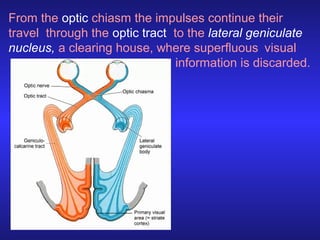
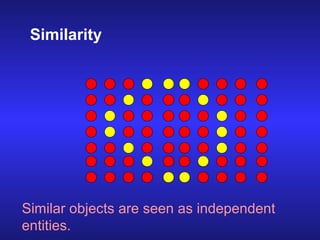
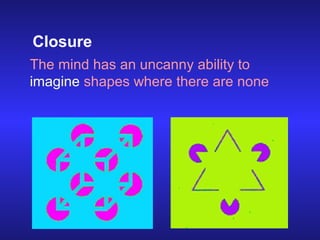
The document discusses visual perception and how the brain processes visual information. It explains that perception is the process by which sensory impulses are organized and coded by the brain. Visual perception involves discriminating various visual attributes like color, shape, distance. It describes how visual impulses travel from the retina to the brain areas involved in visual processing and interpretation. Key areas mentioned are the optic chiasm, lateral geniculate nucleus, and primary visual cortex. The document also discusses factors that can influence perception like quality of vision, culture, drugs, personality, and observation methods. Finally, it introduces Gestalt principles of visual organization like figure-ground, similarity, proximity, continuity, closure, and simplicity.