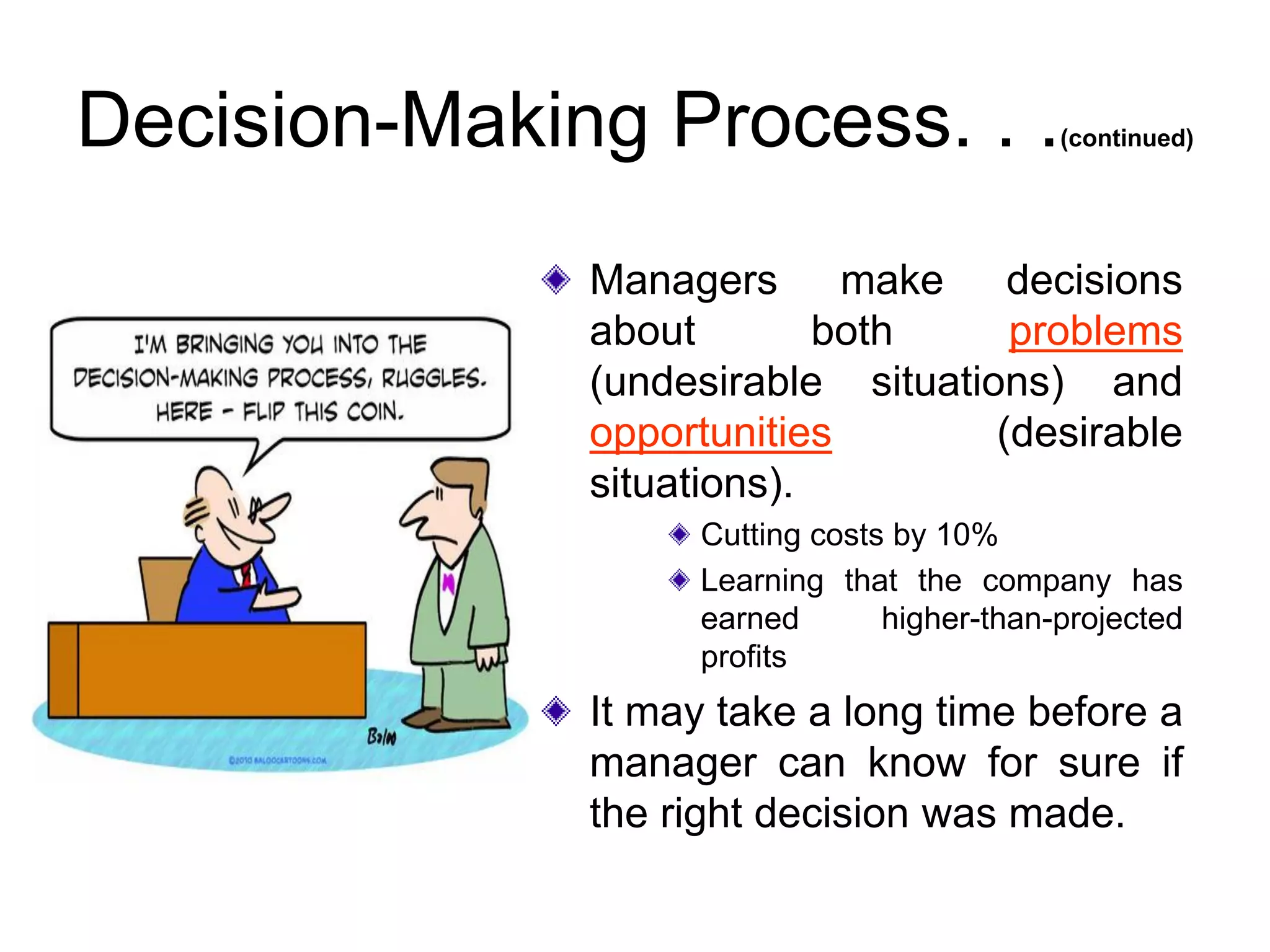
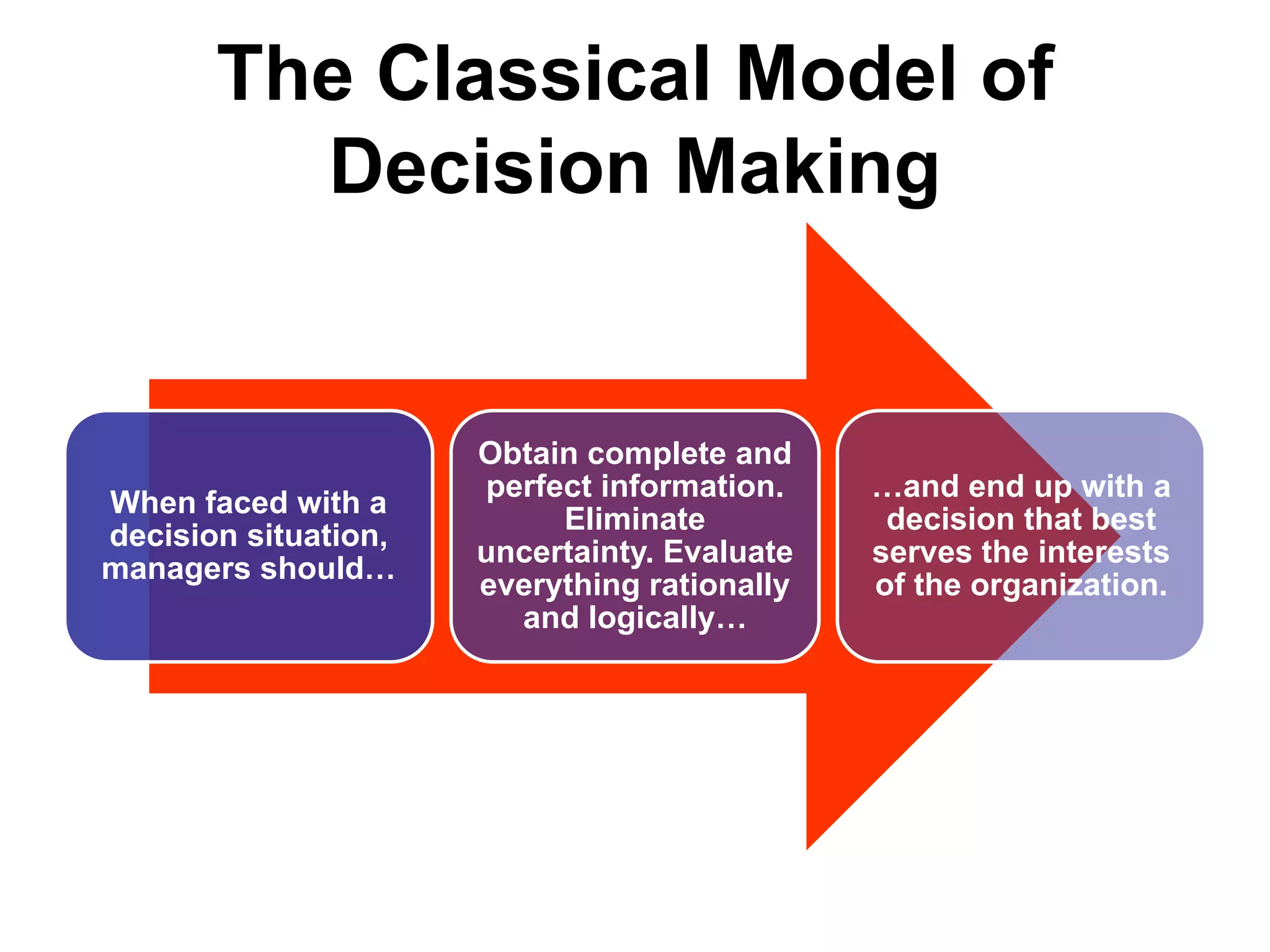
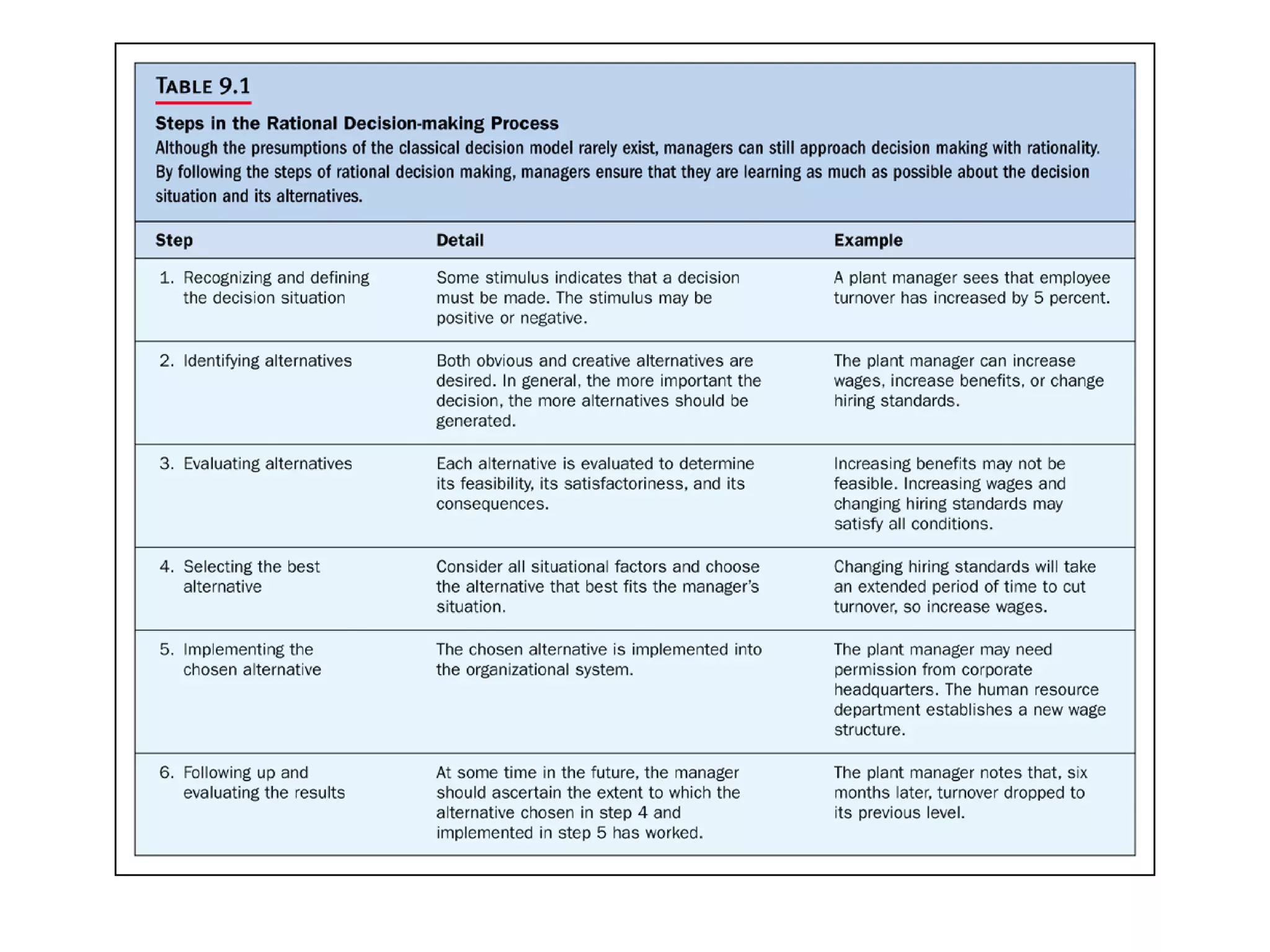
Decision making is one of the most important managerial activities. There are several approaches to decision making, including the classical model which assumes rationality and perfect information, and the administrative model which recognizes limitations like bounded rationality. Effective decision making involves defining the problem, identifying alternatives, evaluating alternatives based on feasibility, satisfaction and affordability, selecting the best alternative, implementing it, and following up on results. Behavioral aspects like intuition, politics and risk preferences also influence decisions.



