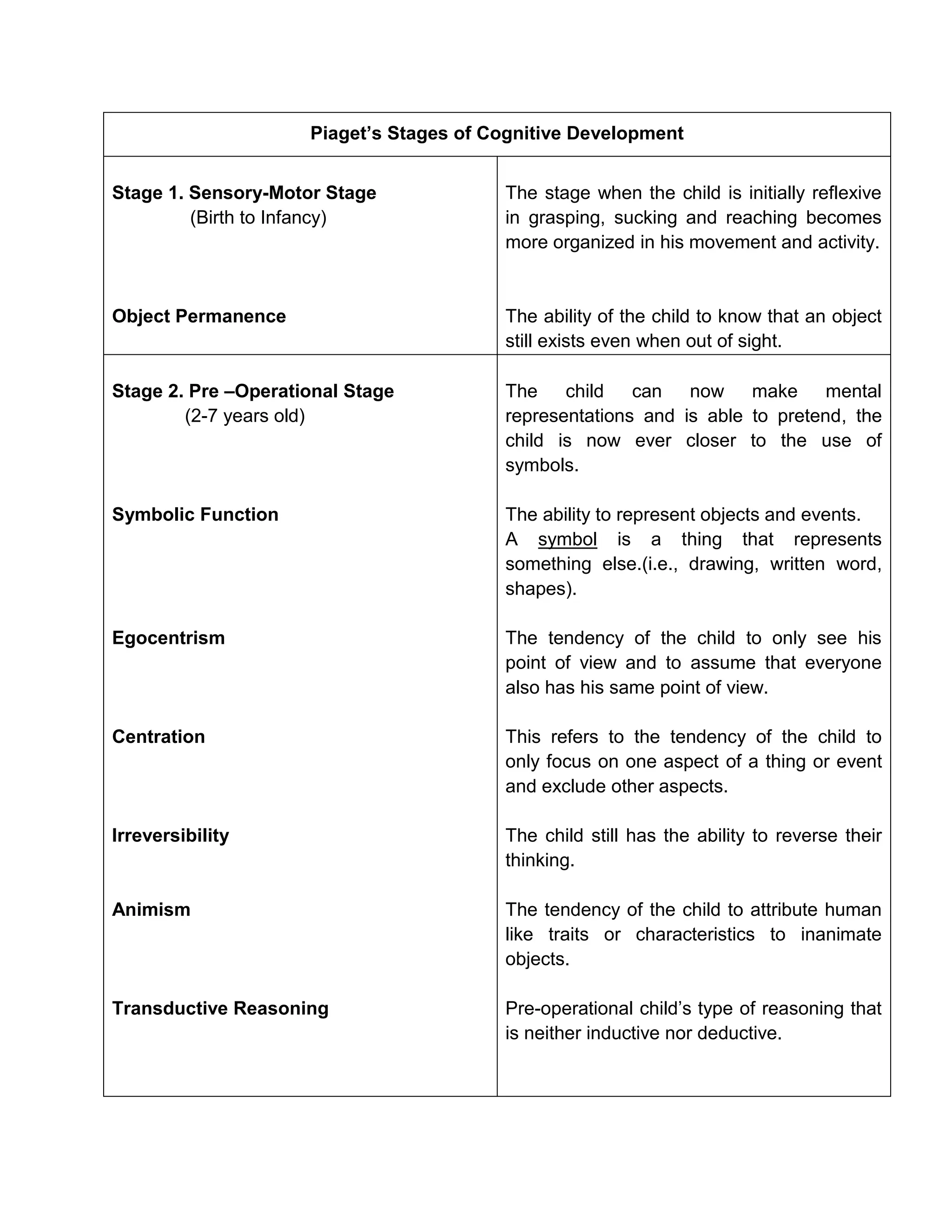
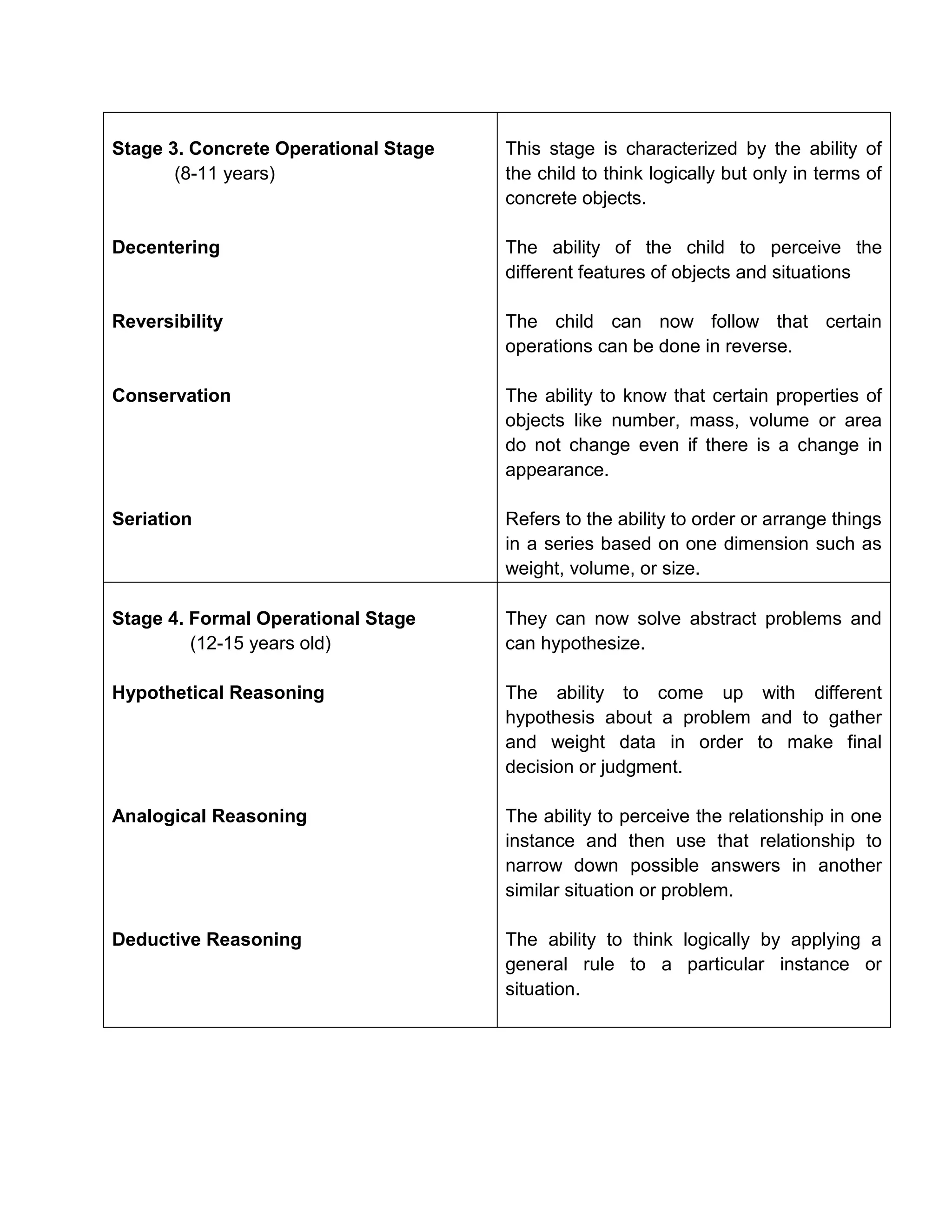
Jean Piaget's theory proposes that children progress through four stages of cognitive development:
1) Sensory-motor stage from birth to age 2 where infants learn through senses and motor skills
2) Preoperational stage from ages 2 to 7 where children use symbols and language but cannot yet think logically
3) Concrete operational stage from ages 7 to 11 where children can think logically about concrete events
4) Formal operational stage from age 11 onward where abstract reasoning emerges. Piaget observed his own children and developed this model of cognitive development.