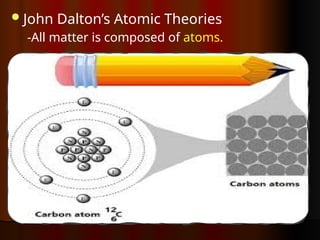
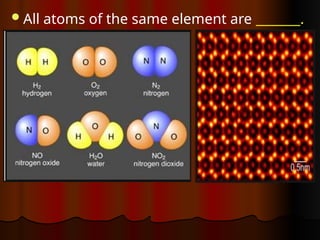
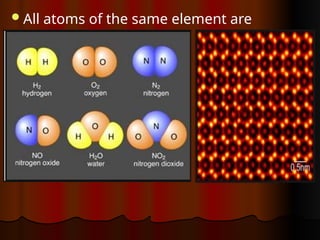
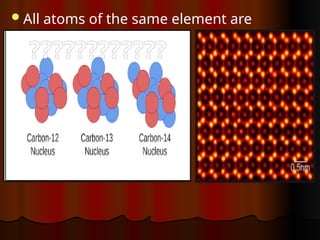
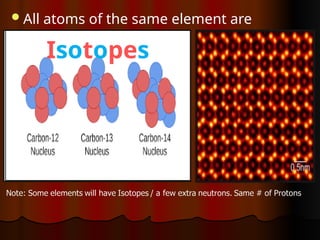
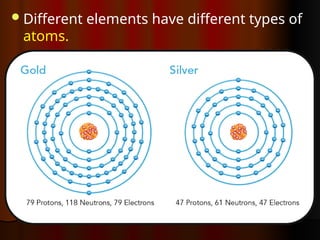
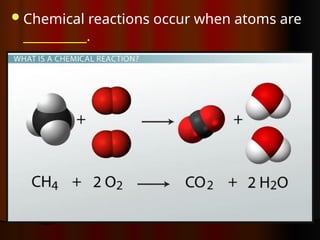
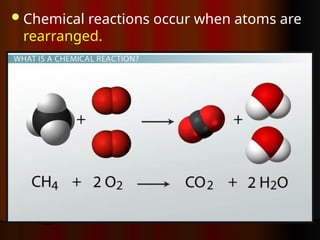
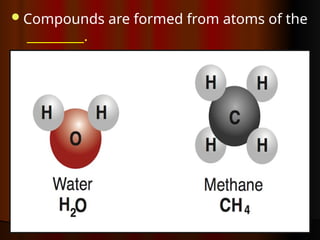
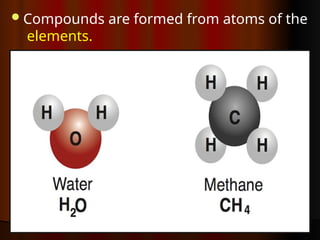
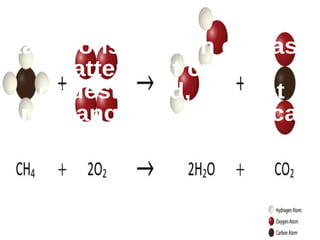
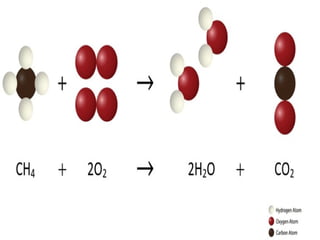
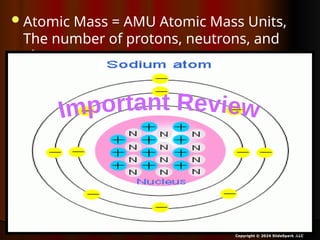
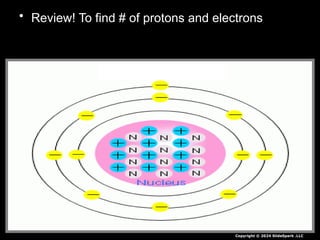
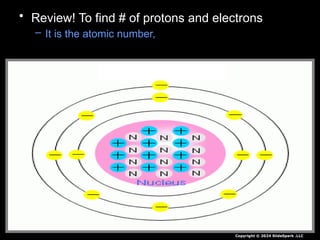
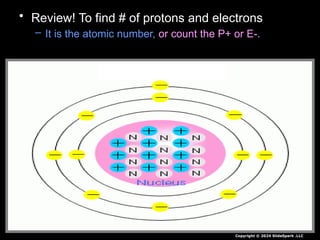
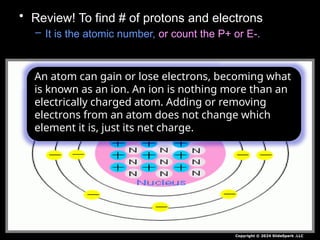
