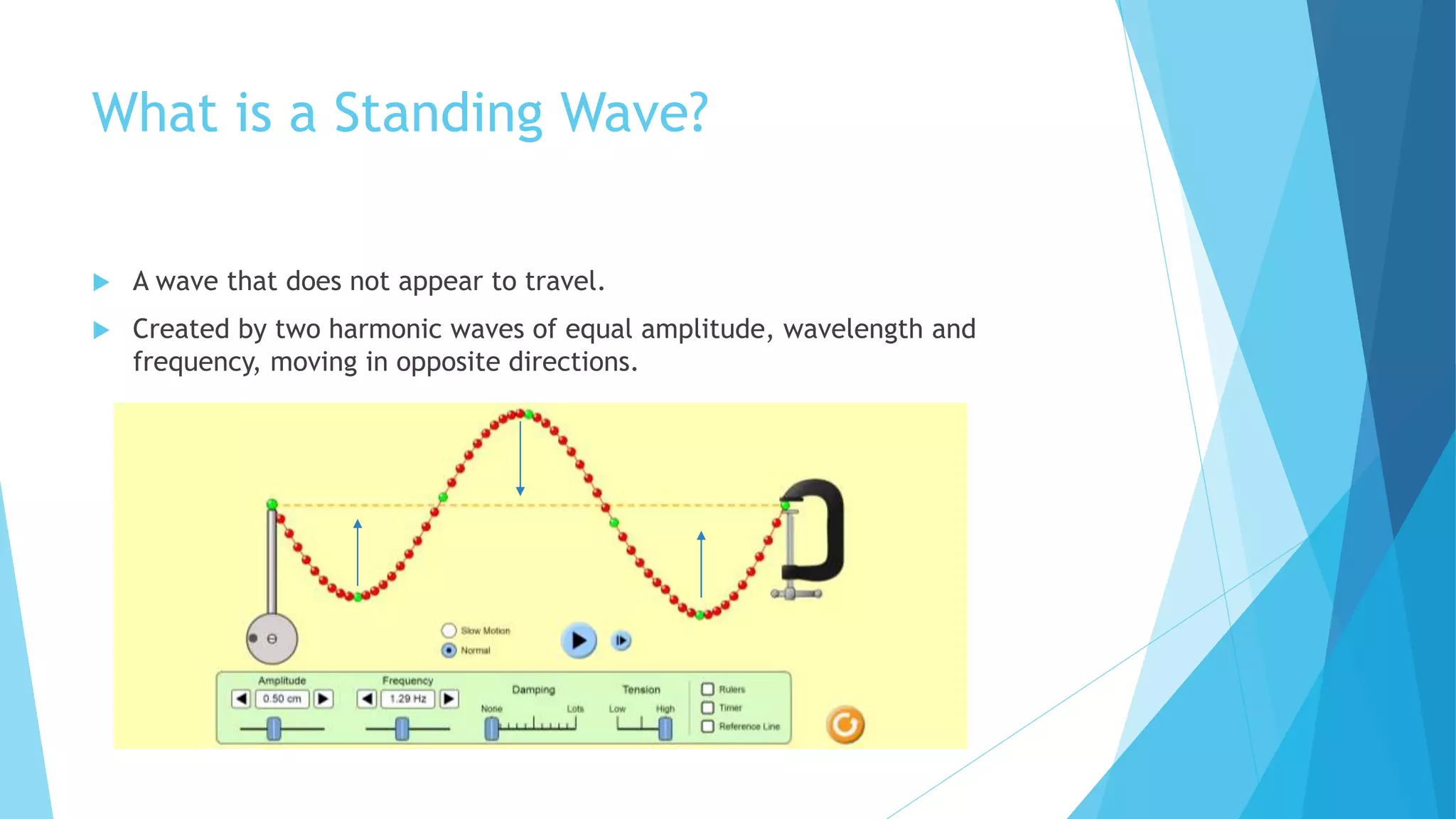
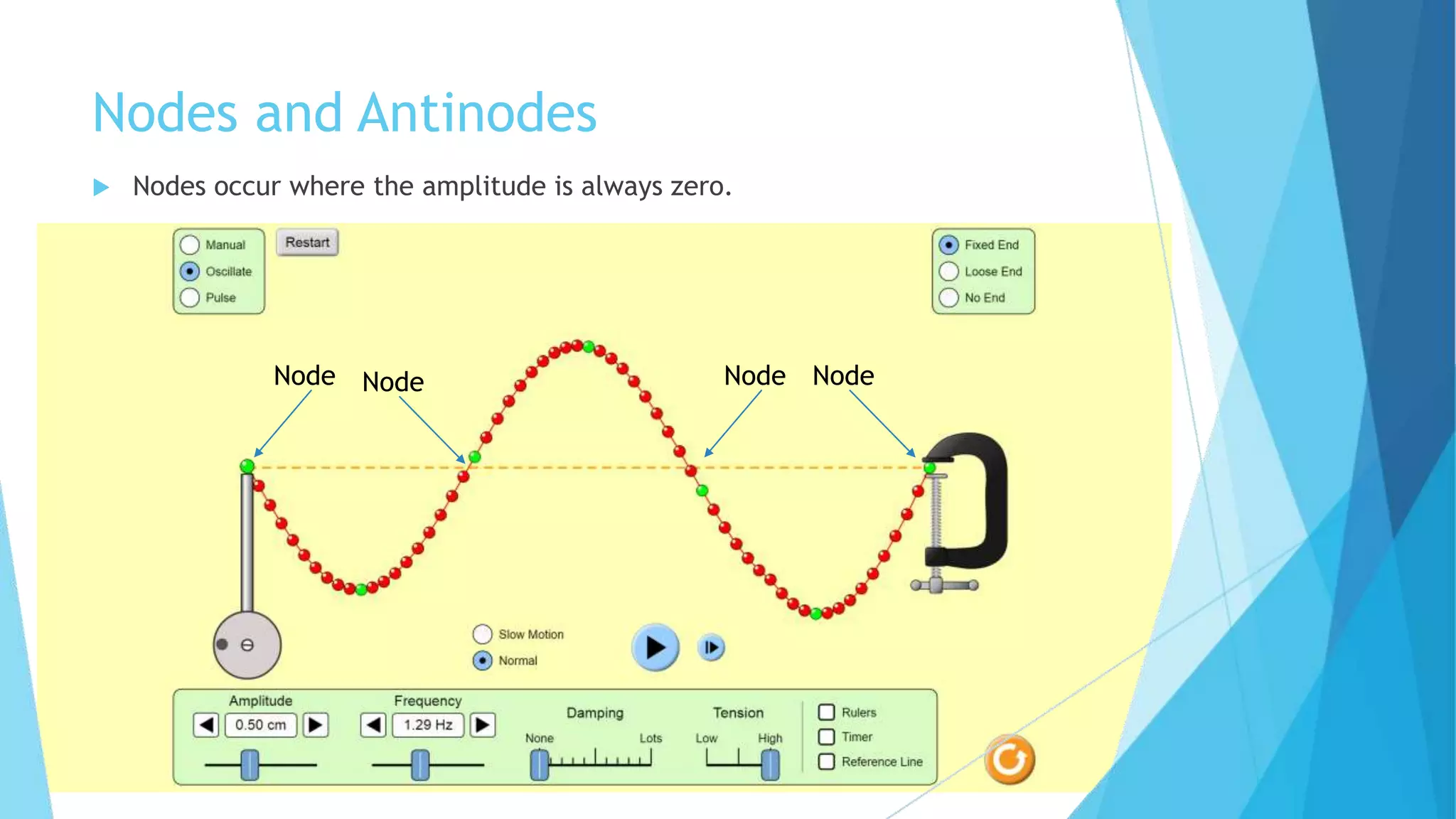
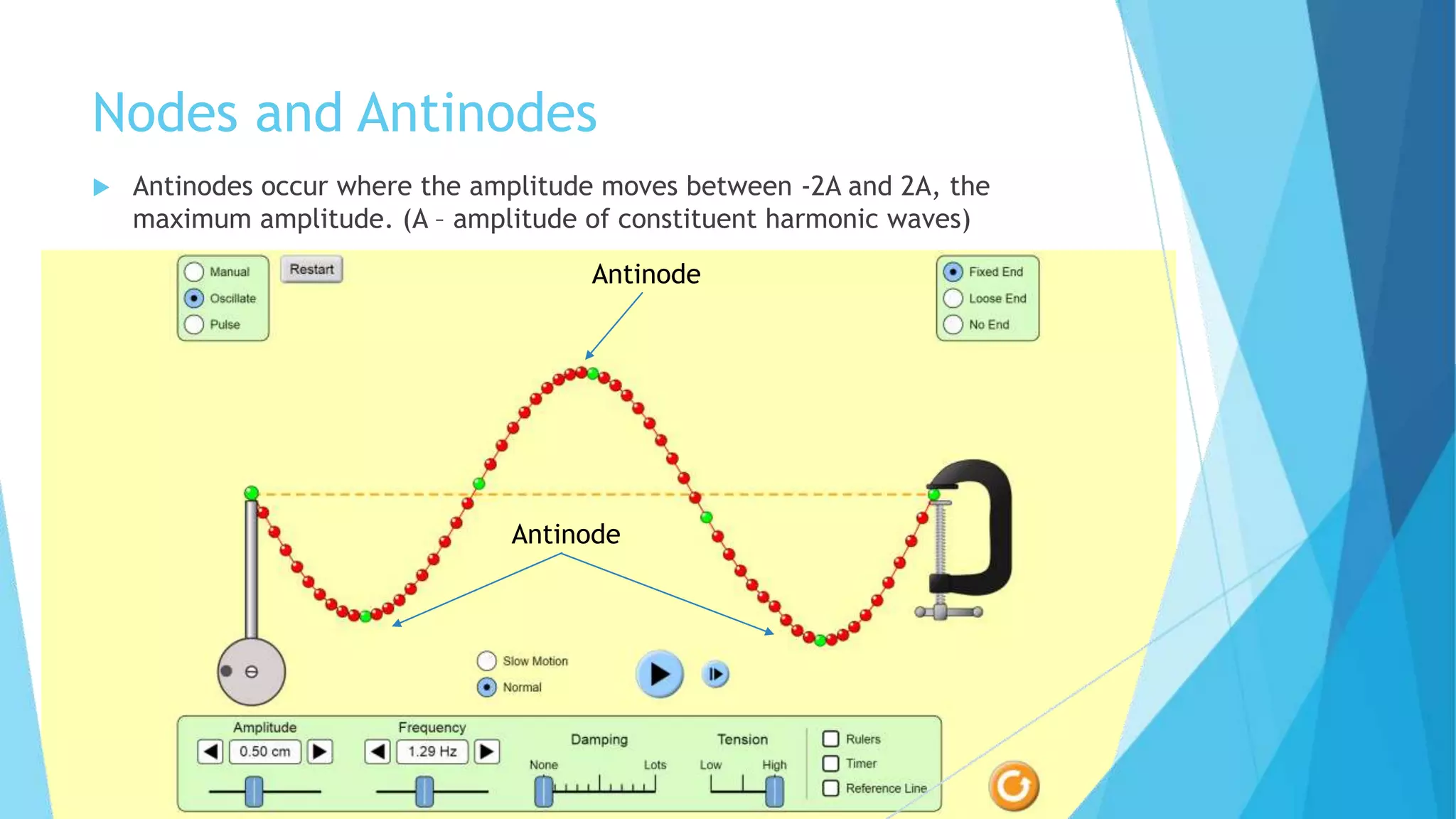
