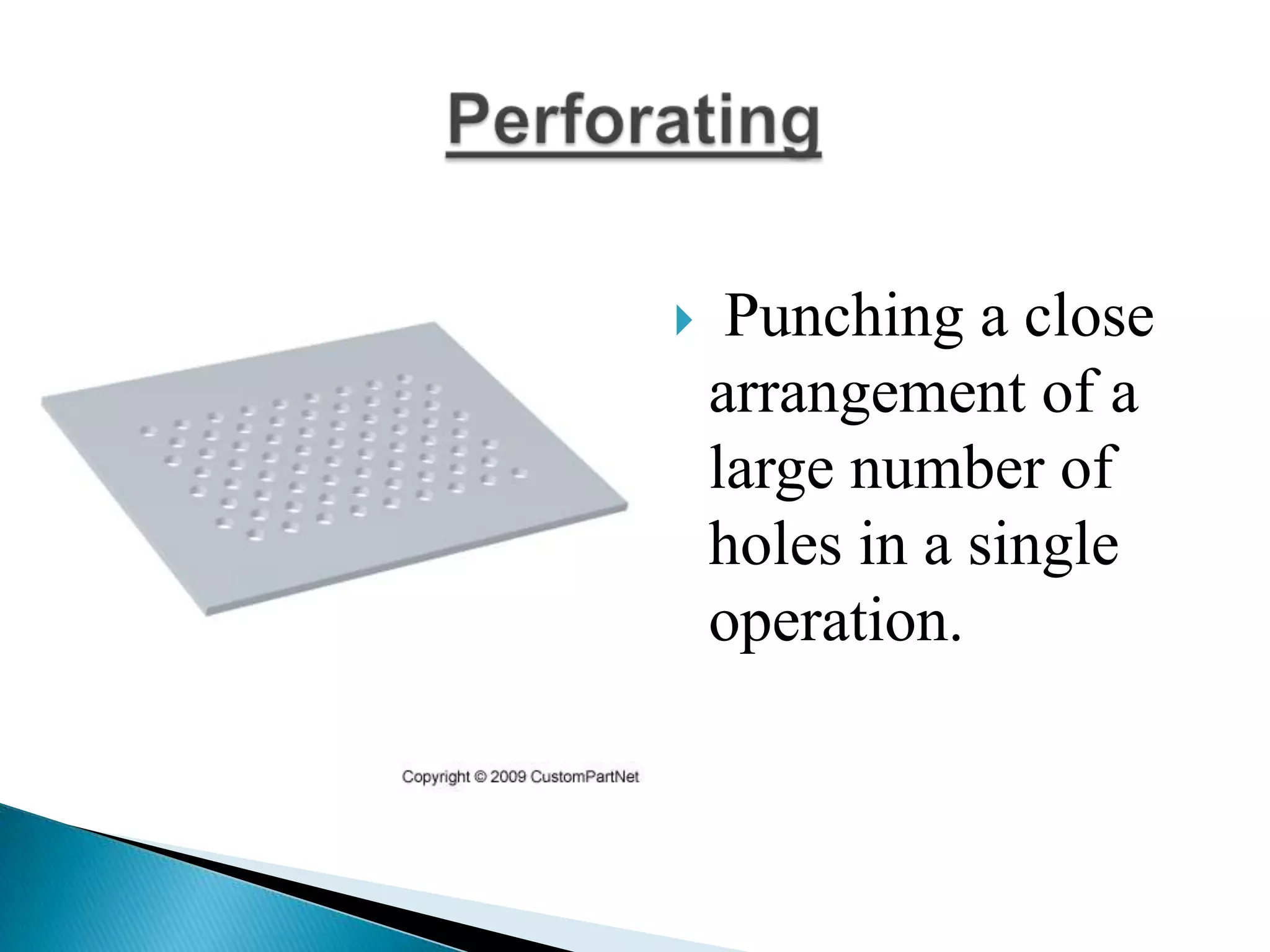
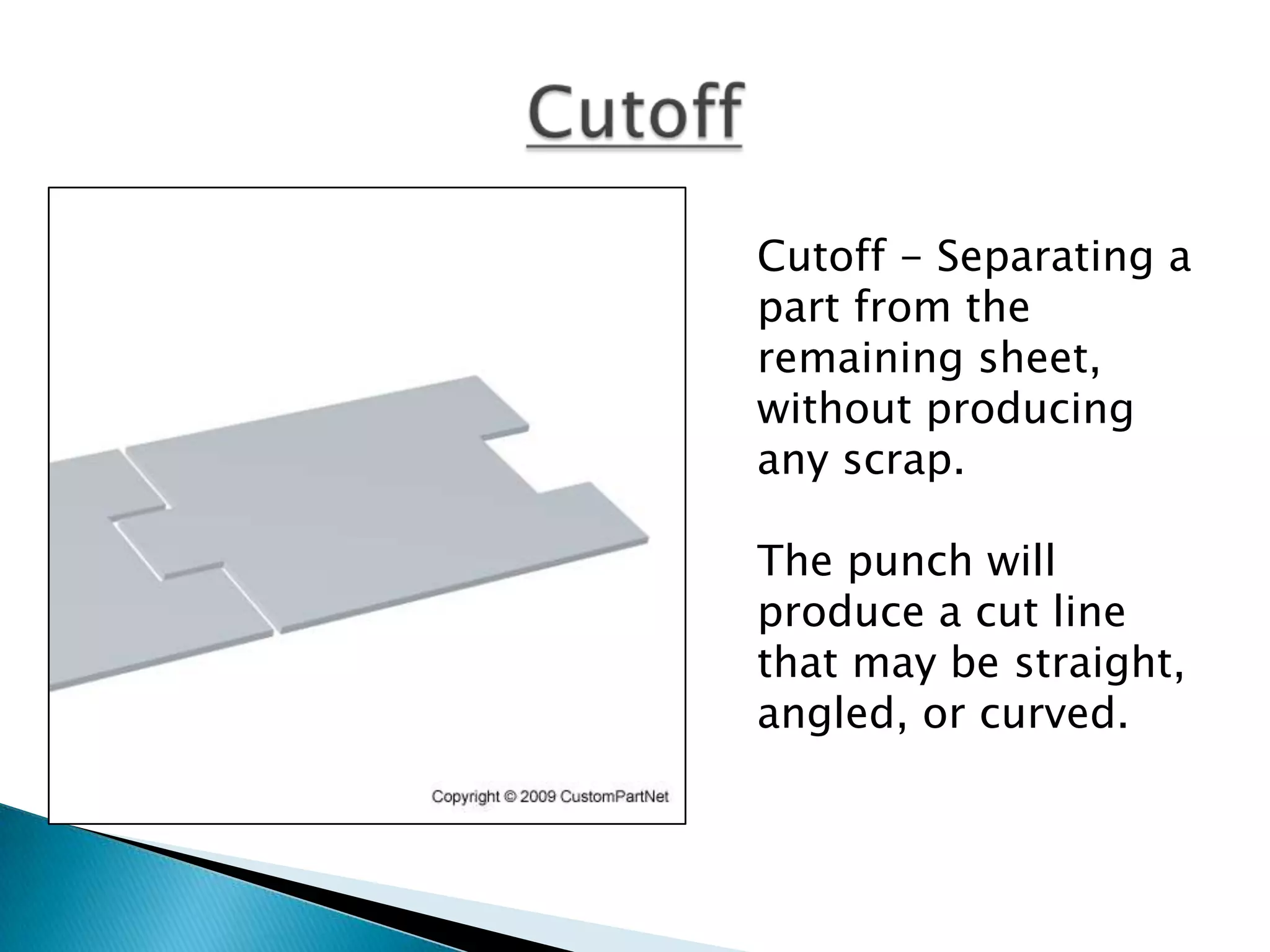