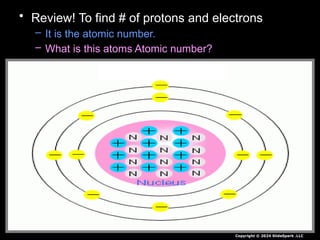
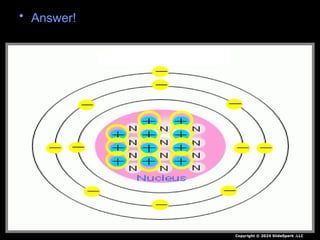
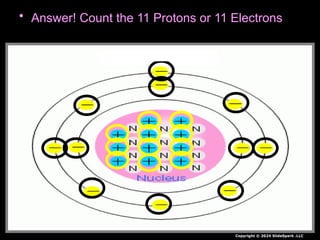
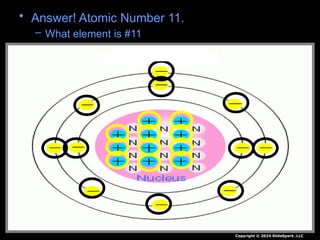
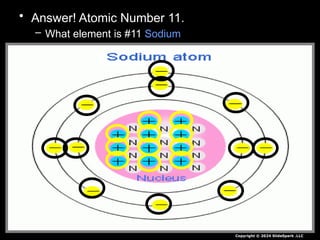
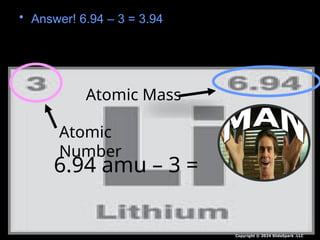
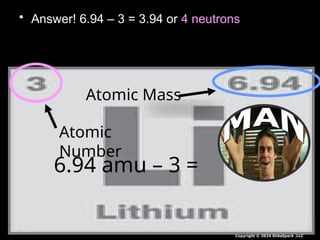
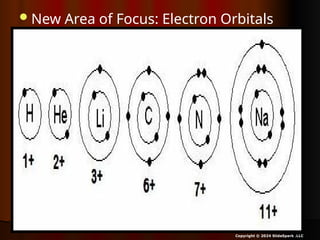
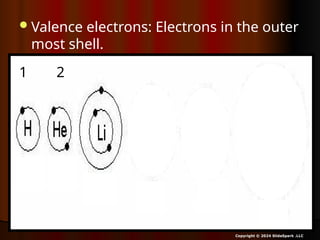
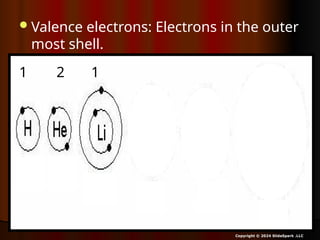
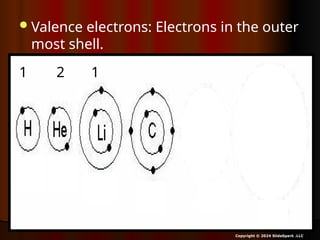
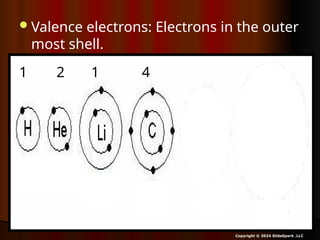
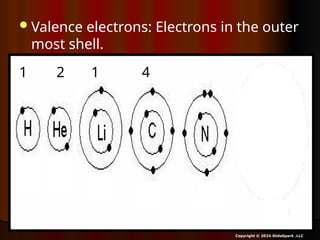
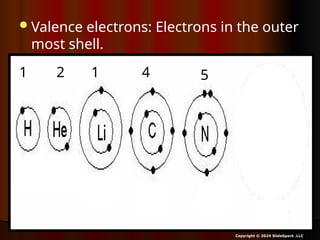
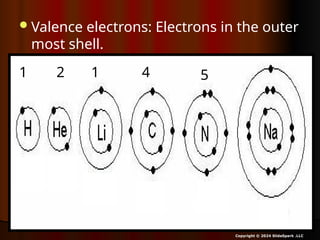
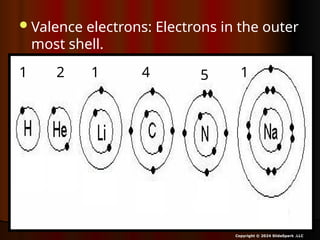