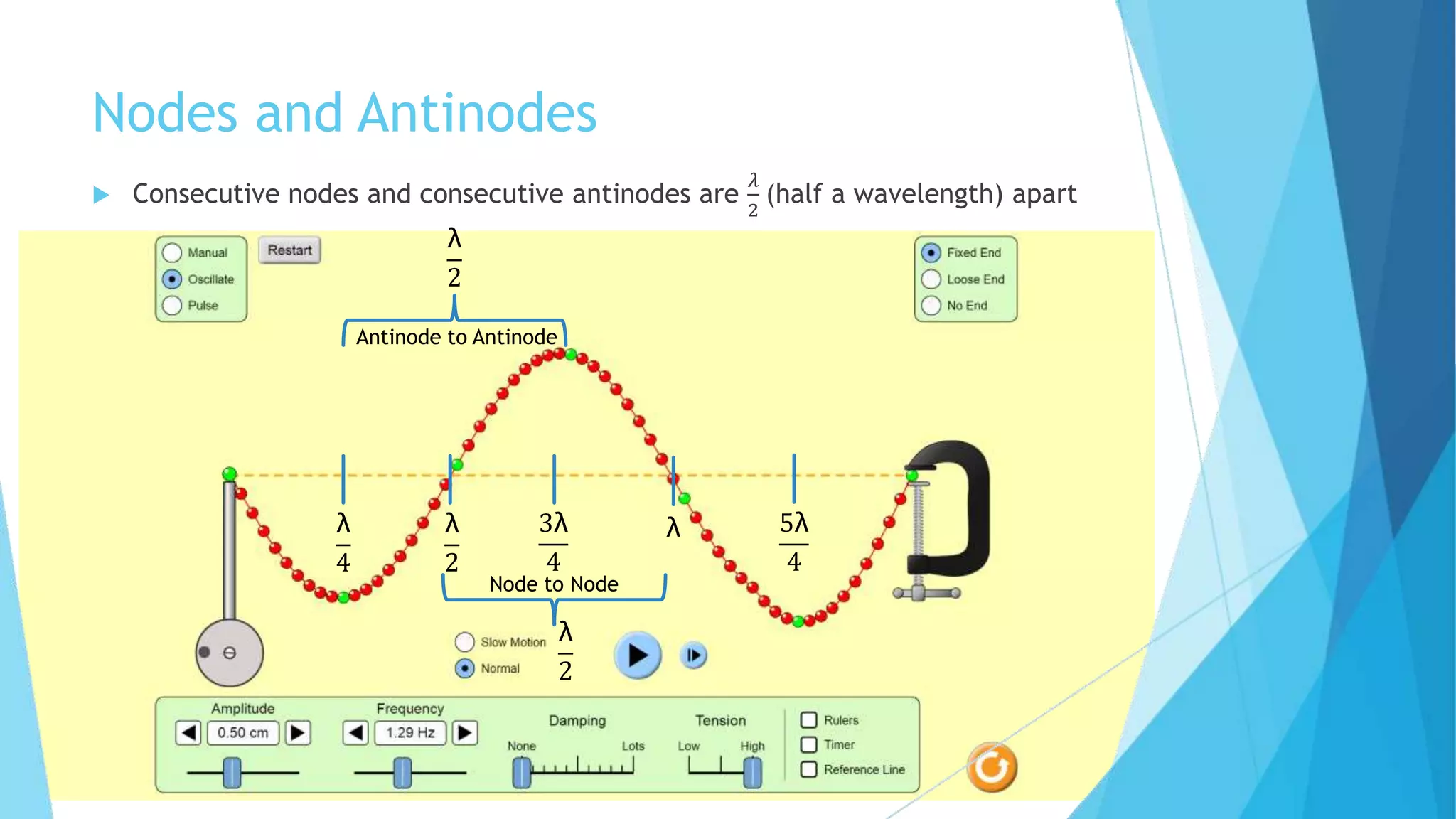
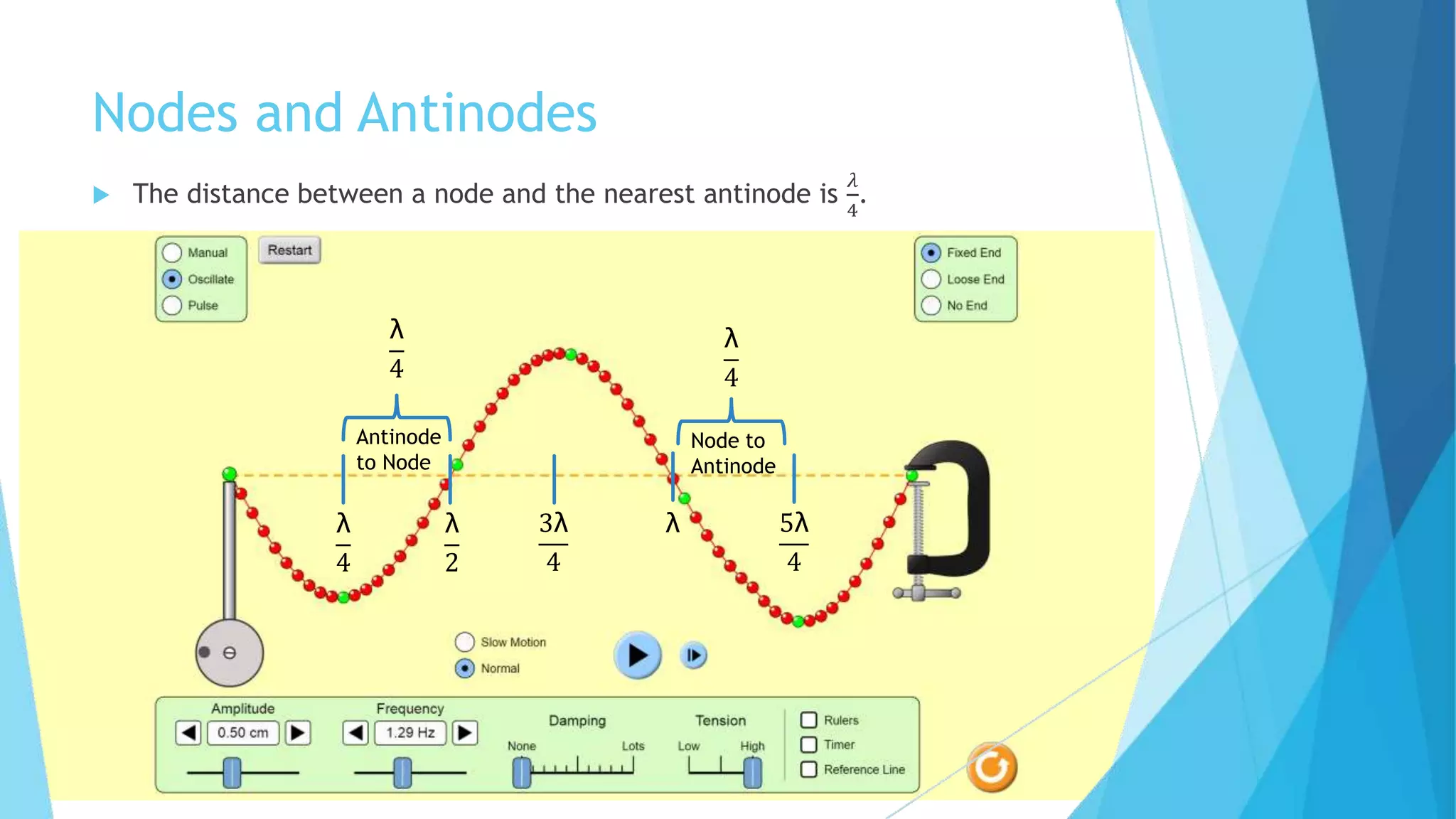
