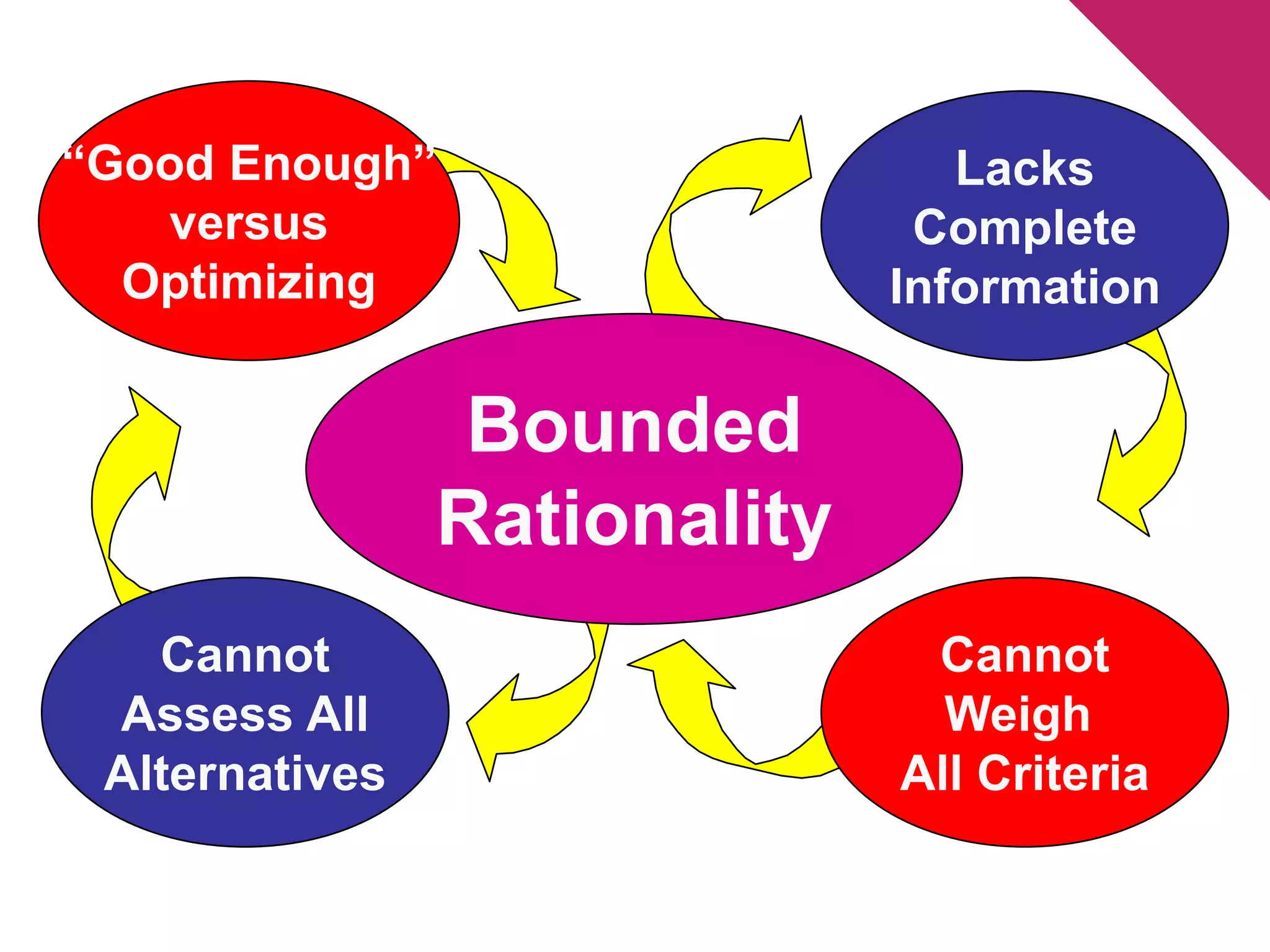
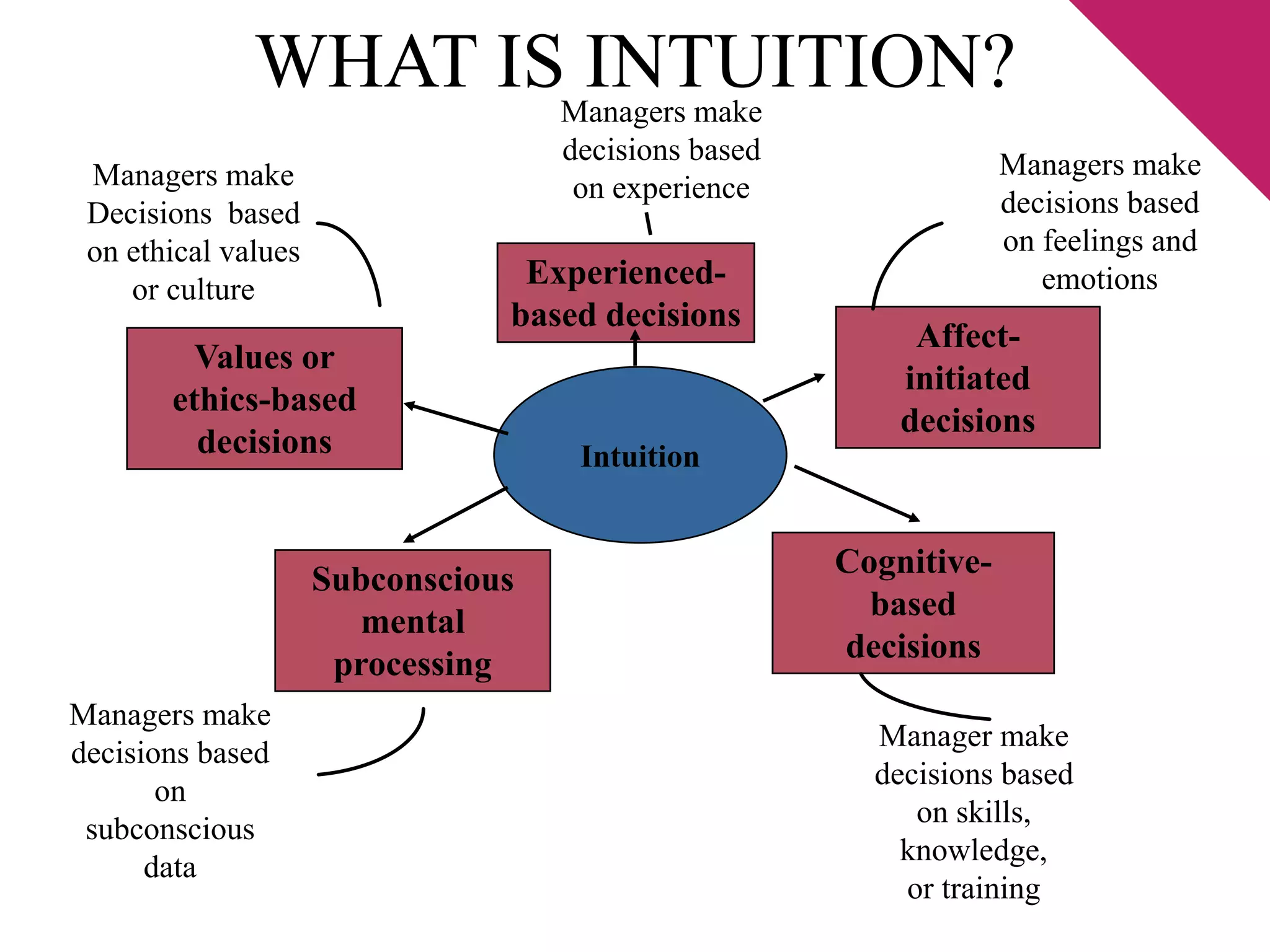
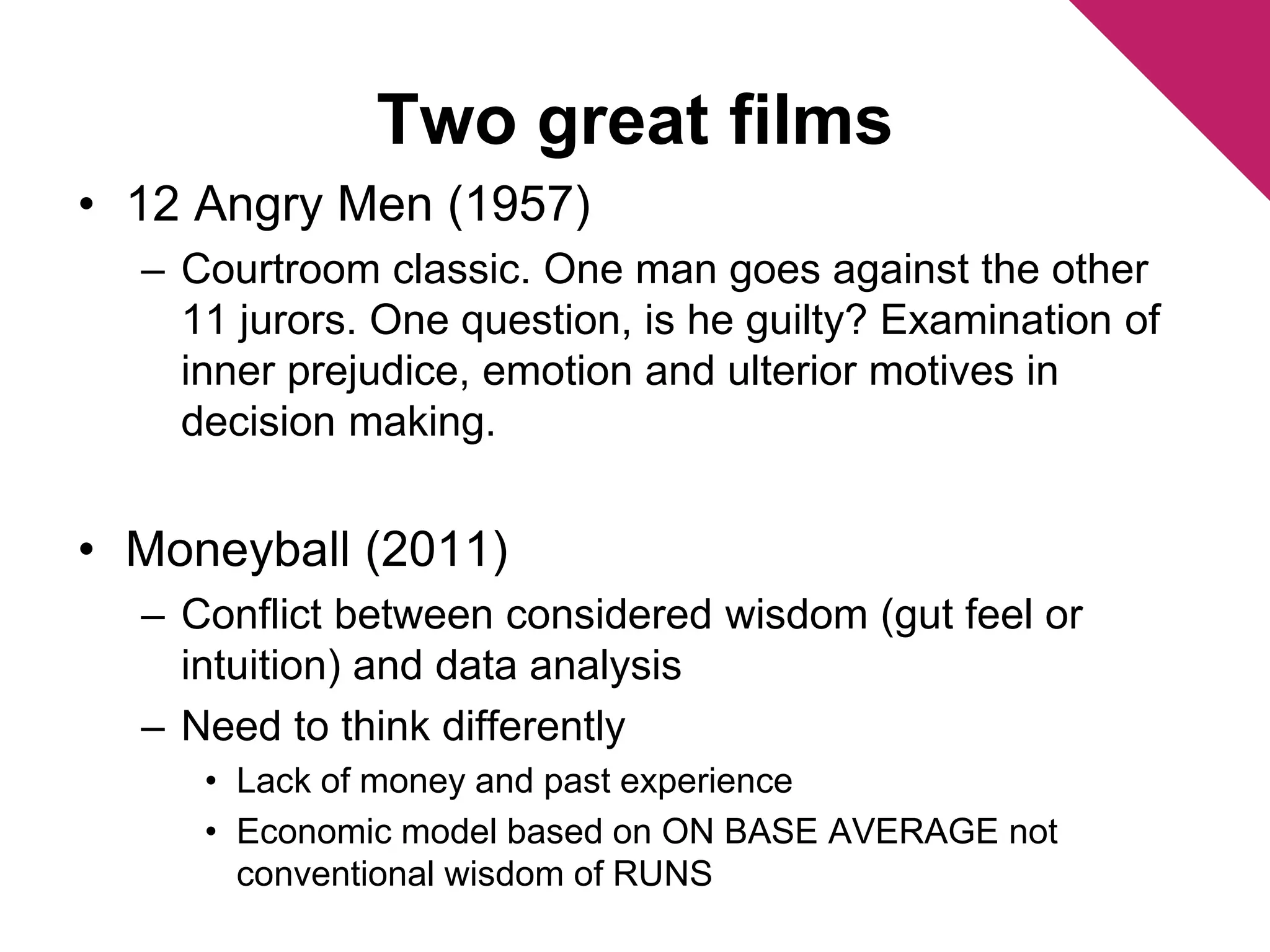