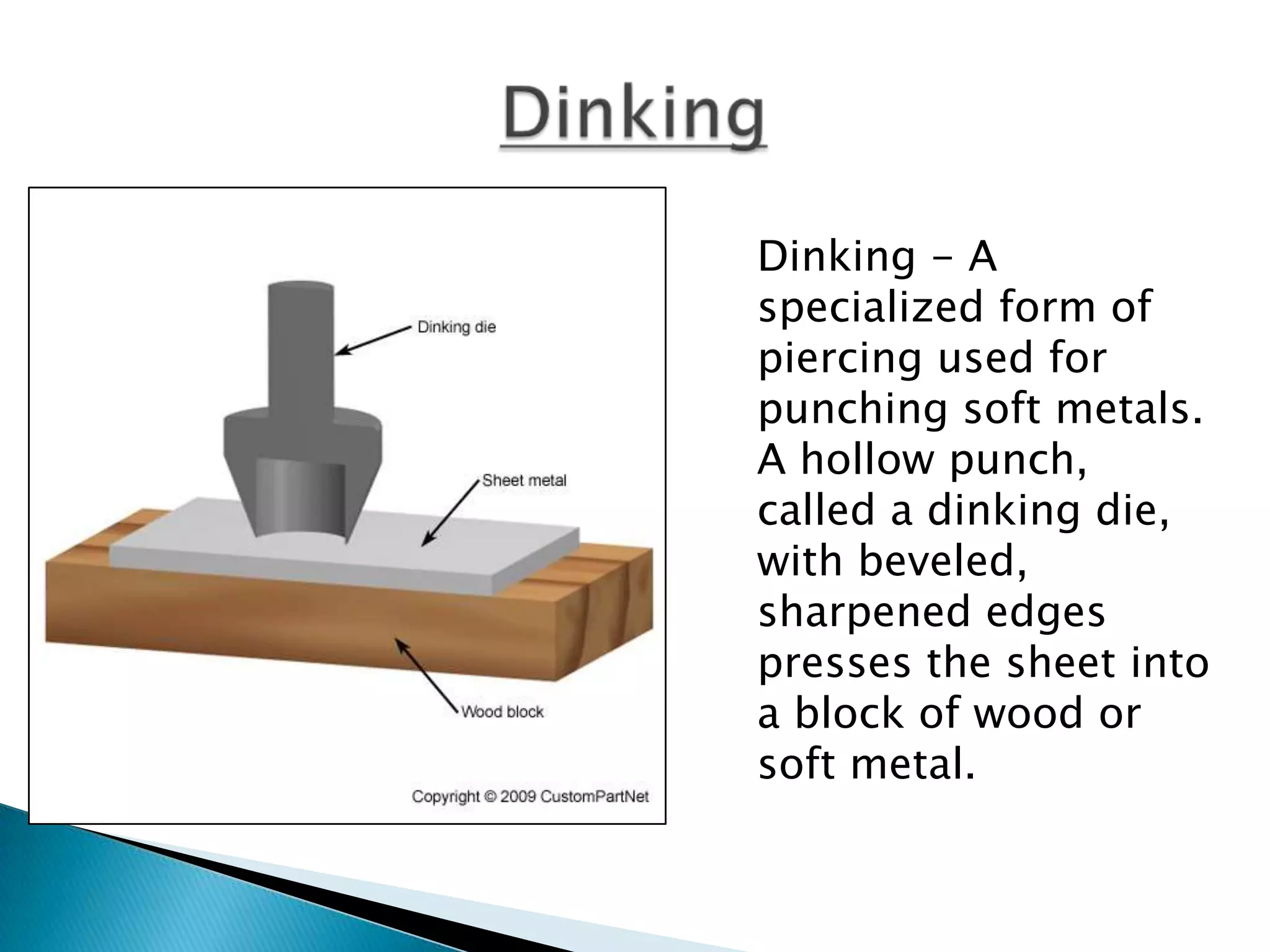
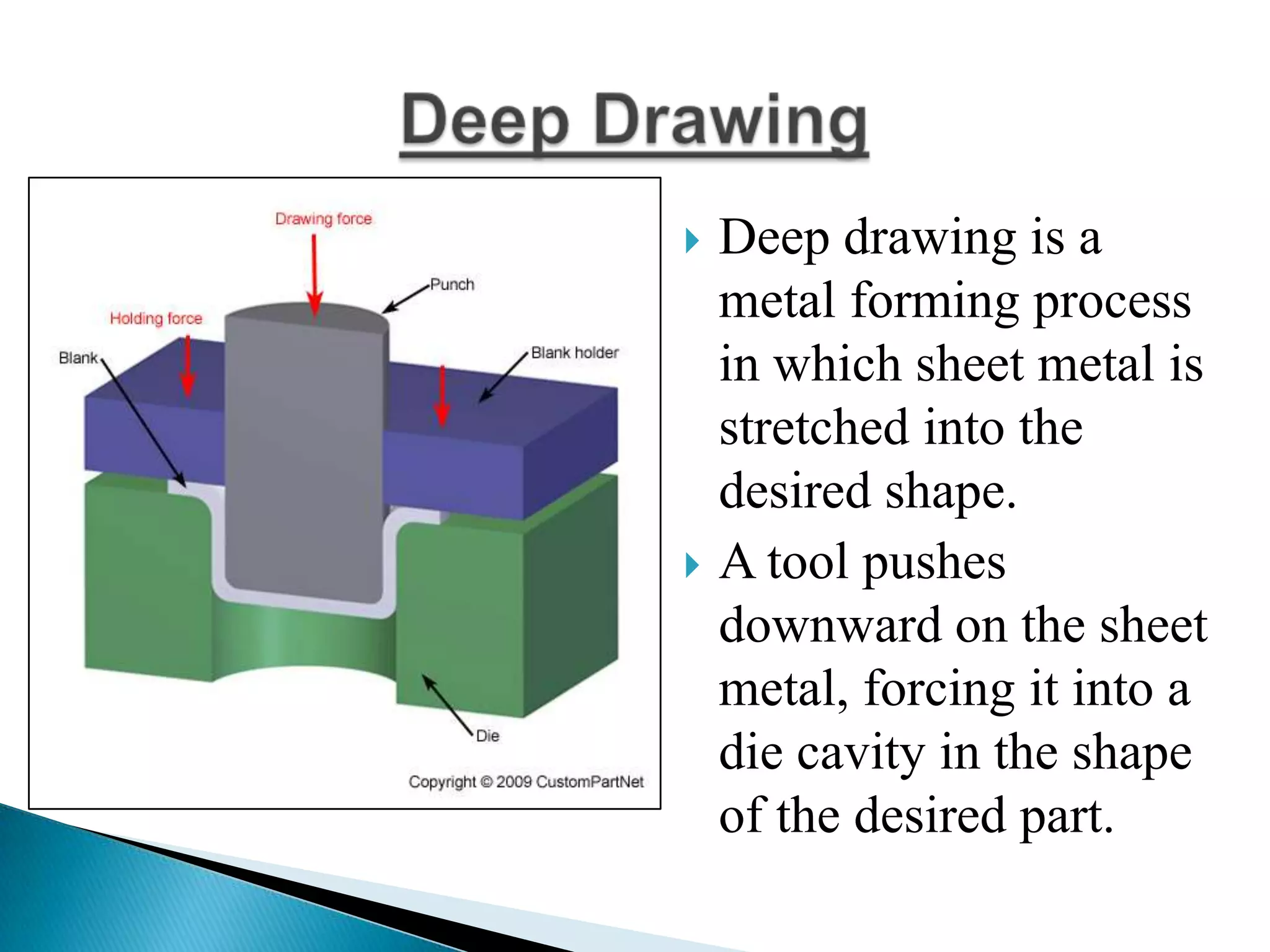
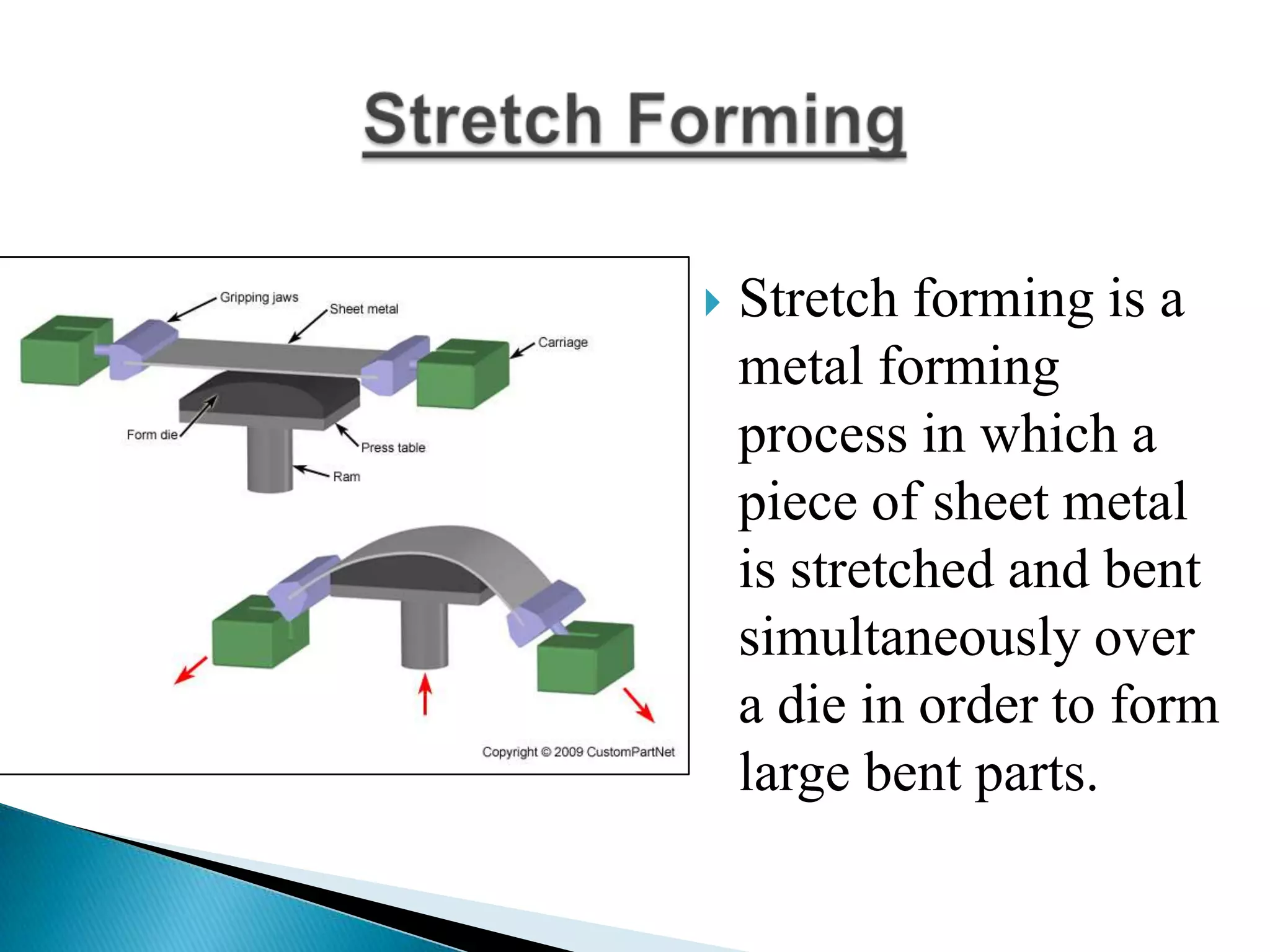
