Waterproofing and insulaton
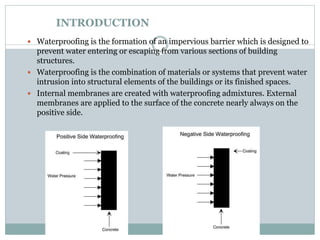
- 1. INTRODUCTION Waterproofing is the formation of an impervious barrier which is designed to prevent water entering or escaping from various sections of building structures. Waterproofing is the combination of materials or systems that prevent water intrusion into structural elements of the buildings or its finished spaces. Internal membranes are created with waterproofing admixtures. External membranes are applied to the surface of the concrete nearly always on the positive side.
- 3. BASEMENT WATERPROOFING Waterproofing is required in every structure but especially needed in case of basements where ground water causes hydrostatic pressure to be exerted underneath basement floors and against basement walls & may result in mold, decay and other moisture related problems. Effective below ground waterproofing will include both drainage and sealers.
- 4. TYPES OF BASEMENT WATERPROOFING SEALANT a) EXTERIOR SEALANT b) INTERIOR SEALANT WATER DRAINAGE
- 5. sealant Sealant is a substance used to block the passage of gases or liquids through the surface or joints or openings in materials. sealant is sometimes synonymous with caulking and also serve the purposes of blocking dust, sound and heat transmission they can provide thermal and acoustical insulation, and may serve as fire barriers.
- 6. •These types of sealants are applied as a coating on the exterior surface of basement wall(positive side) •They can be in a form of film(eg.bitumen sheet, PVC) or paints(polymer). EXTERIOR SEALANT The principal exterior substrates that are sealed are: exterior wall joints (masonry, concrete,plaster/stucco,) •door and window frames •concrete paving joints •metal flashings •roof joints •seismic movement joints
- 7. Basement where adequate space is available for excavation- The excavation of ground for basement is carried out in such a manner that working space of at least 60 cm is available around external walls. If water level is high, the excavated area should be kept dry by continuous pumping. 1) On dry and leveled ground 75 to 100 mm thick lean concrete is laid to serve as a leveling course for water proofing. 2) The bitumen based primer is applied with brush on entire area after cleaning the surface. 3) This layer should be protected by construction of flat brick flooring. 4) After construction of structural slab and walls, water proofing treatment on external face which is in contact with earth is done. 5) After the surface is cleaned, bitumen primer is applied. 6) Self adhesive S B S rubber bitumen membrane with high density polyethylene film is applied on vertical walls. 7) Before back filling the soil an outer protective wall leaving a space about 100 mm around should be made and the space should be grouted subsequently.
- 8. Basement where limited space is available for excavation 1) The base slab of lean concrete is laid followed by construction of external protective wall. Its internal face is rough plastered. Horizontal damp proofing treatment is carried out. 2) vertical damp proofing treatment is applied on inside plastered surface of the protective wall. 3) The treatment should be continuous on the wall and the floor. 4) For vertical damp proofing continuous with horizontal a fillet cement mortars should be provided at the junction of the slab and outer protective wall. 5) The horizontal and vertical damp proofing is protected against damage during subsequent operations. 6) Flat brick flooring and an inner protective wall are constructed. 7) The space of 100 mm left between vertical damp roofing treatment and internal protective wall is grouted after laying damp proofing membranes. 8) Thickness and reinforcement of RCC structural slab and walls are designed according to depth
- 9. INTERIOR SEALANT •Sealants are applied on the negative side of the wall •Sealants are in a form of solution (organic silicon compounds) that are injected in the wall to make it impermeable. • These types of sealants have a time period of few years • liquid silicification contains chemical, that penetrate into the concrete surface making the concrete itself part of the waterproofing. The principal interior substrates that are sealed are: •gypsum board; •plaster; •floor control and expansion joints; •kitchen and bathroom wet joints
- 10. BITUMINOUS TYPE – A kind of waterproof sealant that is less suitable for floors. A few versions of this product are particularly fuel-resistant or able to withstand hot and cold temperatures. can be used as concrete sealant on airport decks and roadways. Roof sealant also is often made with this substance to protect the tops of houses and buildings from water damage. bituminous sealant is usually one of the best to use around a lot of water, such as in tanks that hold several tons. POLYURETHANE SEALANT can be easily painted over. This is helpful when it comes to blending waterproof sealant with the surrounding décor. It also does not usually shrink, and is not easily damaged by abrasion, which means it is used often with both flooring and cars. shorter lifespan than silicone sealant, and has lesser ability able to withstand extreme temperatures and UV rays. not known for being friendly to the environment. SILICONE-BASED protect surfaces from ultraviolet (UV) rays and extreme temperatures. protect against mold or be applied to natural materials like marble or stone without staining silicone sealant cannot be painted over, though there are a few specialized silicone sealants mixed with other substances just for that purpose MATERIALS USED AS SEALANTS Caulking gun Driveway sealant
- 11. WATER DRAINAGE Function by draining underground water from alongside the foundation footers and underneath the basement floor. They then channel it with a French drain, PVC pipe, or through a patented product to a Sump Pump System, which will then pump the water from the basement. Often need to be run on an isolated electric system, in case of power shortage, or during periods of storms. Sump pumps should be placed in a pit, and sealed in with a lid in order to keep the water away from the electricity, and to prevent humidity in the pump from entering the atmosphere of the basement. Keeping the lid airtight ensures that there is no likelihood of poisonous gases seeping out into the house.