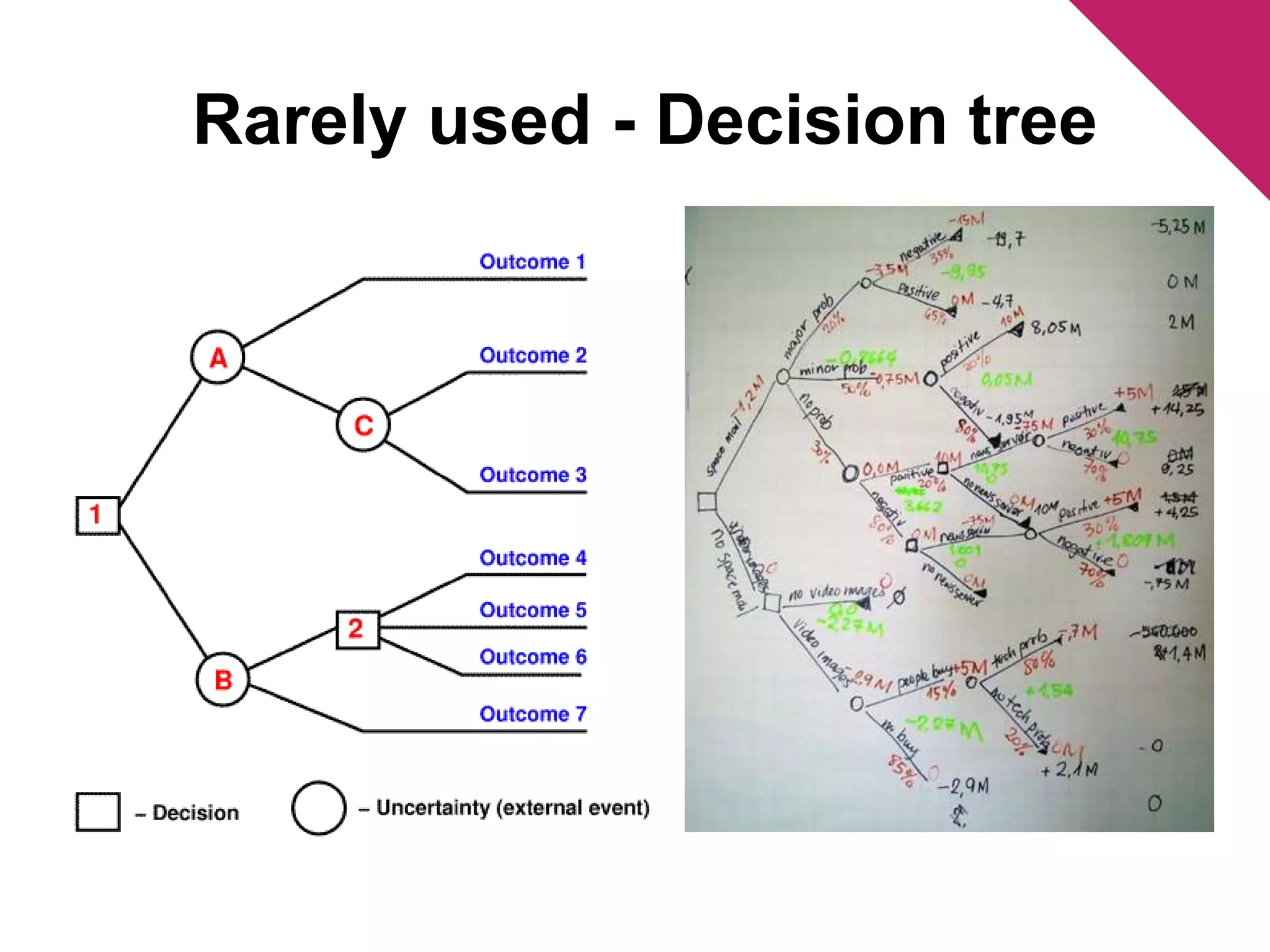
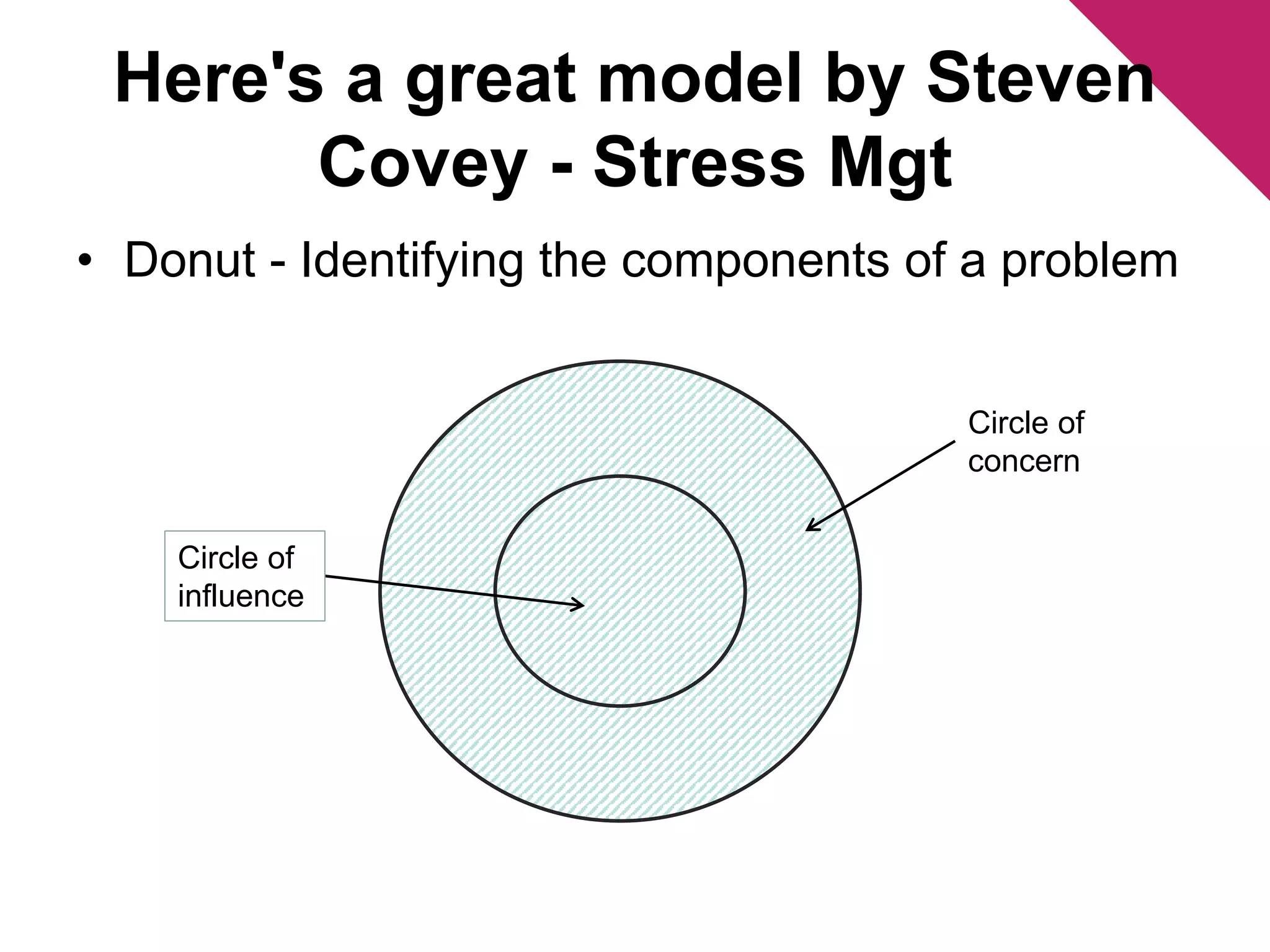