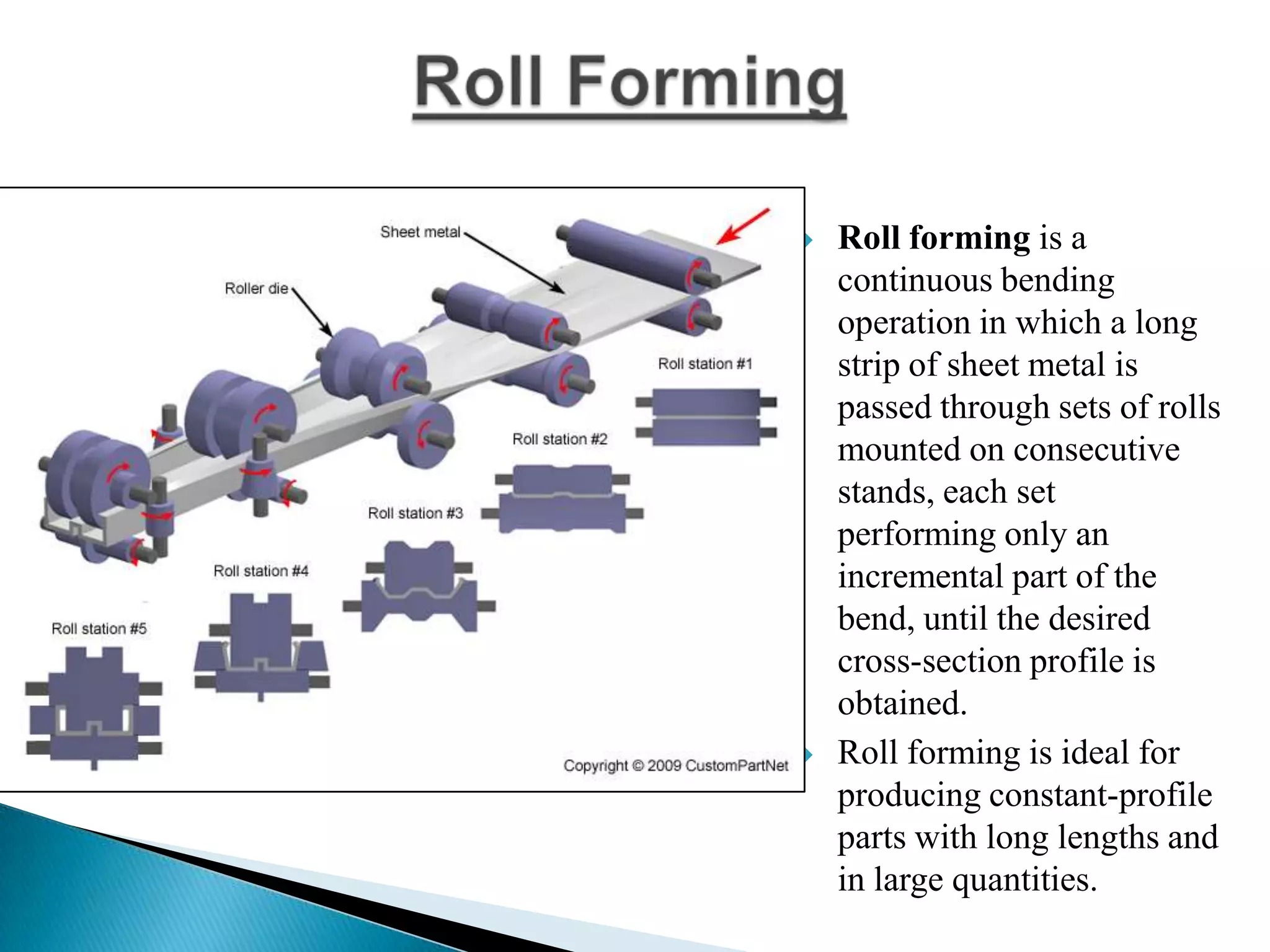
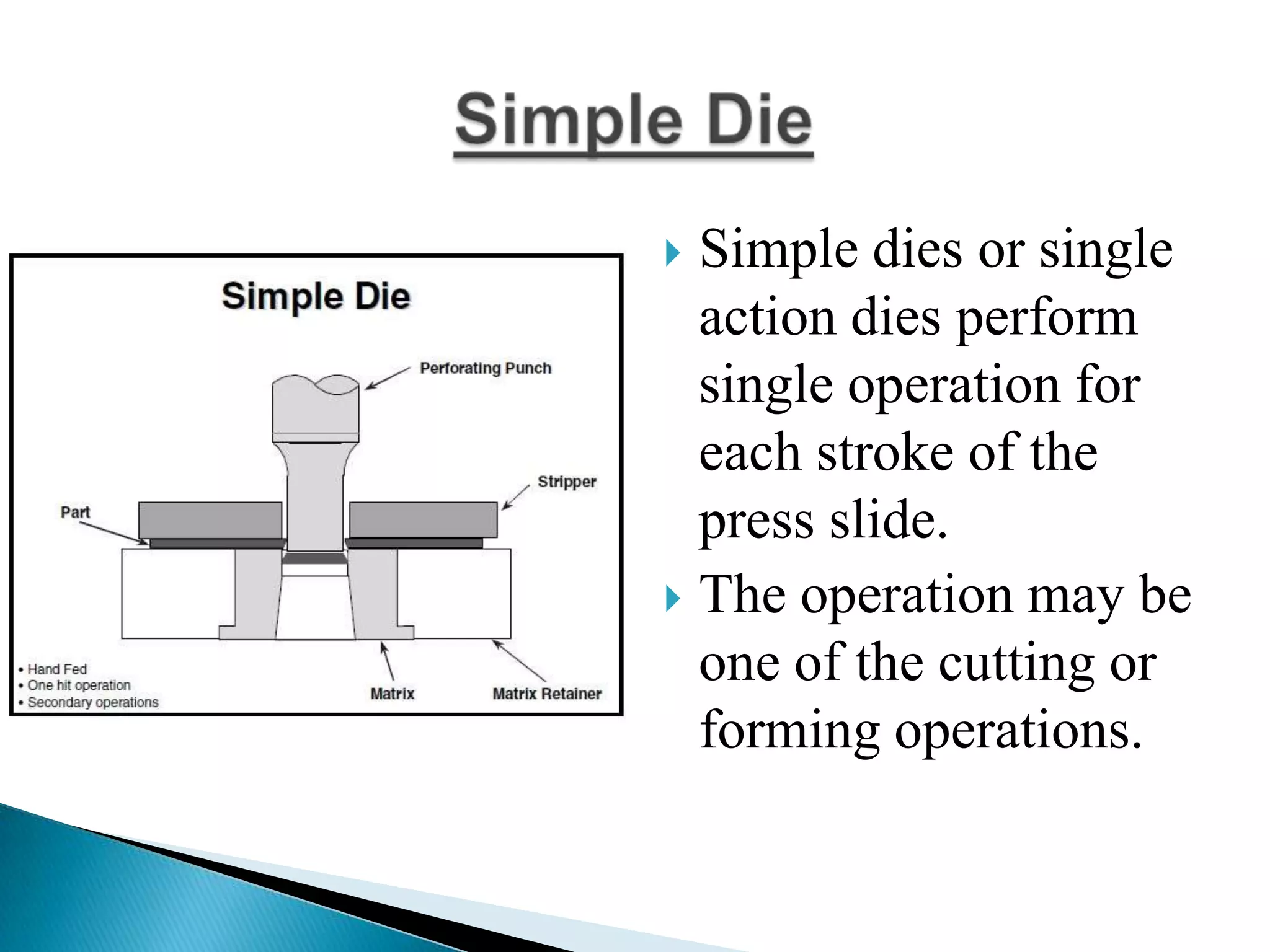