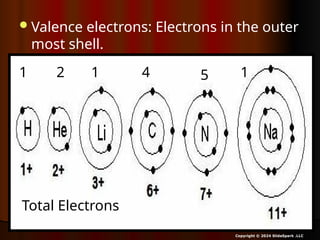
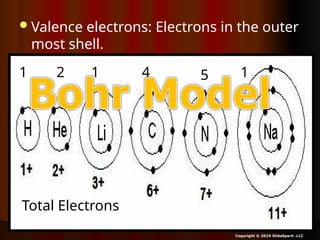
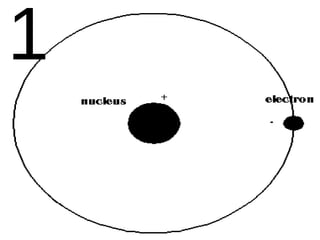
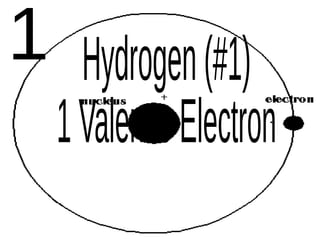
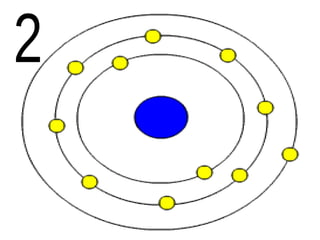
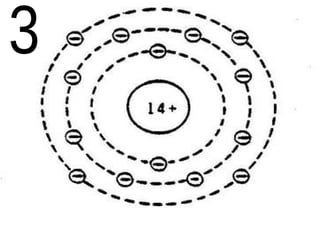
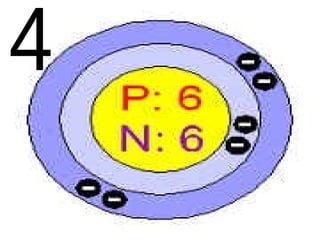
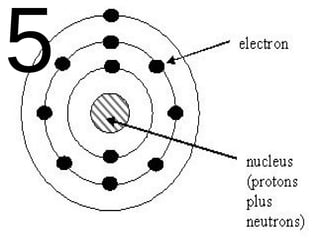
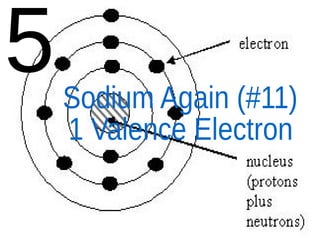
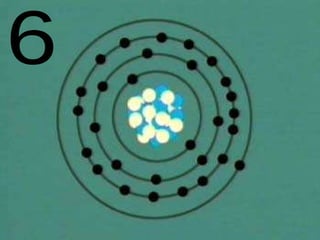
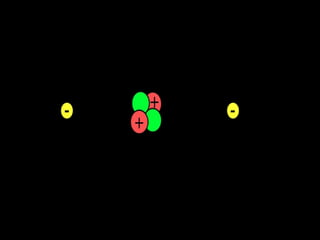
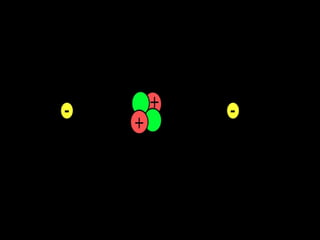
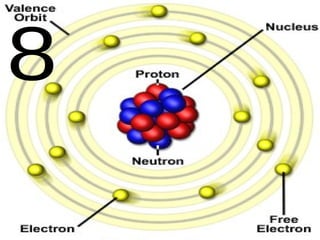
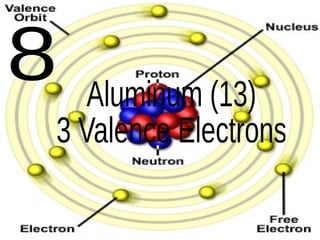
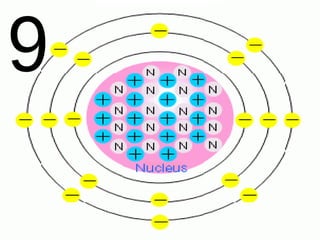
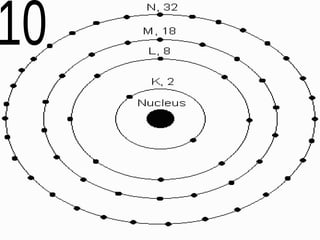
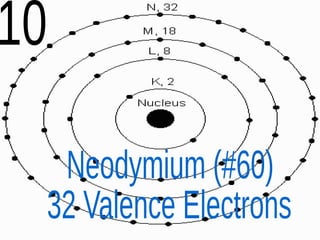