- 12. HOW IT WORKS? Water enters the home via the basement wall/floor joint, through cracks in the foundation walls and/or holes created by faulty or decaying masonry/brick. A perimeter trench drain such as a French drain collects the water before it enters into the basement. Wall vapour barriers/retarders and drip mouldings are used and incorporated into the sub-slab perimeter drain to collect water coming from wall cracks and other foundation wall defects, such as pipe protrusions. The drain directs the water to a sump pump. The sump pump directs the water out of the house.
- 13. WATER IS CAPTURED USING EXTERIOR FRENCH DRAIN SYSTEM -DRAIN PIPE INTERIOR FRENCH DRAIN SYSTEM TRENCH DRAIN SYSTEM
- 14. EXTERIOR FRENCH DRAIN SYSTEM -DRAIN TILE Instead of fighting hydrostatic pressure (and risking major leakage), an exterior footing drain was probably installed when the building was built. Its job is to help relieve this pressure and to move water away from your house. An exterior French drain is typically installed along the outside edge of the footing, after the home's foundation is built but before it is backfilled. First a bed of gravel is laid down around the foundation's perimeter. Then perforated French drain pipe is placed on top.Gravel is then laid on top of the pipe. Sometimes, filter fabric is then laid on top of the French drain pipe to keep fine particles from passing into the pipe. The excavation is then backfilled.
- 15. LIMITATIONS This old-fashioned waterproofing system tends to collect sediment and clog as it ages. Often, the filter fabric itself will eventually be overwhelmed with material and will clog. A drain system may work fine for years, depending upon site conditions and how carefully it was installed. When there’s a problem, however, servicing it is difficult or impossible. These drains eventually clog with silt or plant roots, and aren’t so much effective at preventing water from entering your basement.
- 16. INTERIOR FRENCH DRAIN SYSTEM
- 17. FRENCH DRAINS
- 18. TRENCH DRAIN SYSTEM Effectively captures surface water at building transitions Grated cap can be removed to clear drainage channel. Use TrenchDrain to prevent water intrusion in these locations: Across the basement floor in front of an exterior concrete stairway (bulkhead door). Across the entrance to a garage. Where a patio meets a walkout basement door.
- 19. INSTALLATION A sump pump hole is drilled into the basement floor. The sump pump is then placed into the opening and attached to the water drainage system of the house. Sump pumps run on electrical currents and automatically turn on and off depending on the level of water building up in the basement. It is most useful during periods of heavy rain. If a sump pump fails to work, the basement will eventually flood again.
- 20. PEDESTAL SUMP PUMPS Designed to sit above the water and avoid getting wet. The motor is located on top of the pump where it cannot get wet. Works by using a float activated switch that will turn on the pump when water reaches a certain level. The water is pumped out of basement and away from where it can do damage.
- 21. ADVANTAGES & DISADVANTAGES Cost - cheaper Longevity - Because these pumps are not submersed in water they typically will last longer. Ease of Maintenance - Due to it's design, a pedestal sump pump will be easier to maintain since the motor is located on top of the unit and access is much easier. Noise - Since the motor of the pump is located on top and above ground, it will definitely be audible and easily heard when in operation.
- 22. SUBMERSIBLE P SUMP PUMP Designed, just as its name suggests, to be submerged in water. Designed to be located in the sump pit and is built to totally encase the motor to keep it protected from water. Uses the same float activated switch to automatically turn on when water is detected. This water is then pumped out and away from the house.
