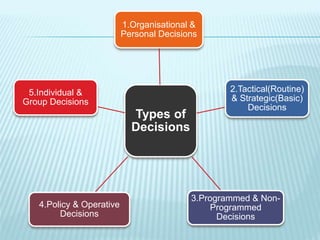
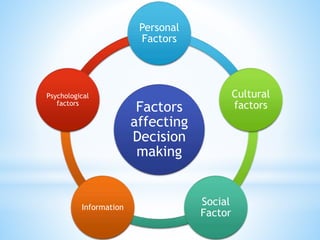
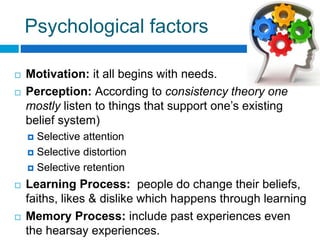
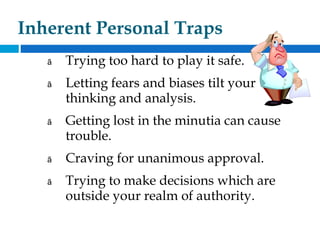
This document discusses various aspects of decision making. It defines decision making and provides definitions from different authors. It outlines the six steps of decision making process as collecting information on alternatives, comparing alternatives, considering what could go wrong, constructing a clear picture of the decision, compiling requirements, and choosing an alternative. It also describes different types of decisions like organizational vs personal, tactical vs strategic, programmed vs non-programmed, policy vs operative, and individual vs group decisions. Finally, it discusses various factors that affect decision making like perception, organizational issues, environmental issues, and personal and psychological factors.