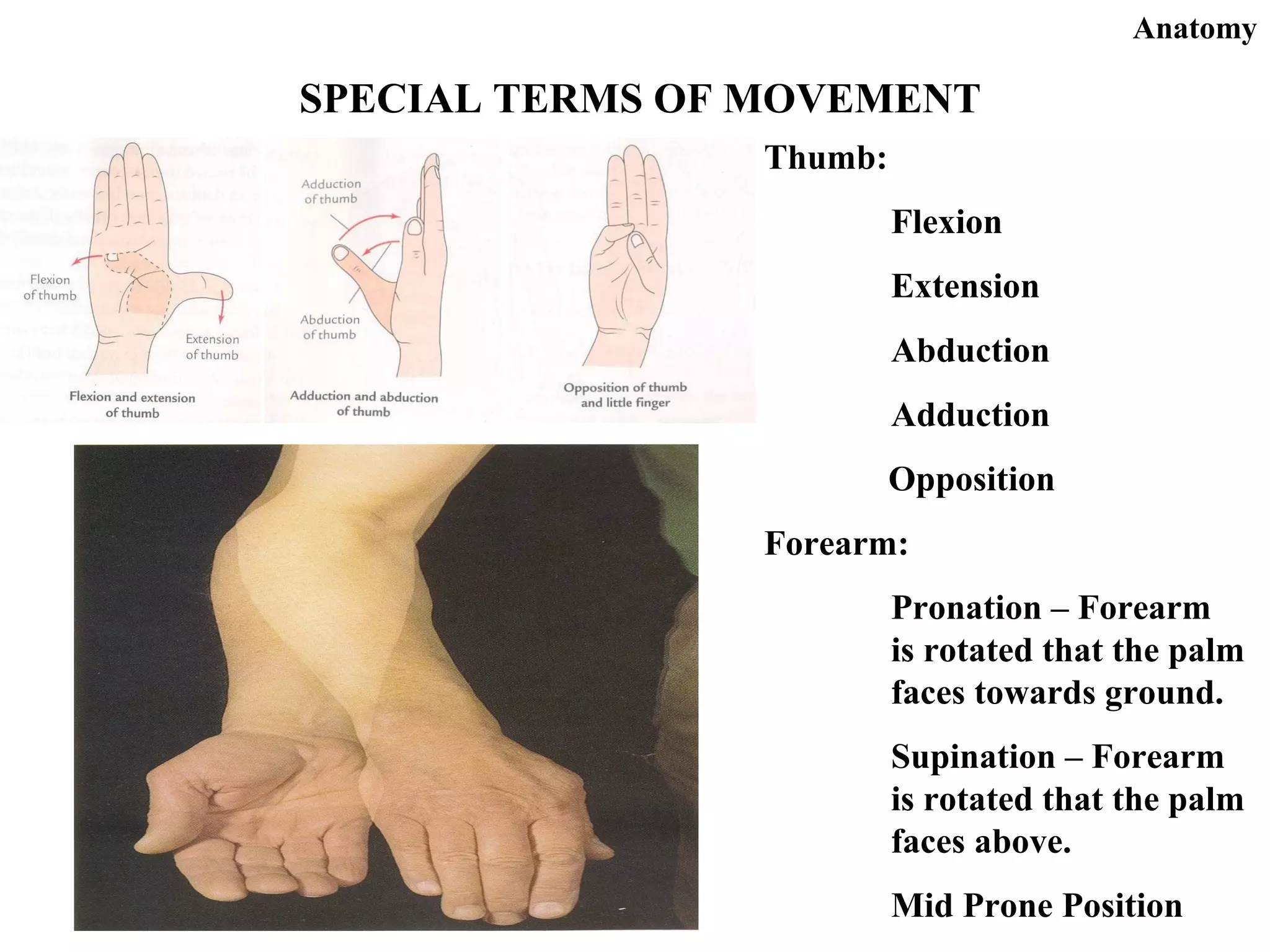
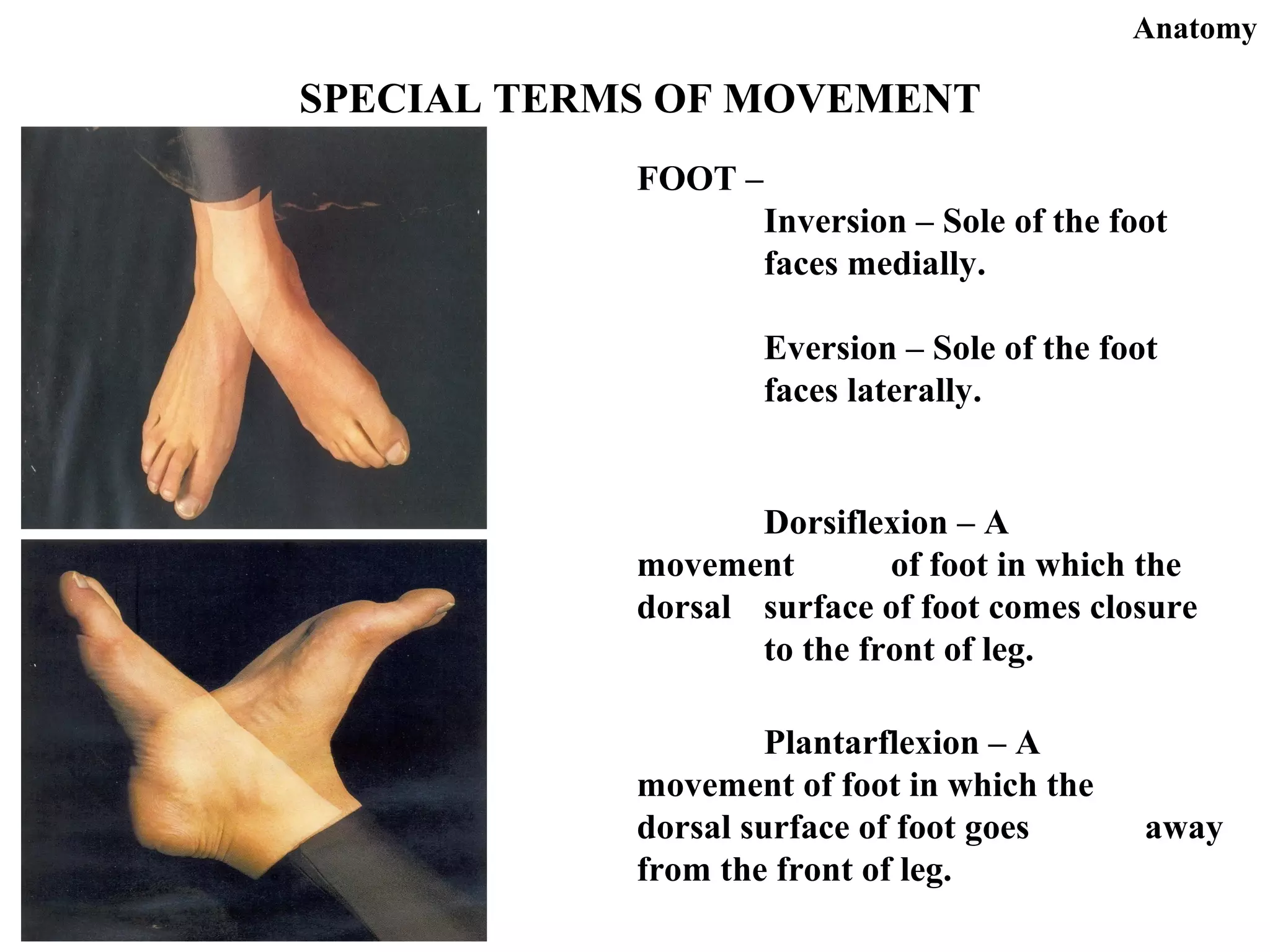
This document provides an overview of general anatomy terms. It discusses important historical figures like Hippocrates, who is considered the father of medicine, and Herophilus, who is regarded as the father of anatomy. It then covers topics like the different types of anatomy, anatomical position and planes, regions and systems of the body, and commonly used terms related to position, movement, and landmarks. Key terms are defined for structures and regions throughout the body. Important references for anatomy are also listed.