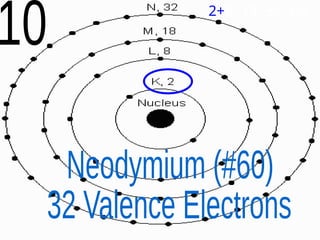
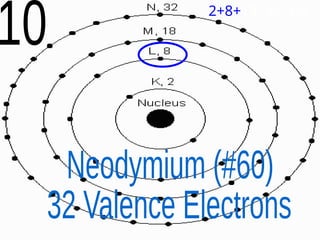
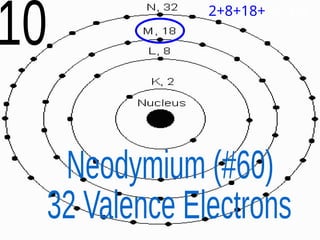
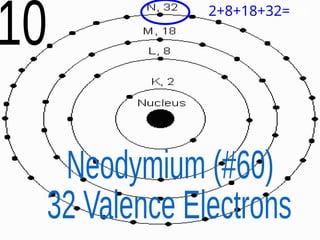
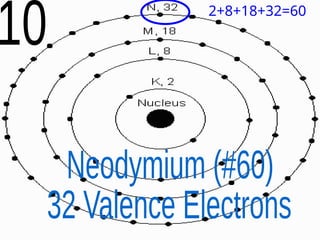
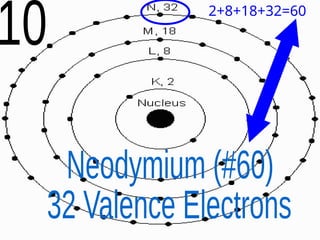
The document outlines key concepts from John Dalton's atomic theory, including the composition of matter, the identity of atoms within elements, and the impossibility of creating or destroying atoms. It also discusses isotopes, the formation of compounds, and introduces concepts of electron orbitals and valence electrons. The content emphasizes the importance of recording notes and staying organized for successful learning.