![Decision-Making Process
• recognizing and defining the
nature of a decision situation
• identifying alternatives
• choosing the ‘best’ [most
effective] alternative and
• putting it into practice.
• Decision-Making Process includes:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/decisionmaking-220104160320/75/Decision-making-4-2048.jpg)


![Programmed Decisions. .
Many decisions regarding
basic operating systems
and procedures and
standard organizational
transactions fall into this
category.
McDonald’s employees are
trained to make the Big Mac
according to specific
procedures.
Starbucks, and many other
organizations, use programmed
decisions to purchase new
supplies [coffee beans, cups
and napkins].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/decisionmaking-220104160320/75/Decision-making-8-2048.jpg)



![Decision Making Under Risk
A state of risk exists when a decision maker
makes decisions under a condition in which
the availability of each alternative and its
potential payoffs and costs are all
associated with probability estimate.
Decisions such as these are based on past
experiences, relevant information, the
advice of others and one’s own judgment.
Decision is ‘calculated’ on the basis of
which alternative has the highest probability
of working effectively. [union negotiations,
Porsche’s SUV focus vs high-performance
sports cars]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/decisionmaking-220104160320/75/Decision-making-12-2048.jpg)







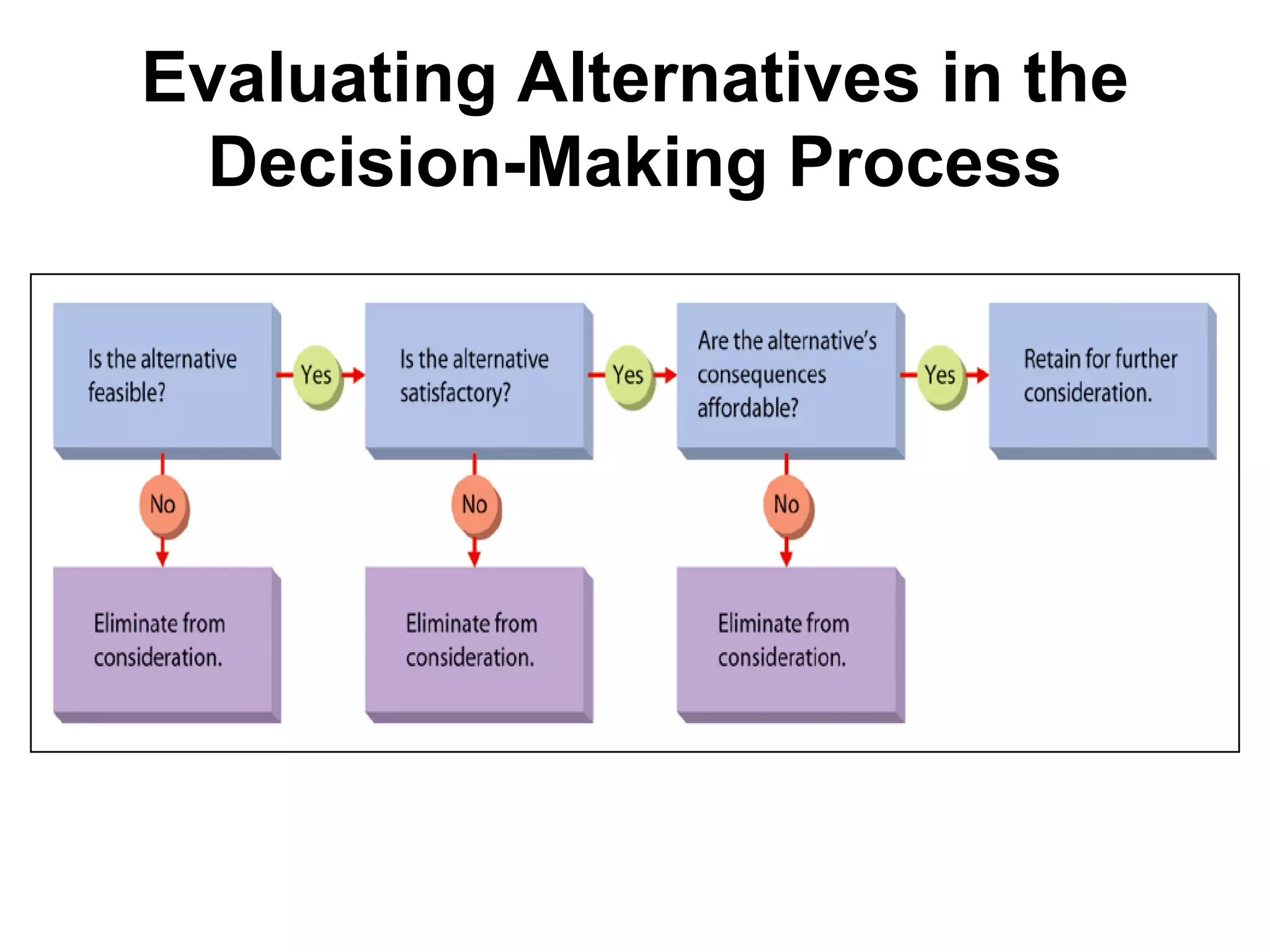
![Rational Decision Making. . .(continued)
3) Evaluating alternatives
a) Each alternative must pass successfully
through three stages before it may be worthy of
consideration as a solution.
1. Feasibility – Is it financially possible? Is it
legally possible? Are there limited
human, material and/or informational
resources available?
2. Satisfactory – Does the alternative satisfy
the conditions of the decision situation?
[50% increase in sales]
3. Affordability – How will this alternative
affect other parts of the organization?
What financial and non-financial costs are
associated?
b) The manager must put ‘price tags’ on the
consequences of each alternative.
c) Even an alternative that is both feasible and
