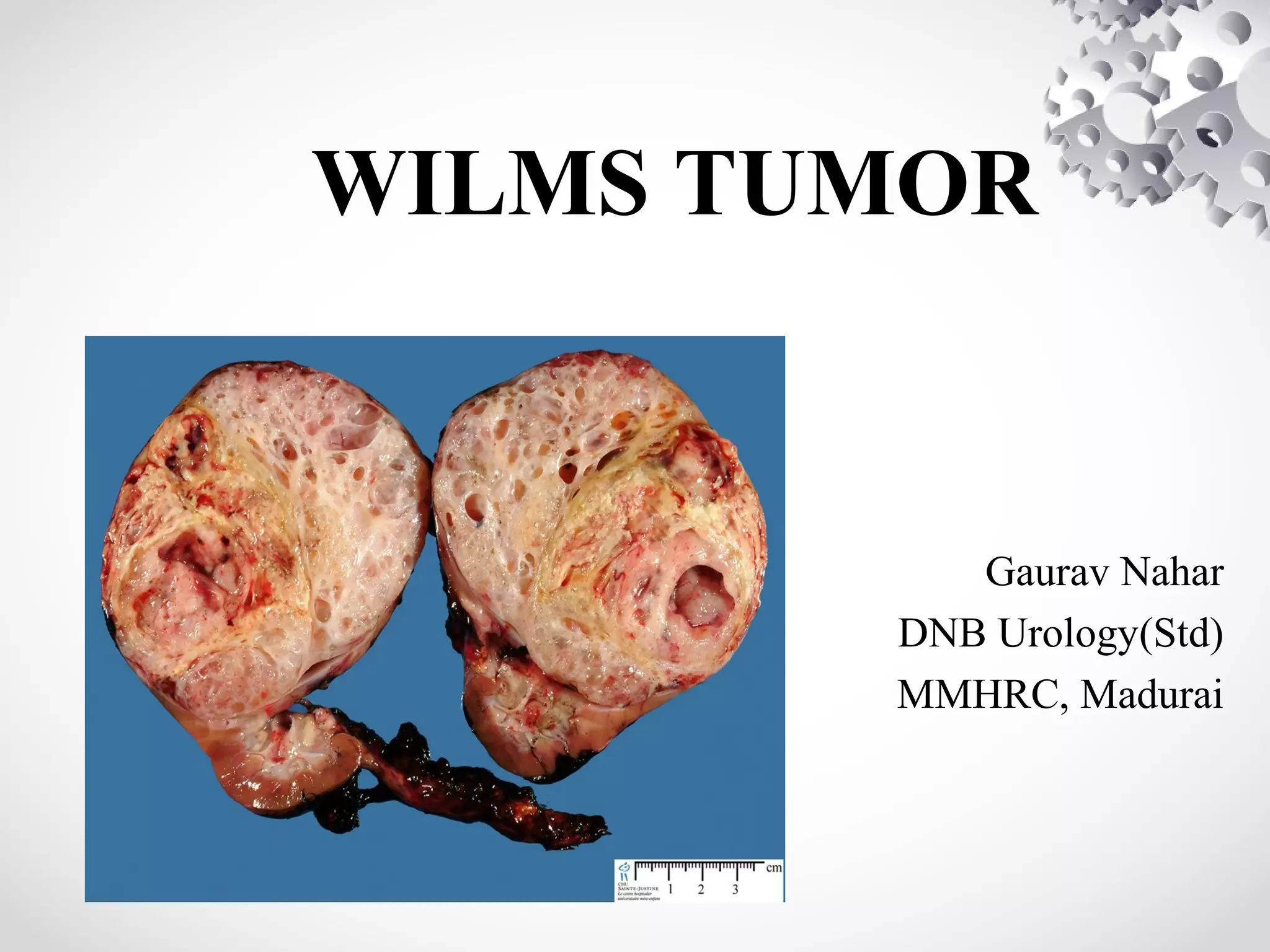
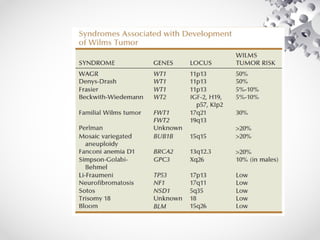
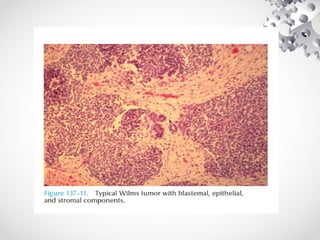
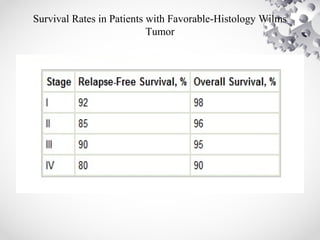
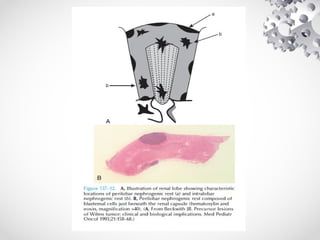
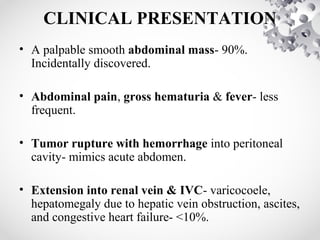
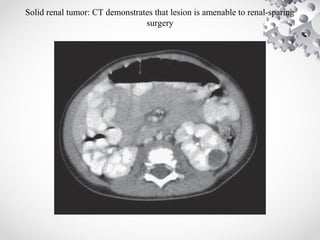
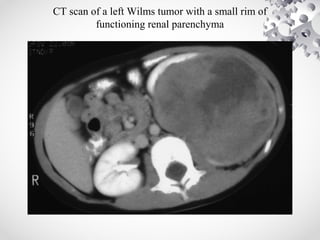
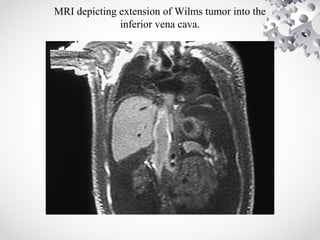
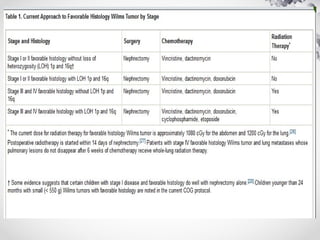
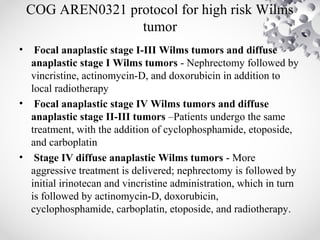
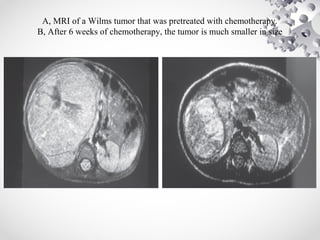
Wilms tumor, also known as nephroblastoma, is the most common malignant renal tumor of childhood. It develops from embryonic kidney tissue and accounts for 6-7% of childhood cancers. The tumor is usually diagnosed before age 5 and may be detected via abdominal mass or hematuria. Staging involves imaging like CT or MRI to determine extent. Prognosis depends on histology and stage. Treatment typically involves nephrectomy followed by chemotherapy, with radiation sometimes used. Late effects can include growth issues, infertility, and second cancers. Long term follow up is important after treatment ends.