- 23. ADVANTAGES & DISADVANTAGES Efficiency - Because submersible sump pumps are located close to the water level, they don't have to work as hard as a pedestal sump pump to remove the water. Quieter- Because the motors are contained within the unit and the placed within the sump, submersible pumps are typically quieter than other style pumps. Difficult to repair- Since these pumps are submerged in to a pit, they are not easily accessible and thus when they need maintenance they are more difficult to access.
- 25. INJECTION GROUTING Injection Grouting is the injection of specially formulated cement-based mixes into the ground to improve its strength or reduce permeability. It is used for remedial or redevelopment applications. cement grouting technologies are increasingly chosen for cost- effective, permanent solutions. Cement grouting is most commonly performed by drilling holes into the foundation to intercept open cracks, joints, fissures or cavities, then pumping under pressure balanced and stabilized grout mixes using a combination of cement, water, and additives.
- 26. Area of Application: Applied to cracks in concrete, masonry, solid stone walls, cavities, rock pockets, floor toppings, prefabricated concrete parts Used of injecting concrete surface areas in order to strengthen them Used for the closing, sealing and impregnation of cracks, cavities and porous, low strength concrete Injection grouting is used either for sealing the leakage’s or for attending cracks in the structural members In order to fill the pores, honey combs inside the structures injection grouting is adopted before waterproofing and repairing
- 27. INJECTION GROUTING BOX METHOD BRICK-BAT COBA Rs 250/sqm Without material Rs 250/sqm Without material Rs 250/sqm Without material Rs 600/sqm with material Rs 550/sqm with material
- 29. INTRODUCTION A terrace is a fully supported, above ground level exterior space devoted to social activity. Unlike a balcony, which is cantilevered, a terrace is supported from below with walls. A terrace is also always open to the sky.
- 30. BRICK COBA TERRACING Brick coba terracing laid with grout consisting of cement admixed with acrylic based chemical is an effective water proofing method used in heavy to moderate rainfall regions. PROCESS : The cleaned surface of the roof slab is coated with 15mm thick slurry made of cement mortar (1:4) mixed with acrylic based chemical . A layer of broken brick bats in cement mortar (1:4) admixed with acrylic based chemical is laid with slope for drainage. This layer is cured for about 2 days. Again a layer of cement mortar of same composition is provided to fill up any voids A 20 mm thick layer of cement mortar (1:4) admixed with acrylic based chemical is applied on top and finished smooth. The joint between wall and slab is rounded off The terracing is cured for 2 weeks The acrylic based chemical is added @ 1% i.e. 1 kg of chemical to be mixed with 100 kg cement
- 31. SECTION DETAIL ROOF SLAB 20MM THICK MORTAR WITH WATERPROOFING COMPOUND 80MM BRICK BAT COBA 15-25MM JOINTS 20MM BRICK PLASTER
- 33. Wallbarn Protecto-Joint • Offers the solution for fully waterproofing and protecting buried expansion joints, bonding to most surfaces and membranes effectively. • It is a tough, highly flexible butyl rubber membrane used for waterproofing and protecting preformed expansion joints on roofs, car parks and podium decks. • It has an elongation of 1,000%, far higher than many other expansion joint systems on the market, and can tolerate direct contact with hot materials such as mastic asphalt and hot rubber solutions. • It is ideal for buried expansion joints, roof decks and upstand flashings. It is used for trafficked surfaces and sealing joints in decks where continuous movement in the structure occurs. It can even be permanently immersed in water. BY VULCANIZED RUBBER SHEETS • It is vulcanized and cannot be welded or heat bonded. It can be used in horizontal-to-vertical applications, or where the joints are irregular or misaligned, extremely effectively. • Because it is so flexible, it can be folded and shaped around even complicated details in one seamless layer. Therefore, no weak spots are exposed in the areas where leaks most often appear.
- 34. BY POLYETHYLENE AND ELASTOPHENE SHEETS
- 35. BY TORCHING • Torch Down Roof or modified bitumen is the most common type of roofing used on flat roofs. • The name is derived from the method of torching the bitumen sheets onto a fiberglass base sheet in the roofing overlap areas during Torch Down Roof installation. • Rubberized asphalt is typically the material used in the roofing torch down process. • Melting of the bitumen by torching creates highly resistant and durable roofing lasting up to 20 years. • The blend of synthetic rubberized polymers with asphalt makes Torch Down Roof extremely flexible. • During climate change or extreme weather conditions, Torch Down Roof can shift as required and resist brittleness. • Torch Down Roof also provides excellent insulation qualities, and is a fire, wind, and hail rated roofing system.
