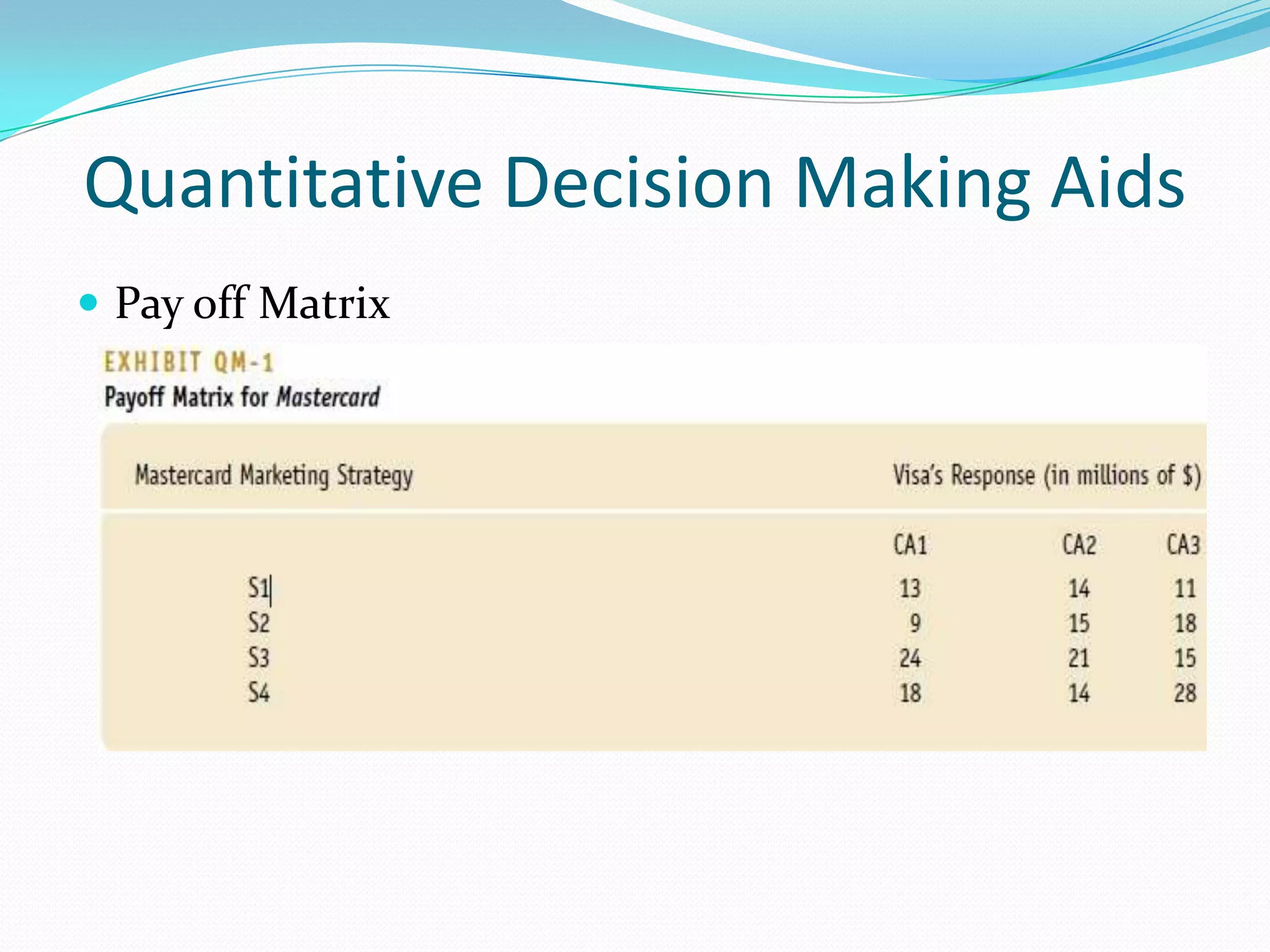
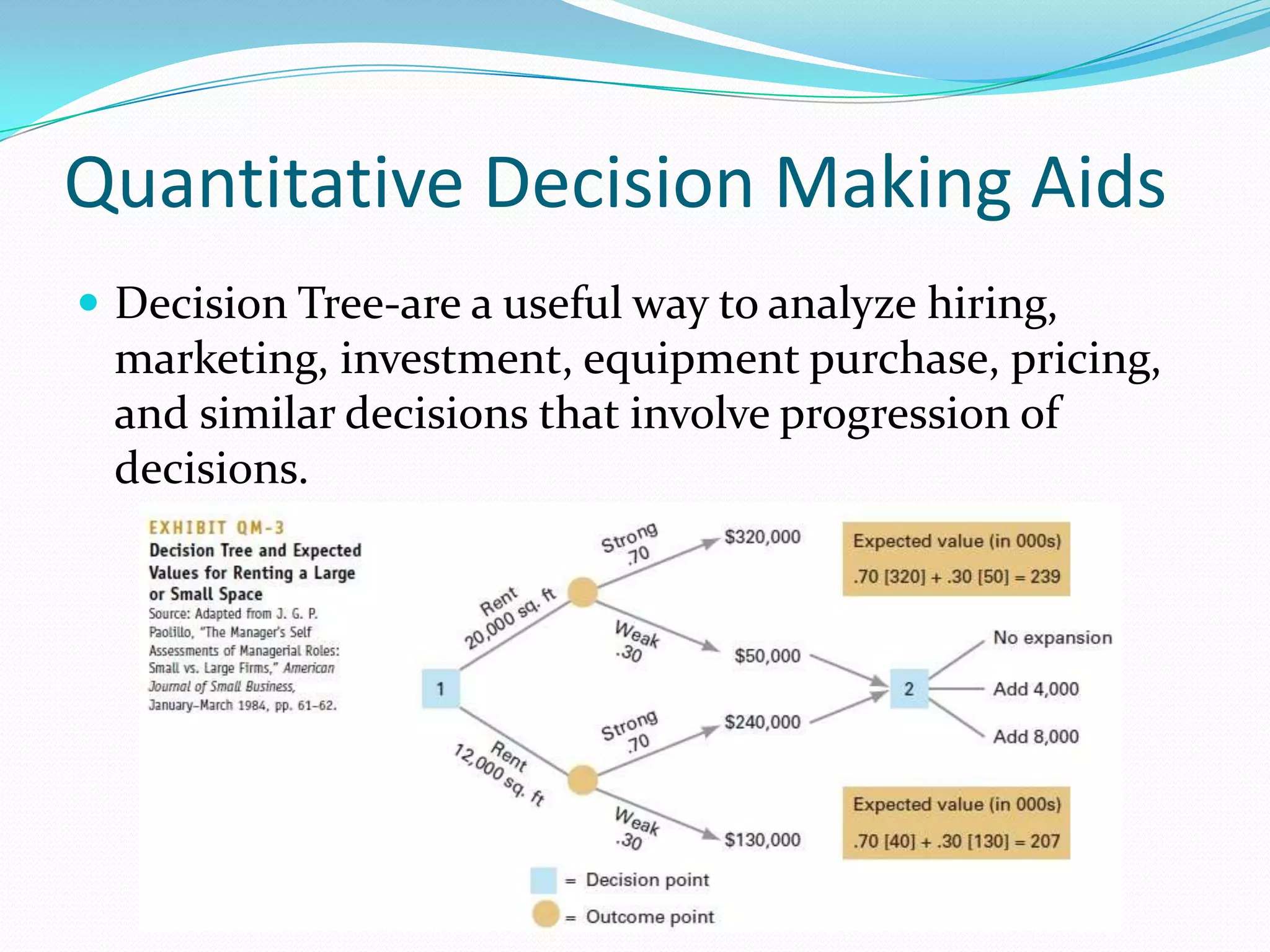
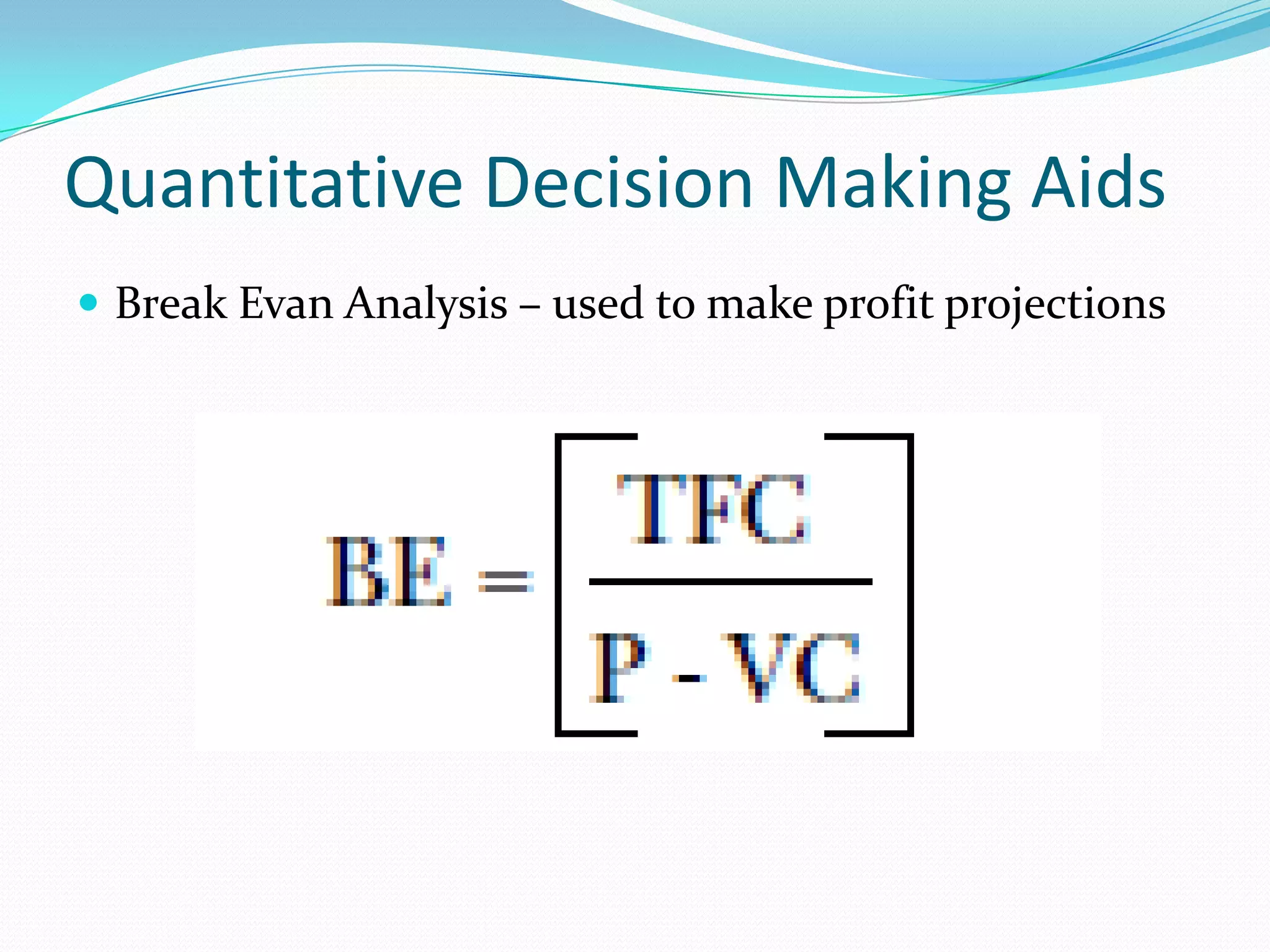
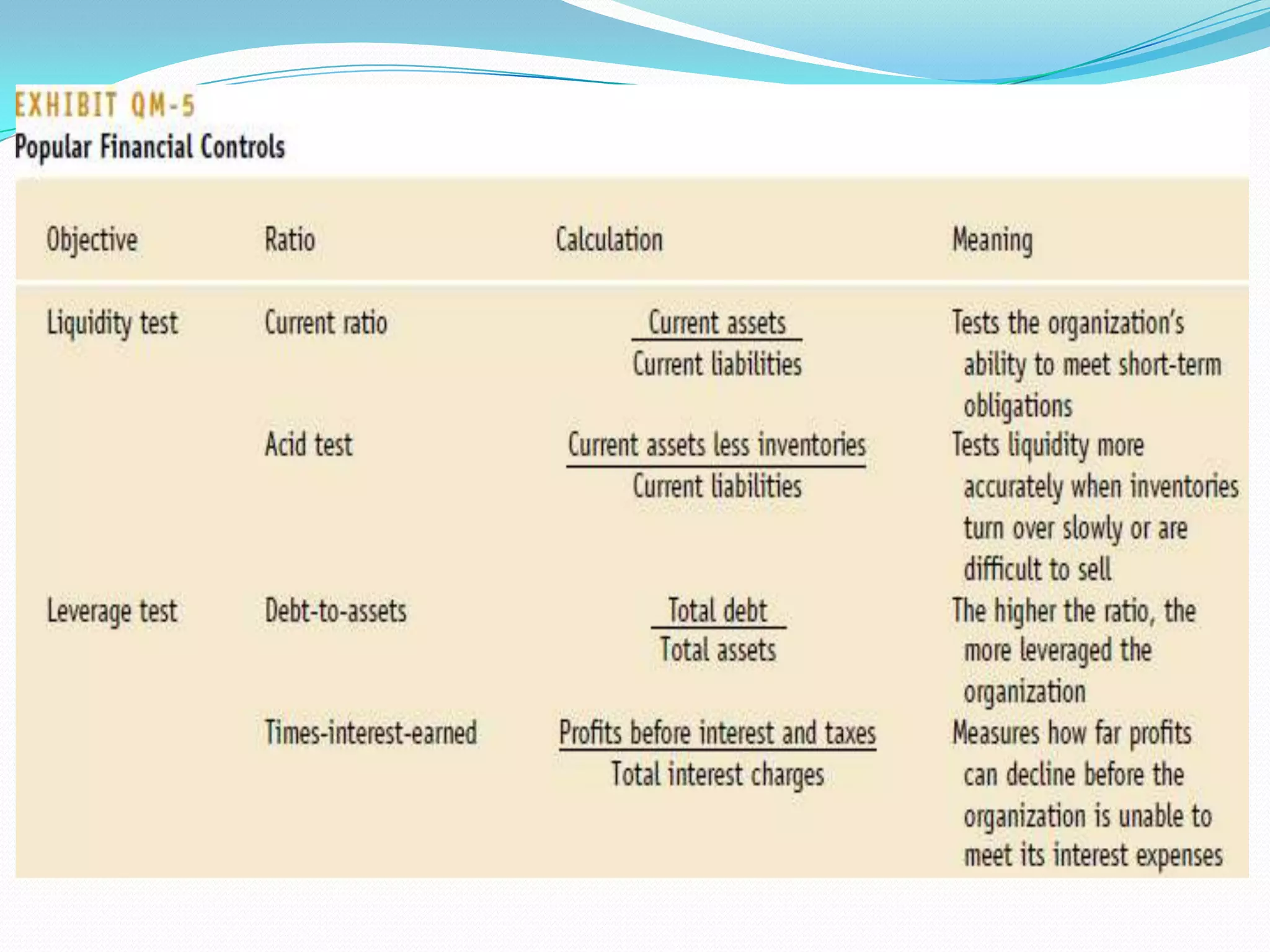
The document outlines the 8 step decision making process managers follow which includes: 1) identifying the problem, 2) identifying decision criteria, 3) allocating weights to criteria, 4) developing alternatives, 5) analyzing alternatives, 6) selecting an alternative, 7) implementing the alternative, and 8) evaluating the decision. It also discusses types of decisions, decision making styles, biases that can influence decisions, and quantitative tools that can aid the decision making process such as decision trees, payoff matrices, and break even analysis.