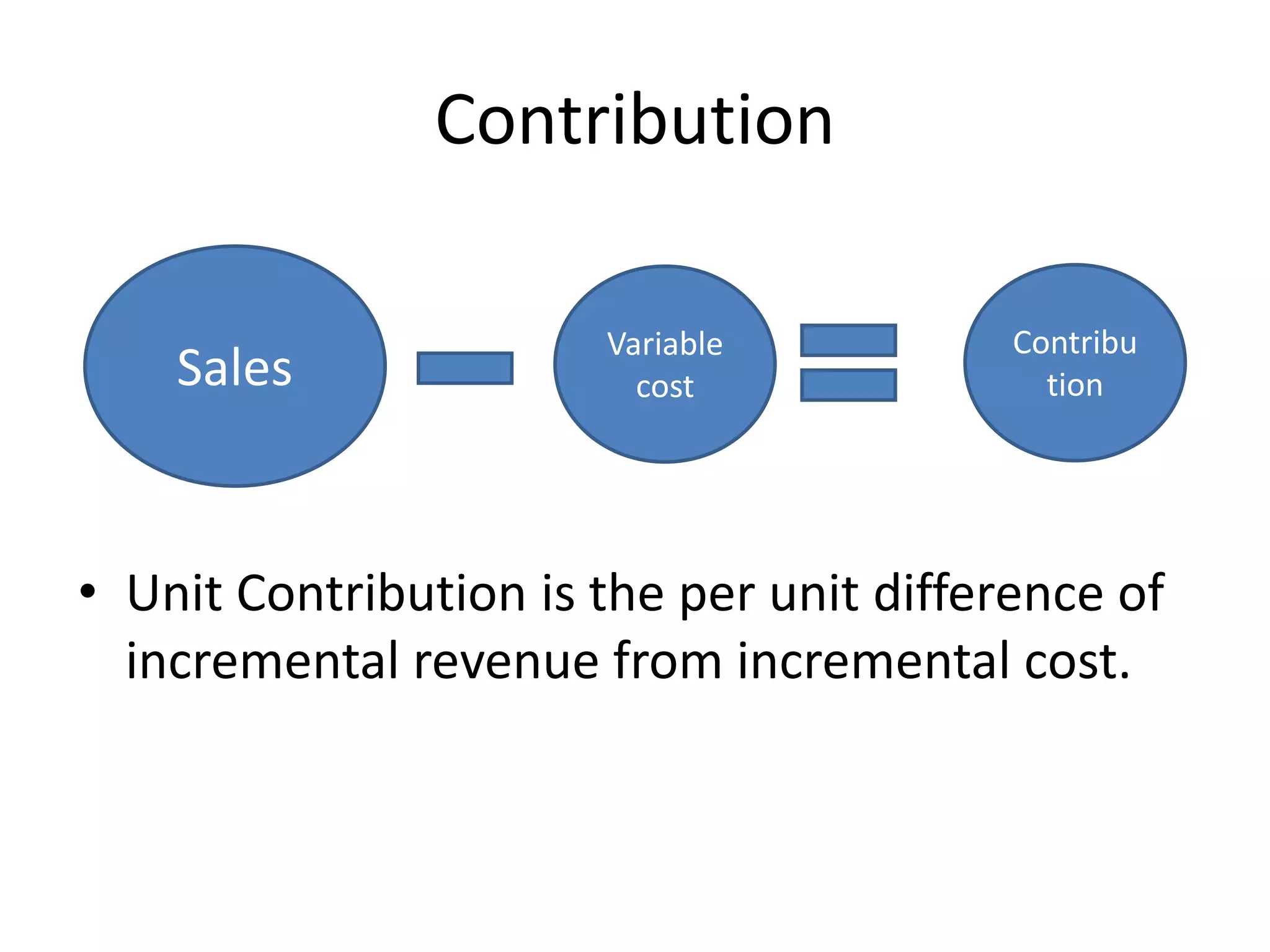
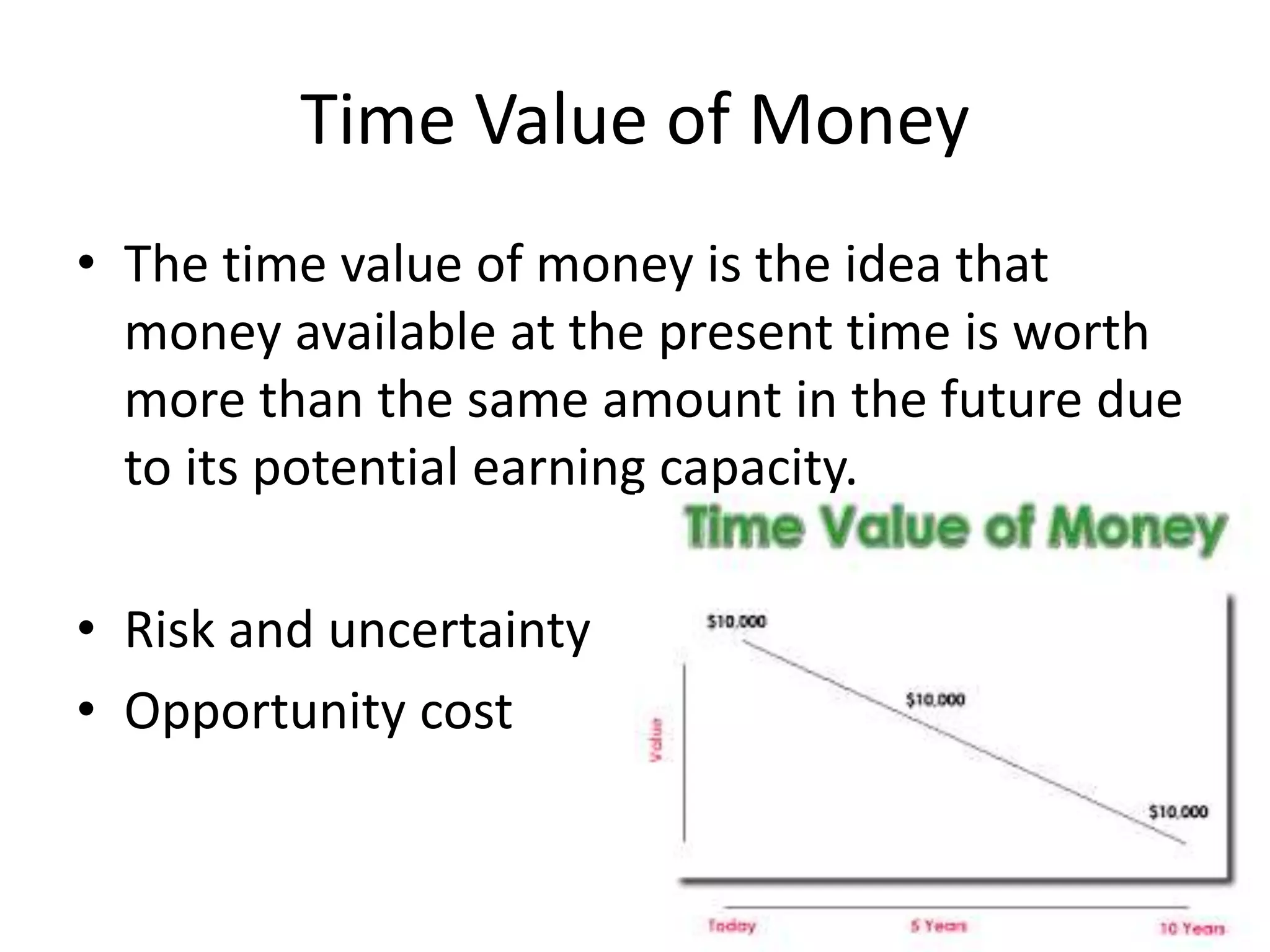
This document discusses key fundamental concepts in managerial decision making including incremental reasoning, opportunity cost, contribution, time perspective, time value of money, and risk and uncertainty. Incremental reasoning involves estimating the impact of alternatives and considers incremental cost and revenue. Opportunity cost refers to the revenue forgone by choosing one option over another. Contribution is the per unit difference between incremental revenue and cost. Time perspective considers decisions from both a short and long run view. The time value of money recognizes that money available now is worth more than the same amount in the future. Risks are known uncertainties while uncertainty involves unknown unknowns.