- 36. BY EPDM MEMBRANE •Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer, better known as EPDM, is a common roofing material in the construction and building industry. •In low slope roofing applications, EPDM is considered one of the best thermoset types of flexible single ply sheet materials, meaning there is only one ply of roofing material, not multiple plies laminated together.
- 37. Pro-Coat • Pro-coat is a polyurethane and rubber based compound which is spray applied and solvent free. • Anti corrosion coating; but it is proving equally as useful in the structural waterproofing sector. • Pro-coat delivers a one-coat solution, offering superb performance against water ingress and damp, corrosion, impact and abrasion, vibration and heat variation. • It is extremely tough and flexible, able to withstand vehicular traffic and even military tanks. It can be used roof and structural waterproofing, tanking, bridge decks, expansion joints, car parks and as a hard wearing floor surface for walkways and station platforms. BY SPRAYING APP MODIFIED BITUMEN MEMBRANES
- 38. •Simple application (roller or airless spray) •When applied it forms seamless membrane without joints. •Resistant to water, heat and frost •Resistant to root penetration •Crack-bridging •Water vapor permeable •Provides excellent thermal, weather and UV resistance. •Waterproofs old bitumen-, asphalt felts by covering them •Provides high sun reflectivity, contributing to thermoinsulation •Remains flexible over a temperature span of -40oC to +90oC •Provides excellent adhesion to almost any type of surface •Can be used for pedestrian and vehicular traffic •Resistant to detergents, oils, seawater and domestic chemicals •Application does not need the use of open flames (torch). FOAM SPRAYS Polyurethane spray
- 39. INJECTION GROUTING BOX METHOD BRICK-BAT COBA Rs 250/sqm Without material Rs 250/sqm Without material Rs 250/sqm Without material Rs 600/sqm with material Rs 550/sqm with material
- 40. MARKET SURVEY CICO DR. FIXIT
- 42. CICO NO.1: Normal setting integral waterproofing compound for concrete and mortar Feature reduces water absorption and dampness. Uses • plastering mortar, masonry Mortar and concrete • tunnels, canals • swimming pools, • basements, • manholes • excellent to arrest dampness of wall Method of application 1kg to 1.5kg per 50 Kg cement may be add to the wet concrete in concrete mixer. Uses/Location: • rendering/plastering work on all brick walls in residential structures. • Both underground and overhead water tanks concreting/plastering . • basement structures, damps-proof course in residential buildings.
- 43. CICO Super: Normal Setting Liquid Integral Waterproofing Compound for Concrete/Mortar Uses • used in RCC as well as Plain Cement Concrete intender • water tank, • roof slab, • basement, • lift pit or in a situation where hydro-insulation is a must. Features: • Permeability of concrete is greatly reduced, act as a hydrophobia. • Increases cohesion, reduces segregation and bleeding significantly. • Improves surface finish of concrete. Method of application Add measured quantity of cico super to mixing water. Add solution only into the dry mix of cement and sand.
- 44. CICO ACRYl : • An acrylic latex based integral waterproofer for cement concret and mortar. • acrylic latex is white colored liquid integral waterproofing compound. • Add in concrete and mortar where high degree of waterproofing is needed. • integrally contained compound resists and reverses the normal tendency of hardened concrete to absorb water by capillary action Uses for floors, roofs and walls of cement concrete. Pre-cast panels, water tanks Features: • Reduces amount of mixing water. • Increases plastic workability. • Allows normal setting and curing. • Reduces shrinkage. • Promotes increased density. • Minimizes capillary water movement. • Lowers permeability. • Promotes high strength. • Waterproofs integrally.
- 45. CICO NO. 2 : Rapid/Quick Setting/Hardening Compounds for Cement mortar and concrete extra fast setting waterproofing/plugging compound. It is a red colored liquid. Features: Excellent quality plugging compound - consistent performance. High early strength – plugging is completed within 5- 20 minutes. Uses For emergency/ immediate repair work. used as plugging compound for basements, pipe joints, Retaining walls, tunnels and sewage works where water is leaking under pressure. Application: Cut back the opening of leaking hole to form concave shape tapering to a narrow mouth at the entrance, place the gelled cement/CICO No.2 mass into the hole and keep the pressure on for 4 to 5 minutes.
