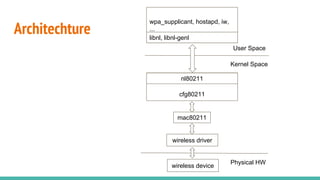
Wpa_supplicant is a widely used implementation of an IEEE 802.11i supplicant for Linux and other platforms. It implements WPA and WPA2 security protocols as well as RSN, PMKSA caching, pre-authentication, 802.11r, 802.11w, and Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS). Wpa_supplicant initializes interfaces by reading configuration files, setting up drivers via cfg80211 and libnl, and starting an event loop to monitor network events. It can access layer 2 packets using l2_packet to support functions like TDLS.