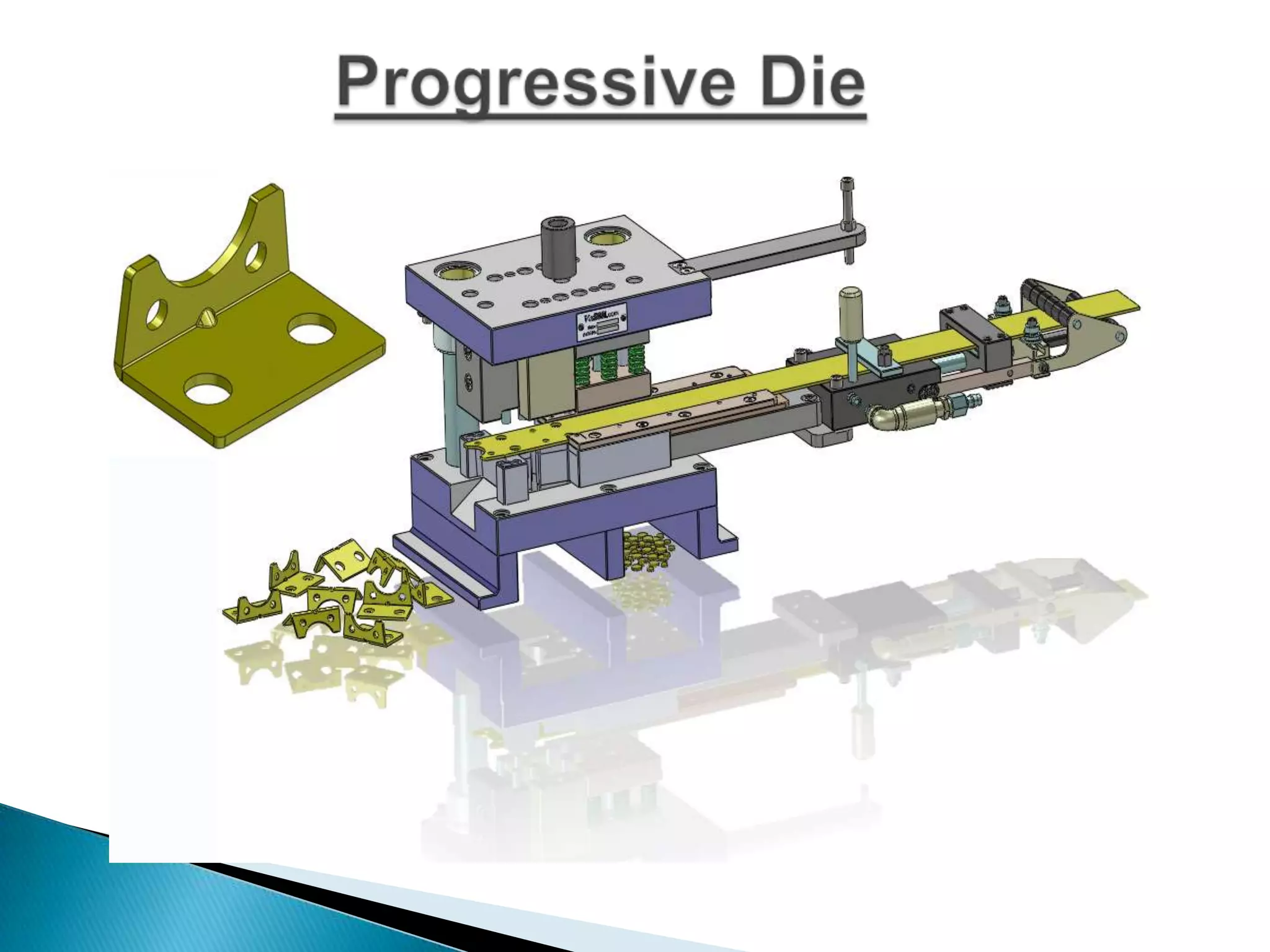
Sheet metal is a thin piece of metal between 0.006 and 0.25 inches thick. Sheet metal can be cut, bent, and stretched into various shapes through forming and cutting operations. Common forming operations include bending, deep drawing, and roll forming. Common cutting operations include shearing, blanking, punching, notching, and slitting. Sheet metal workers use tools like dies and presses to perform these operations and shape the metal.