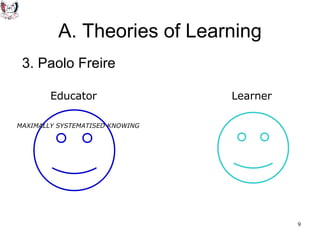
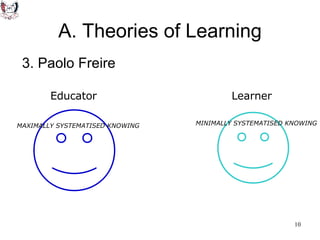
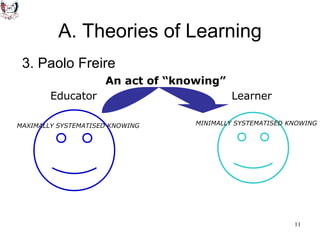
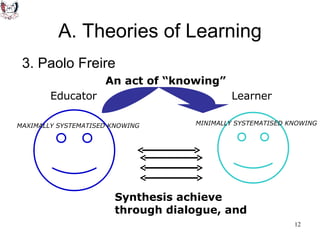
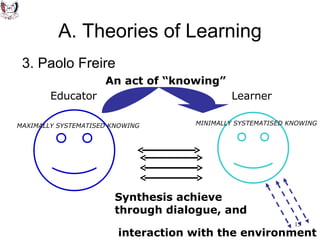
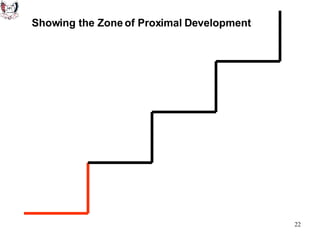
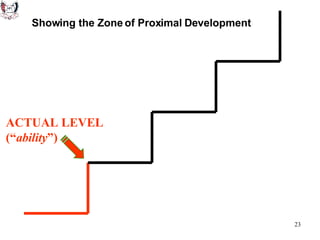
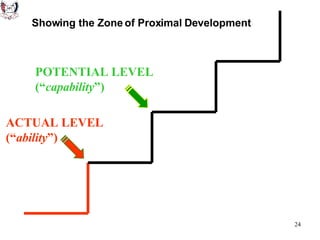
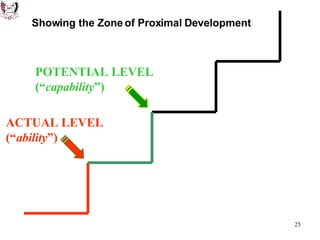
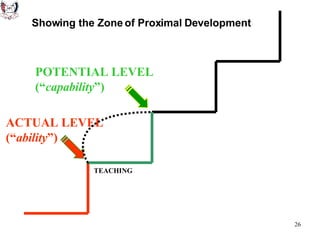
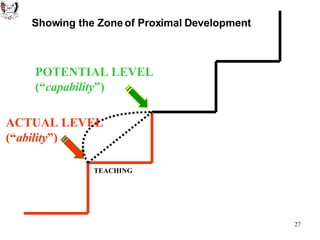
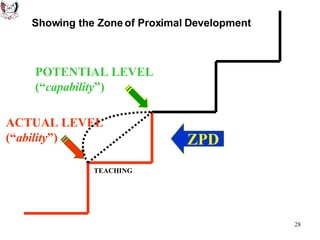
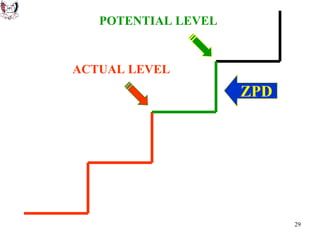
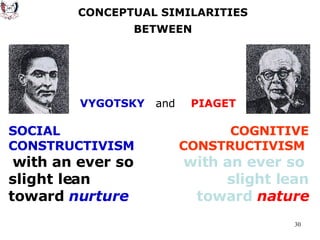
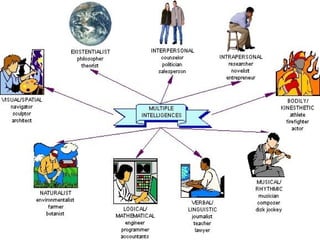
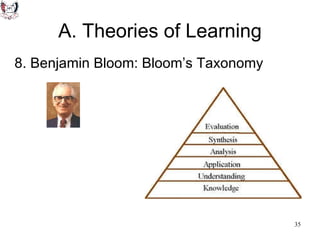
The document discusses key theories of learning by notable figures such as Glasersfeld, Bruner, Freire, Piaget, Vygotsky, Maslow, Gardner, and Bloom. It highlights various aspects of constructivism, cognitive development, social interaction, and educational principles that inform teaching and learning practices. The document aims to provide foundational ideas for the teaching and learning committee's principles.