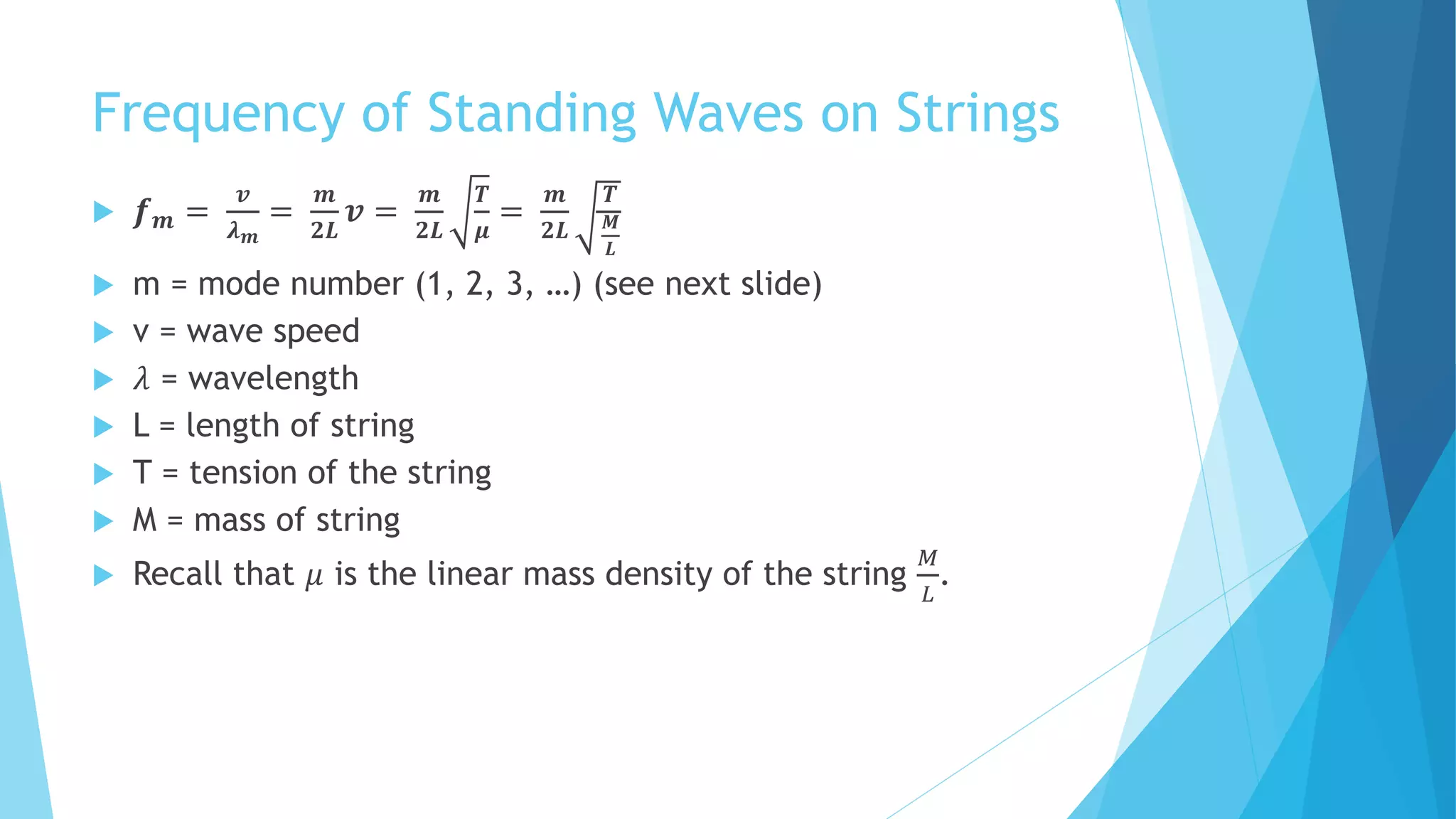
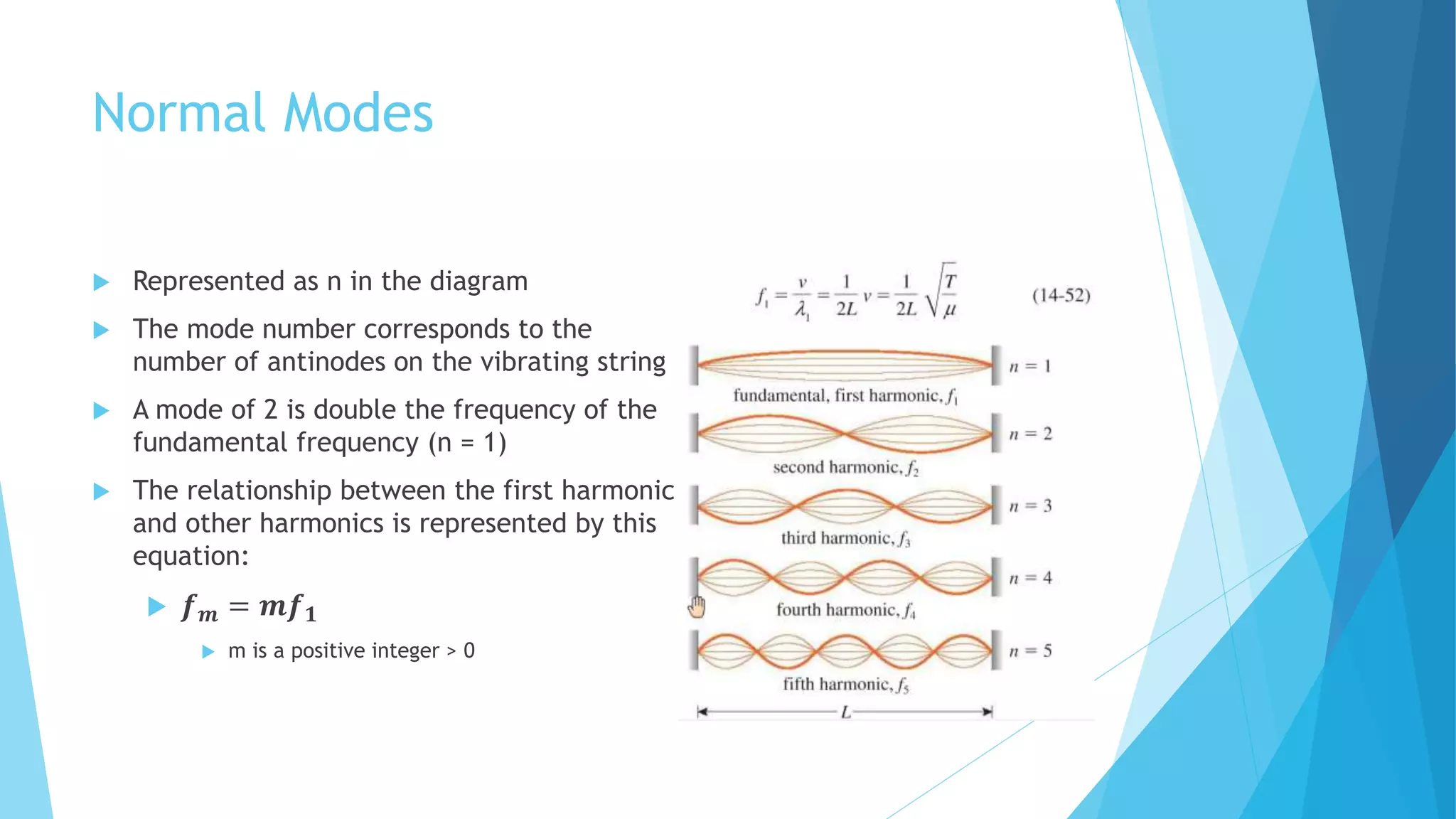
Standing waves are created by two harmonic waves of equal amplitude, wavelength and frequency moving in opposite directions. Nodes occur where the amplitude is always zero, while antinodes occur where the amplitude is at its maximum between -2A and 2A. The distance between nodes and antinodes is λ/2, while the distance between a node and the nearest antinode is λ/4. The frequency of the mth harmonic is given by fm = m*f1, where f1 is the fundamental frequency.