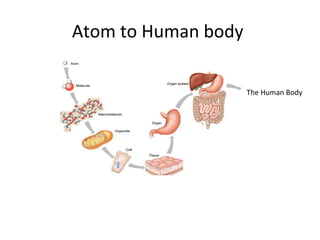
The document discusses anatomy and physiology, specifically the study of the human body. It provides examples of anatomy, which is concerned with the structure of body parts like the stomach, and physiology, which is concerned with the function of body parts like the stomach's role in food storage and digestion. The stomach wall has folds that disappear when the stomach expands during digestion.