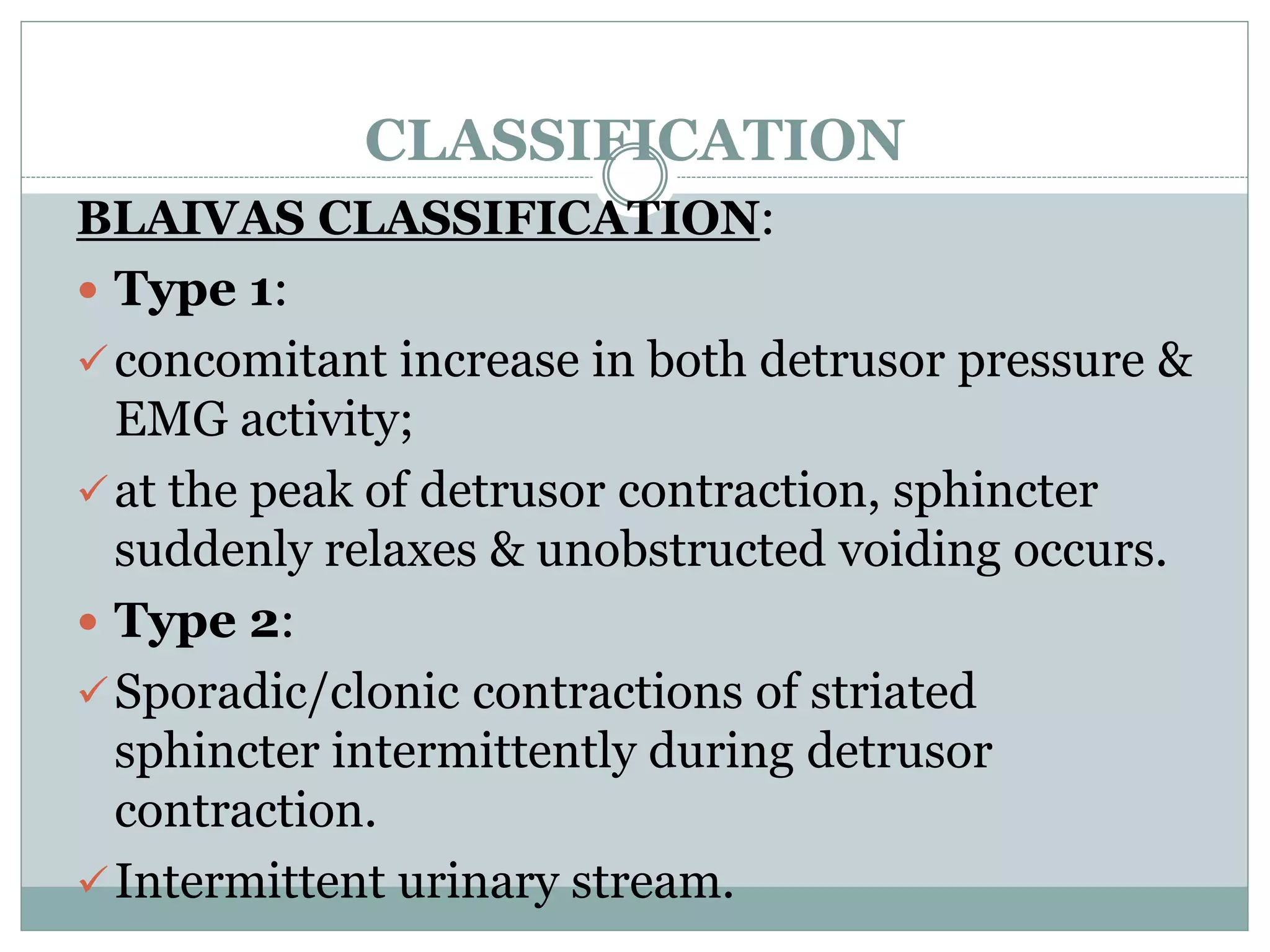
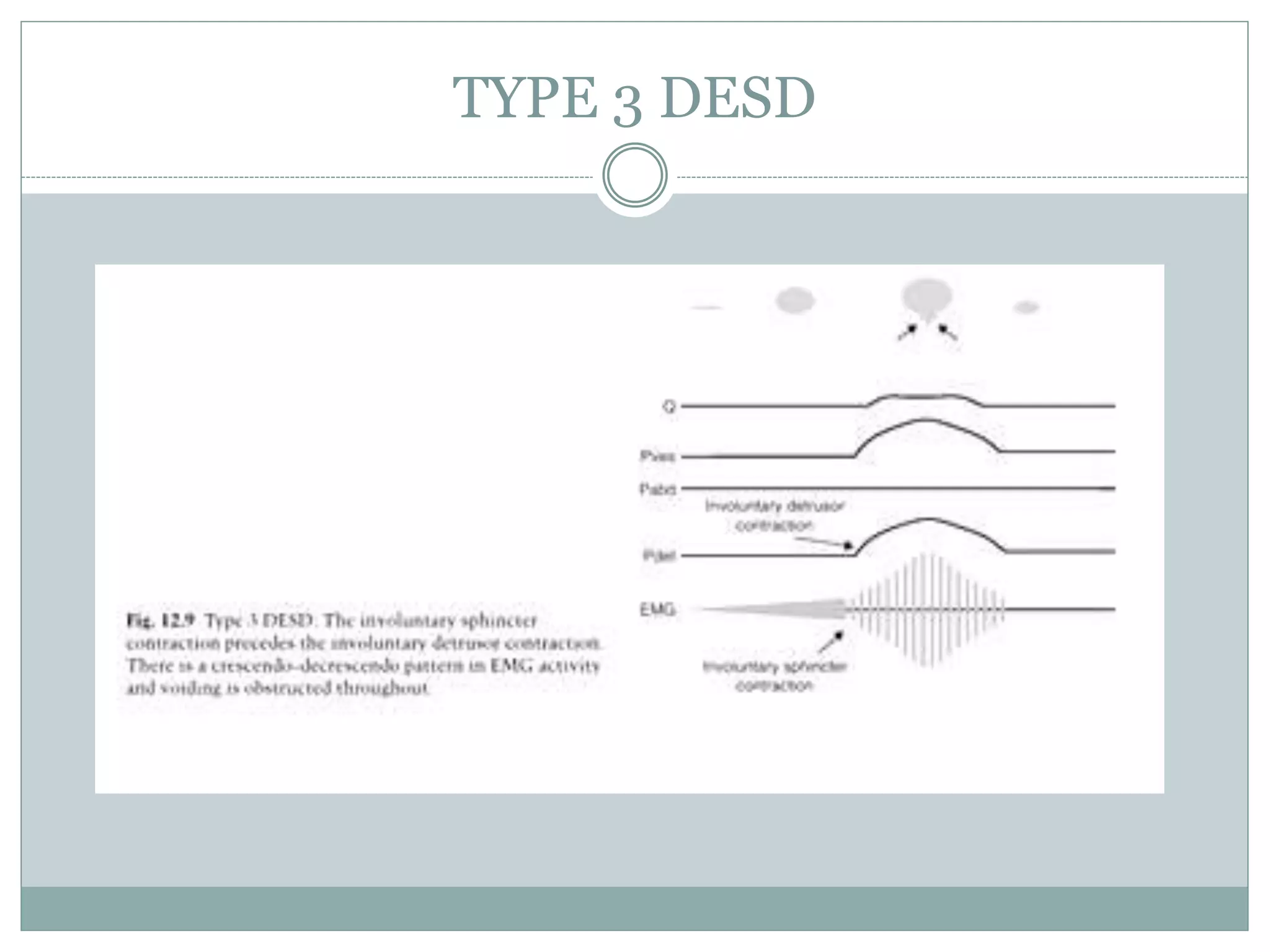
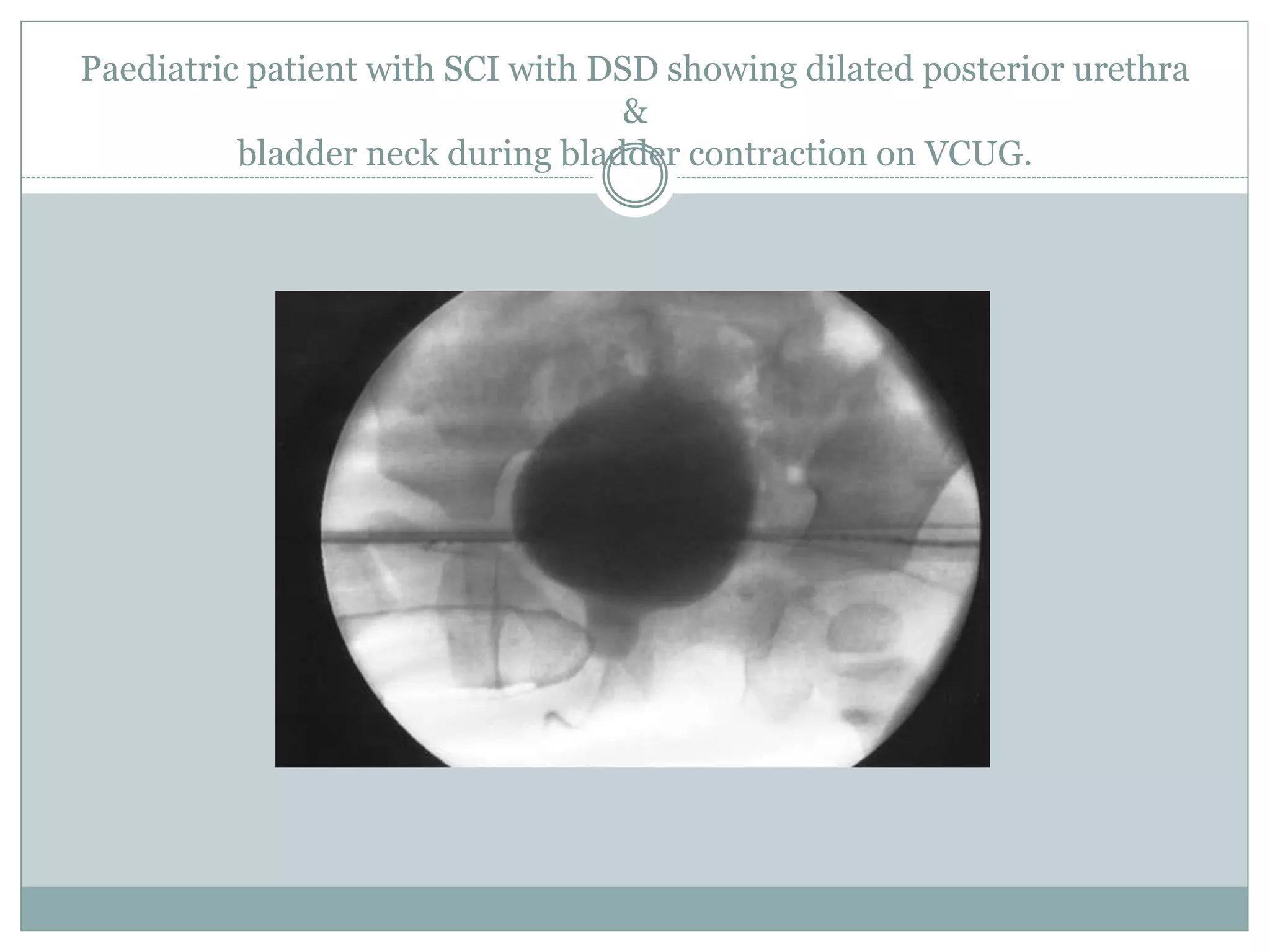
This document discusses detrusor sphincter dyssynergia (DSD), an impairment of coordination between the detrusor and urethral sphincter muscles during urination. It defines DSD and provides details on the micturition cycle, neural control of the lower urinary tract, causes of DSD including spinal cord injury and multiple sclerosis, classification systems for DSD, clinical presentation, diagnostic evaluation including urodynamics, and treatment options. DSD is a common cause of urinary obstruction in patients with neurological conditions that interrupt signaling between the brain and sacral spinal cord controlling micturition.