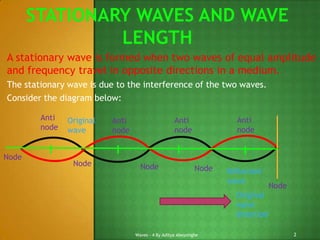
1) A stationary wave is formed by the interference of two waves traveling in opposite directions. Nodes occur where the waves destructively interfere, while antinodes occur where they constructively interfere.
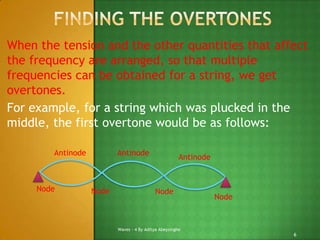
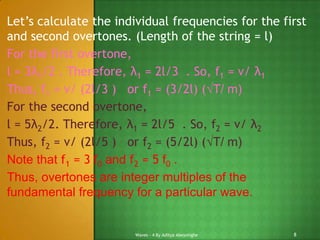
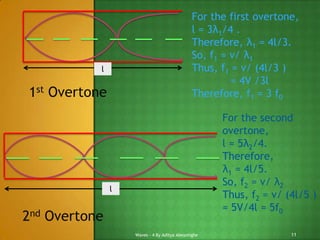
2) The document discusses characteristics of stationary waves in strings and pipes, including how the fundamental frequency and overtones are determined based on the length, tension, and mass properties.
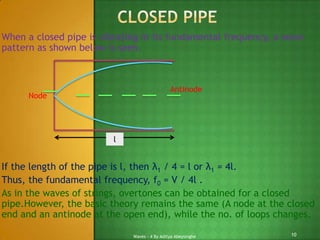
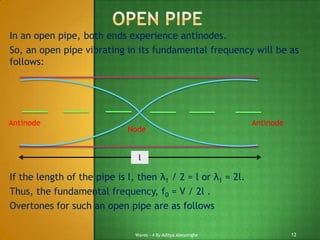
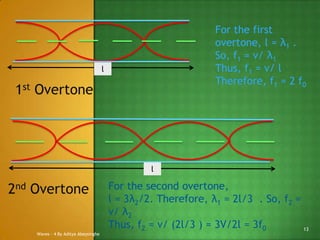
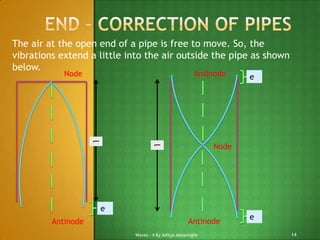
3) For both closed and open pipes, the fundamental frequency and overtones follow specific patterns based on the length and wavelength. There is also an "end correction" to account for the air vibrations extending slightly outside the open end of the pipe.