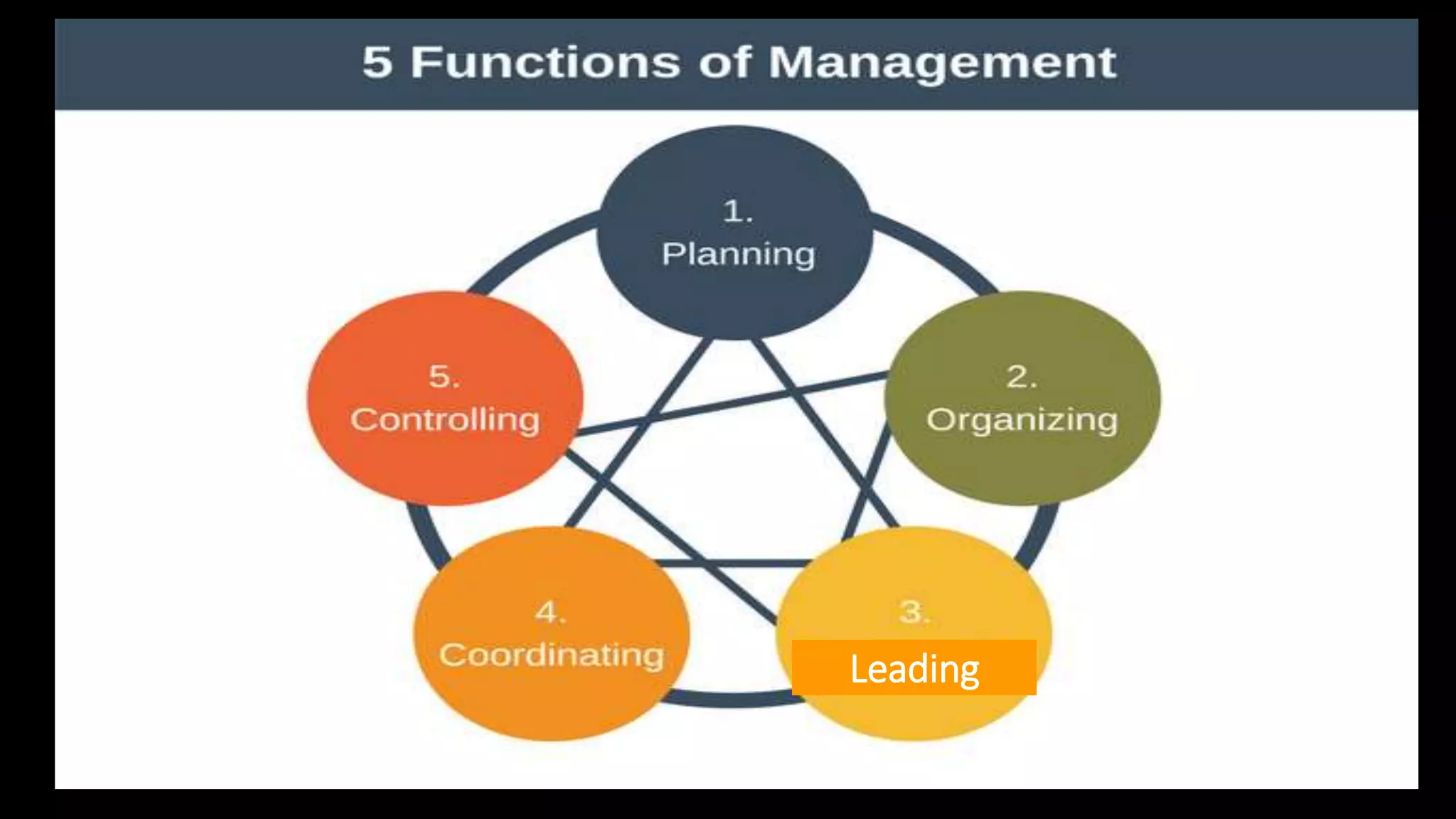
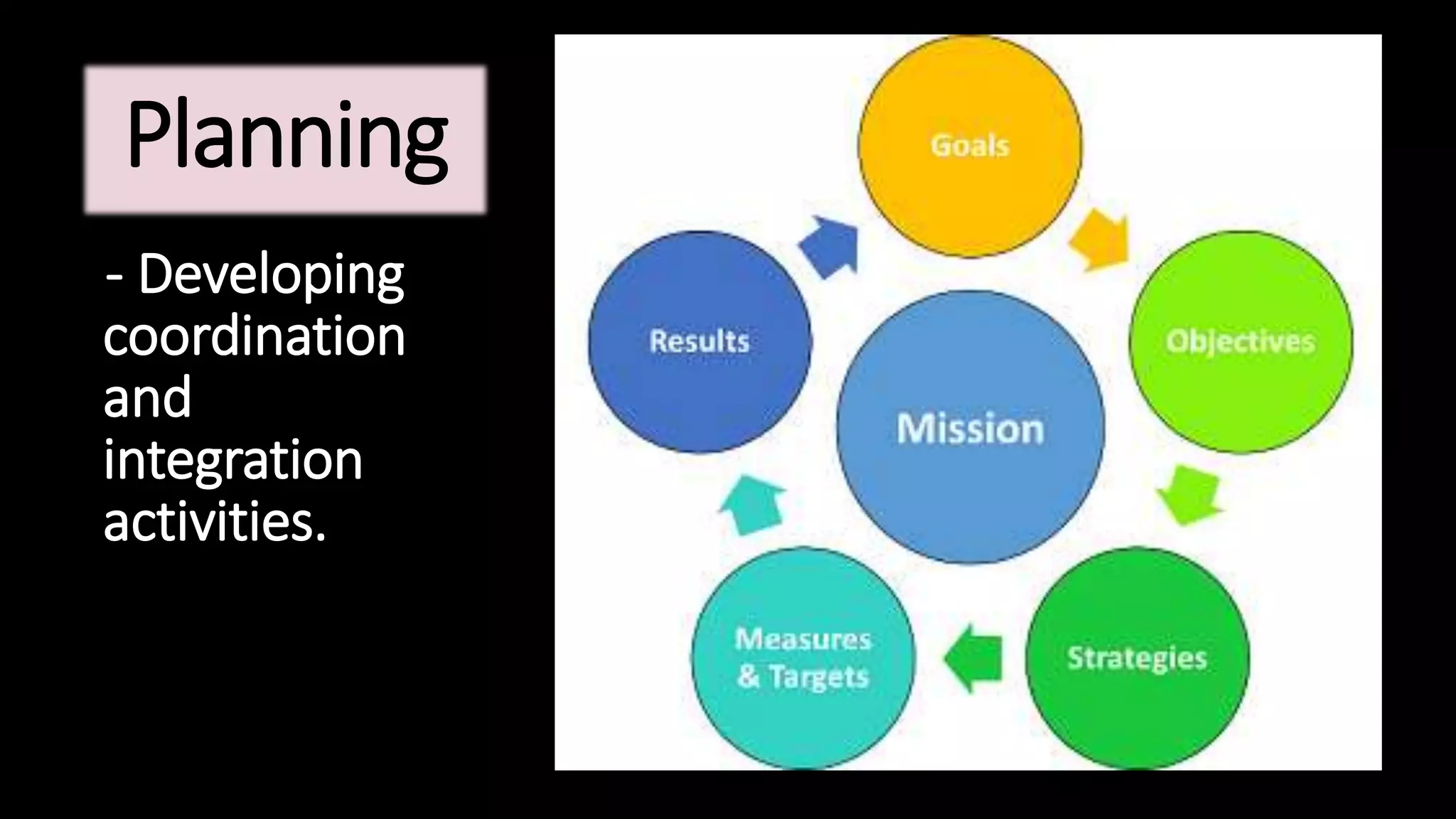
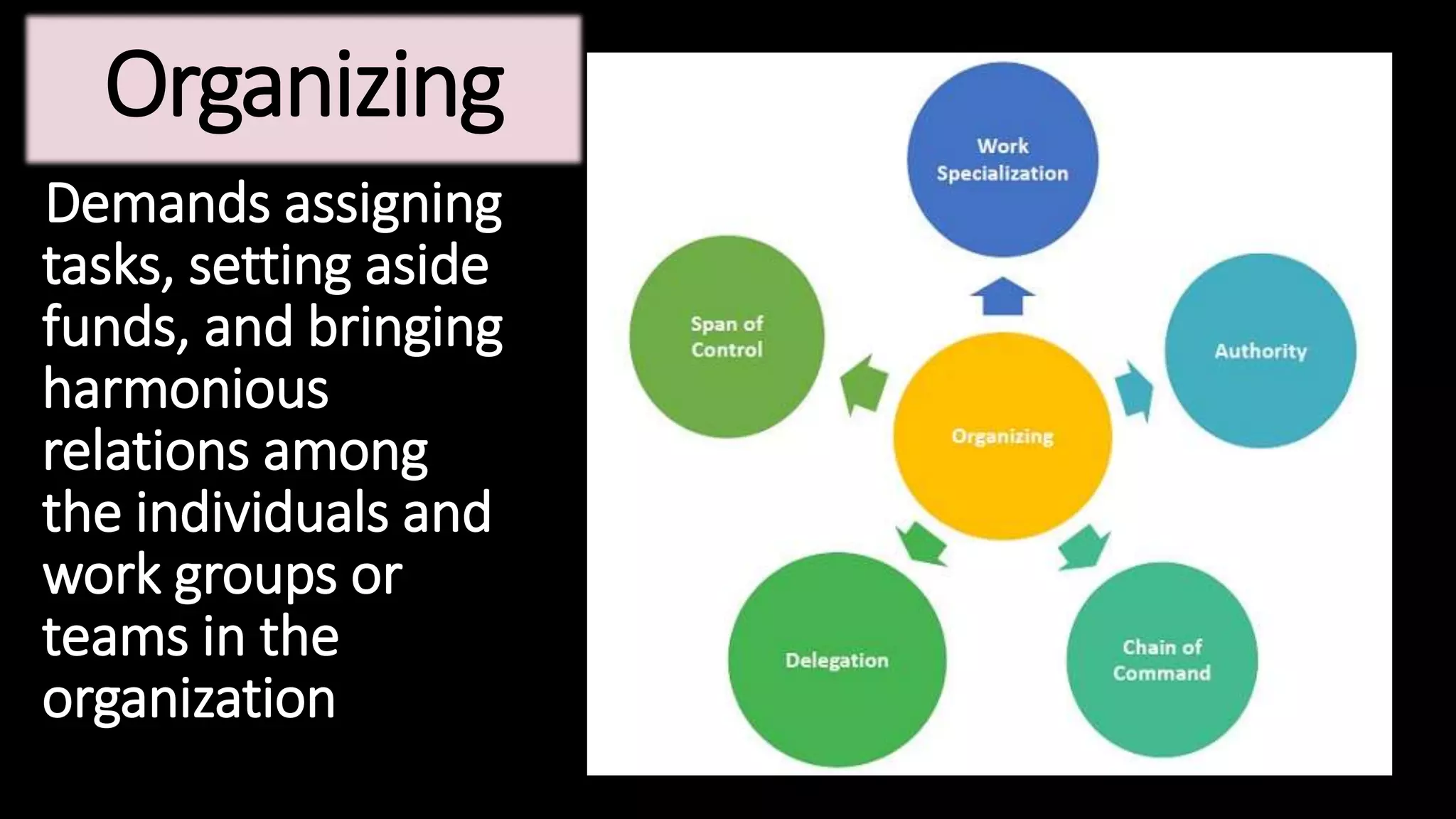
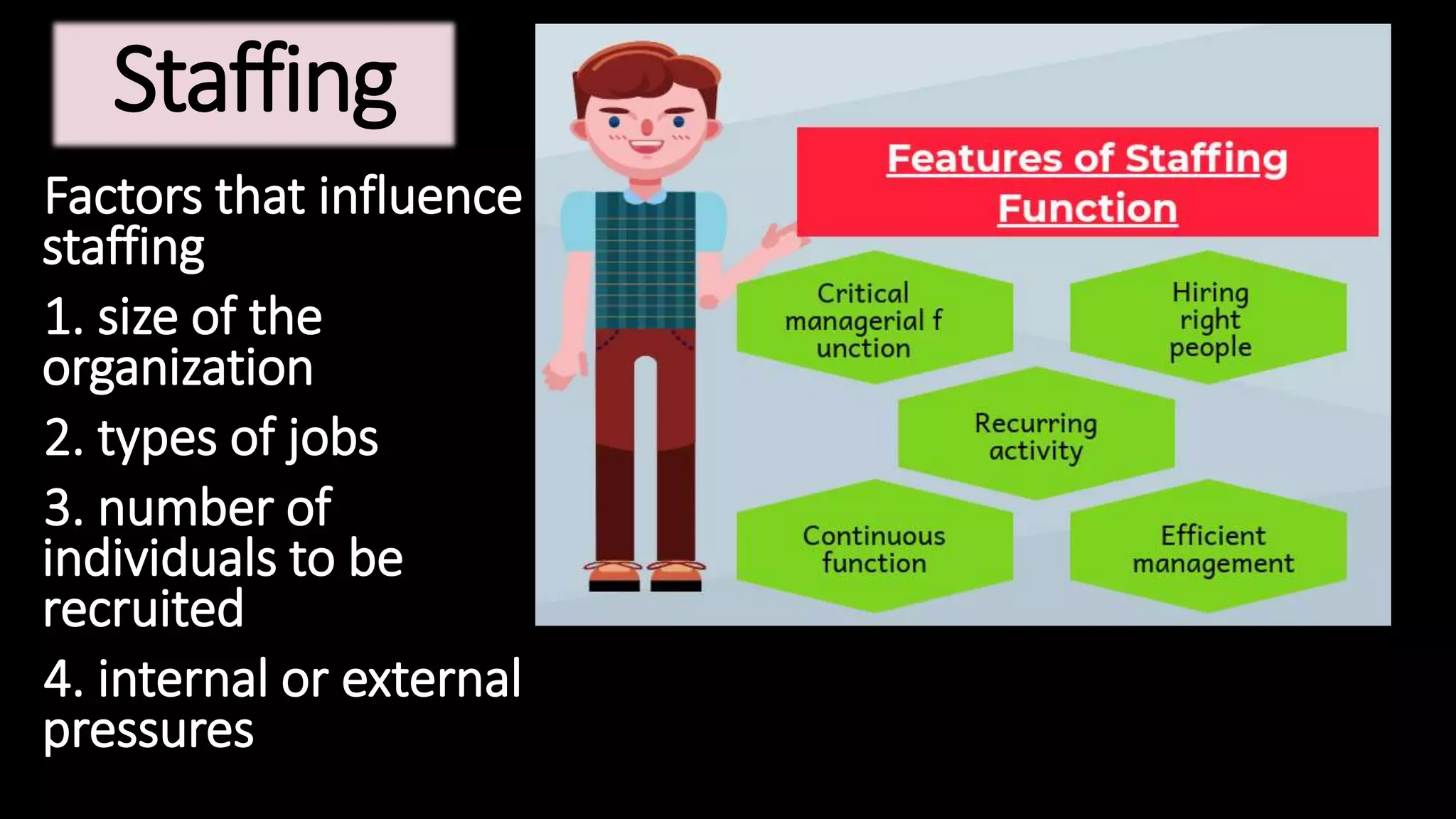
This document provides an overview of management concepts including definitions, functions, theories, and approaches. It discusses early management theorists like Taylor, Fayol, and Weber and their contributions. Total Quality Management and continuous improvement approaches from Deming and Juran are also summarized. The document outlines management roles, skills, and functions. It concludes with an introduction to organizational behavior and a brief definition of SWOT analysis.