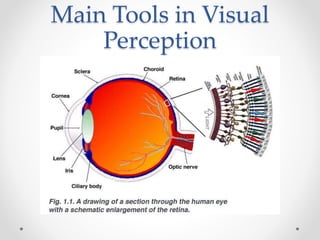
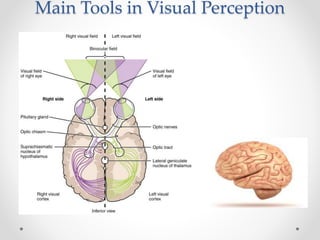
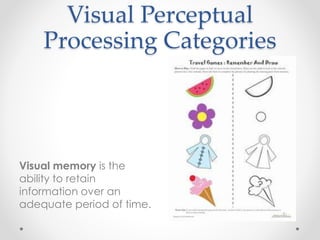
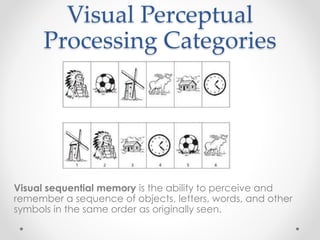
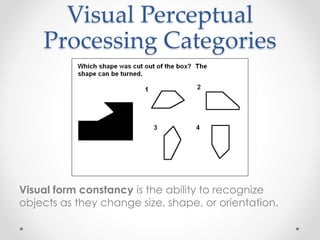
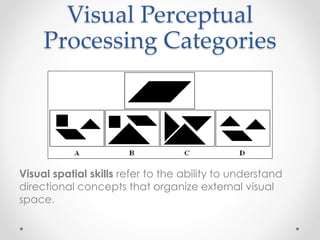
This document provides an overview of visual perception as it relates to art. It defines key terms like visual, perception, and the visual system. The visual system includes physiological components involved in sight. Gestalt psychology views perception as the mind forming meaningful wholes from the environment. There are several visual perceptual skills discussed, like visual discrimination, figure-ground, closure, and memory. The document also outlines gestalt principles and assigns the reader to create drawings demonstrating these principles and discuss the importance of visual perception in design.