Embed presentation
Downloaded 87 times



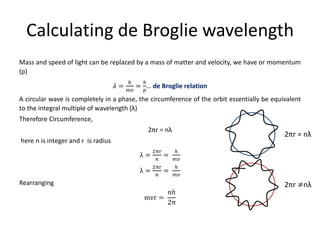

Louis de Broglie postulated that electrons can behave as both particles and waves. He derived the de Broglie relation that shows the wavelength of a particle is inversely proportional to its momentum. This relationship uses Planck's constant and can be applied to electrons or any moving matter. The de Broglie wavelength allows relating the circumference of an electron's orbit to an integer multiple of its wavelength, providing insight into quantized electron orbits around an atom's nucleus.




