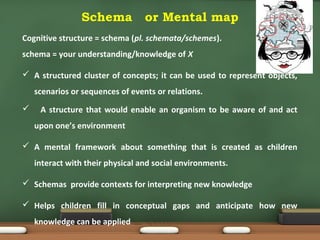
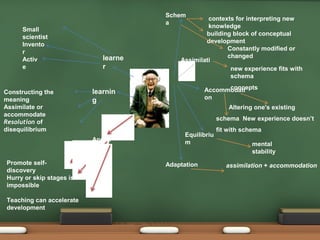
Jean Piaget was a Swiss psychologist who developed a theory of cognitive development in children. His theory states that children progress through four distinct stages as they interact with their environment - sensorimotor, preoperational, concrete operational, and formal operational. At each stage, children develop new cognitive abilities that allow them to understand and learn about the world. Piaget believed that learning occurs through active experimentation and adaptation, as children construct knowledge through assimilating new experiences into existing understandings or accommodating by changing their understandings. His theory emphasizes that children are active learners and proposes educational approaches should match children's developmental levels.