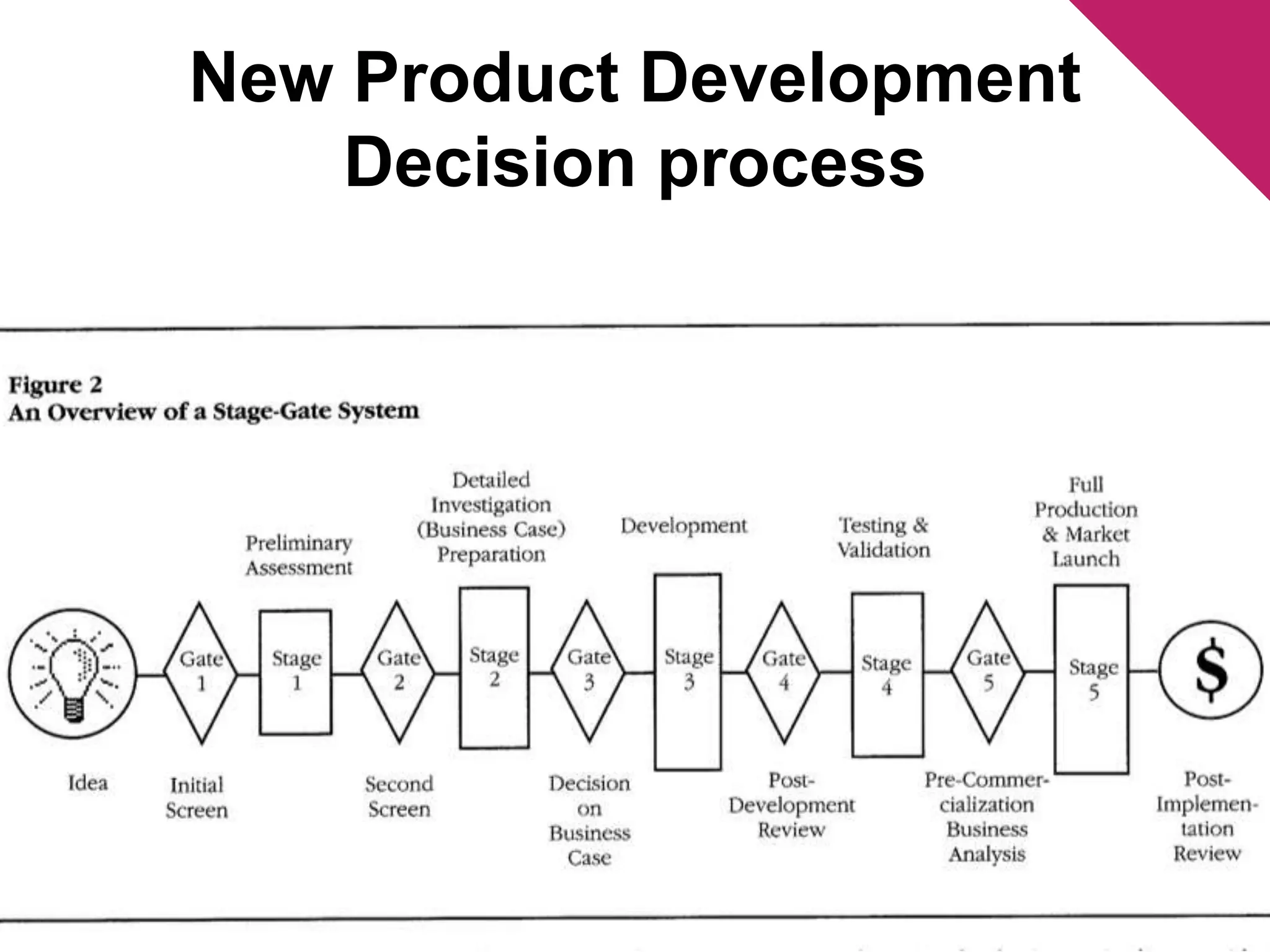
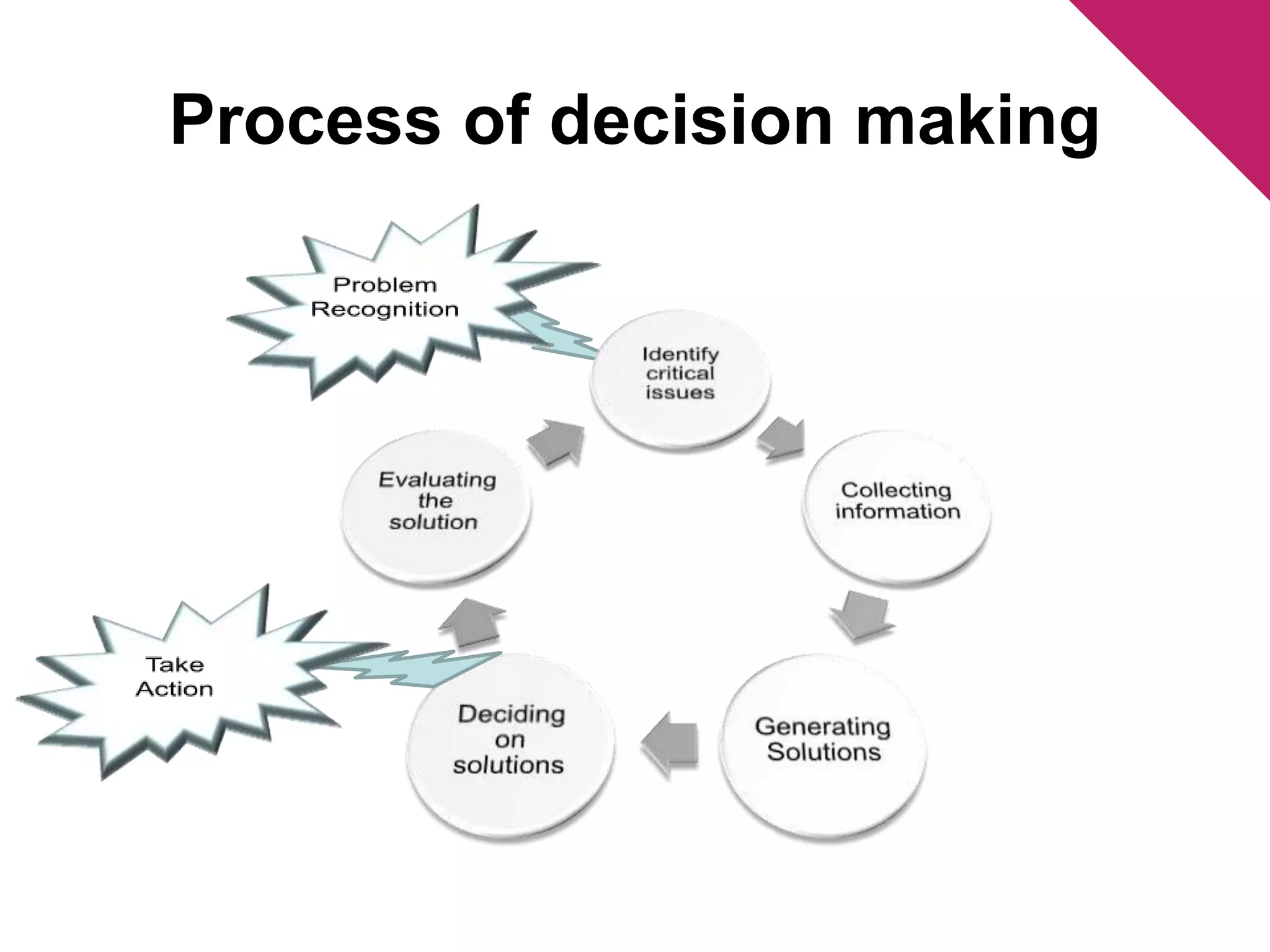
The document discusses the foundations of effective decision-making, focusing on the manager's role, types of decisions, and the decision-making process. It highlights concepts such as bounded rationality, the impact of intuition, and various decision-making styles, emphasizing the importance of using structured frameworks. Practical solutions for enhancing decision-making in teams include clear communication, consensus-seeking, and addressing conflicts directly.