satisfactory must be rejected if the
consequences are too expensive for the total
system.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/decisionmaking-220104160320/75/Decision-making-21-2048.jpg)




![Behavioral Aspects. . . (continued)
The Administrative Model of Decision Making
Herbert A Simon, a Nobel Prize winner in
Economics, developed the model to describe
how decisions are often made rather than to
prescribe how they should be made.
Argues that decision makers have incomplete
and imperfect information, are constrained by
‘bounded rationality’ and tend to ‘satisfice’
when making decisions.
Bounded rationality suggests that decision
makers are limited by their values and
unconscious reflexes, skills and habits.
[American vs foreign automakers]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/decisionmaking-220104160320/75/Decision-making-28-2048.jpg)



![Behavioral Forces Influencing Decisions
Political Forces in Decision Making
Coalition - an informal alliance of
individuals or groups formed to
achieve a common goal
[stockholders, directors, parliament
blocs, etc]
Impact of a coalition may be positive
or negative.
Managers must recognize when to
use coalitions, how to assess if they
are acting in the best interest of the
organization and how to control their
negative effects.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/decisionmaking-220104160320/75/Decision-making-32-2048.jpg)

![Behavioral Forces Influencing Decisions
Escalation of Commitment –
occurs when a decision maker
stays with a decision even
when it appears to be wrong.
[Pan Am holdings]
Decision makers must guard
against sticking too long with
an incorrect decision.
However, managers should
not ‘bail out’ of a seemingly
incorrect decision too soon.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/decisionmaking-220104160320/75/Decision-making-34-2048.jpg)

![Behavioral Forces Influencing Decisions
Ethics
Managerial ethics involves a
wide variety of decisions:
Relationships of the firm to
its employees [closing a dept to
save money]
Relationships of the
employees to the firm
Relationships of the firm to
other economic agents](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/decisionmaking-220104160320/75/Decision-making-36-2048.jpg)
