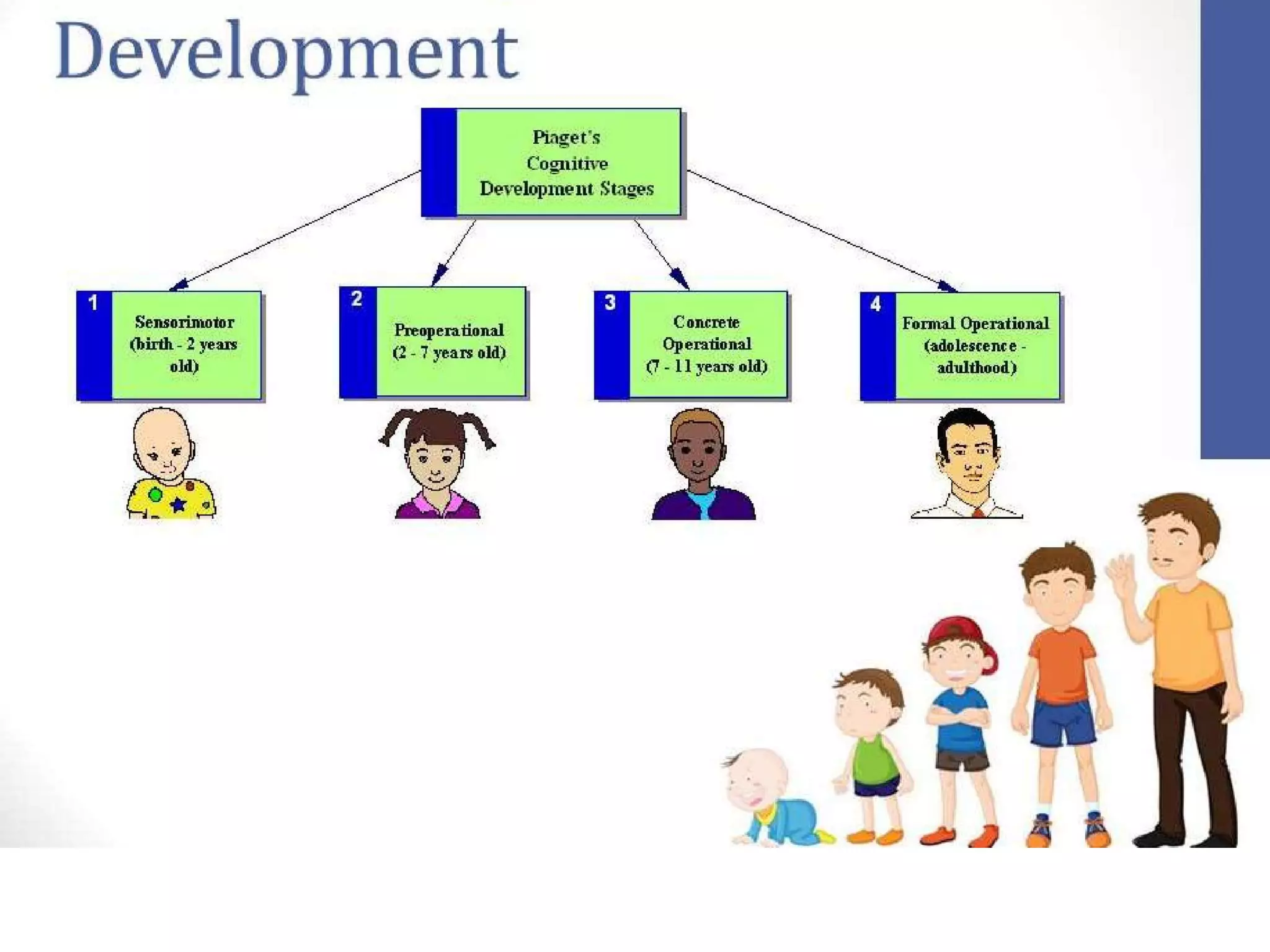
Piaget's theory of cognitive development proposes that children progress through 4 stages - sensorimotor, preoperational, concrete operational, and formal operational. At each stage, children develop new cognitive abilities through the processes of assimilation and accommodation. Piaget observed his own children to understand how their thinking changed as they developed from infancy through childhood into adulthood. His work influenced how educators approach teaching methods and curriculum based on a child's developmental level and abilities.