- 46. CICO NO. 3 : Quick Setting and Rapid Hardening Admixture for Plain Cement Concrete and Mortar colorless concrete additives in liquid form. Uses basement where leakage is moderate or where quick release of shuttering is required Feature Early gain of strength in cement paste/mortar/concrete.
- 48. Dr. Fixit Torchshield AM 3160/4160 APP MODIFIED BITUMEN BASED MINERAL FINISHED MEMBRANES FOR WATERPROOFING , APP modified bitumen membranes, top surface is covered by a uniform layer of natural or colored slate chippings and the underside is finished with a polyethylene film. Method of Application use as a single layer roof waterproofing system. surface preparation all surfaces to receive dr. fixit torch shield must be clean, dry and free from all contaminates prior to the application MEMBRANES are applied by torch-on application using ensuring the PE film on the underside is completely removed as work proceeds and to ensure adequate adhesion to the substrate.
- 49. WATERPROOFING OF NEW ROOFS AND TERRACES
- 51. INSULATION
- 52. Use o Reduces unwanted heat loss or gain and can decrease the energy demands of heating and cooling systems. o Cellulose, glass wool, rock wool, polystyrene, urethane foam, vermiculite, perlite, wood fibre, plant fibre (cannabis, flax, cotton, cork, etc.), recycled cotton denim, plant straw, animal fibre (sheep's wool), cement, and earth or soil are used as insulation material. Introduction o Majority of insulation in buildings is for thermal purposes, also used as acoustic insulation, fire insulation, and impact insulation (e.g. for vibrations caused by industrial applications). o Insulation material may be chosen for its ability to perform several of these functions at once. o Insulation products vary in terms of colour, surface finish and texture, core composition and, importantly, performance. Rockwool
- 53. How insulation works o Insulation products are designed to frustrate the transfer of heat across the material itself. There are three methods of heat transfer: radiation, conduction and convection. o The effectiveness of bulk insulation is commonly evaluated by its R-value, of which there are two - metric (SI) and US customary, the former being 0.176 times the latter. o The higher the R-value of an insulation product, the more effective the insulation properties Planning o Amount of insulation a house needs depends on building design, climate, energy costs, budget, and personal preference. o The insulation strategy of a building needs to be based on a careful consideration of the mode of energy transfer and the direction and intensity in which it moves. o This may alter throughout the day and from season to season. It is important to choose an appropriate design, the correct combination of materials and building techniques to suit the particular situation. o To determine whether you should add insulation, you first need to find out how much insulation you already have in your home and where. A qualified home energy auditor will include an insulation check as a routine part of a whole-house energy audit.
- 54. Mineral wool o Three types of mineral wool ; glass wool manufactured from recycled glass, Rock wool which is made from basalt, slag wool produced from the slag from steel mills. o Available in batt, roll and loose-fill. o Mineral wool has an R-value ranging from R-2.8 to R-3.5 per inch. Area of use o Ceiling, wall, panels and insulation of pipes. Rockwool in batt(unfaced and face Ceiling insulatio TYPES OF INSULATION MATERIALS There are many insulation materials available in market like : cellulose, glass wool, rockwool, polystyrene, urethane foam, vermiculite, perlite, wood fibre, plant fibre (cannabis, flax, cotton, cork, etc.), recycled cotton denim, plant straw, animal fibre (sheep's wool), cement, and earth or soil. Loose- fill pipe insulationWall and ceiling insulation
- 55. Advantages o naturally moisture-resistant. It retains its insulating qualities even when wet. o Sound is blocked much more by mineral wool, so the interior of a building suffers less acoustic invasion . o Will not burn until temperatures reach beyond 1,800°F (1,000°C). The insulation actually performs as a fire barrier, slowing down house fires and giving the fire services more time to get things under control. Disadvantages o Protective gear must be worn when installing, Inhaled slivers irritate the alveoli an can cause lung disease. o Not environment friendly.
- 56. FIBERGLASS o Fiberglass is the most common residential insulating material, composed of glass. o predominantly employed as a residential and commercial thermal insulator. o As an insulator, it slows the spread of heat, cold, and sound in structures, cars and aircraft. o By trapping pockets of air, it keeps rooms warm in the winter and cool in the summer and thereby serves as a convenient method to increase energy efficiency. Fiberglass batt Fiberglass spray Fiberglass rollFiberglass batt
- 57. Advantages o It could be easily be moulded into any shape, o Fibreglass last a long time. o It is low maintenance, fire resistant, good electrical insulator and weatherproof. o Available in a variety of presentations (e.g. blankets, mats, loose fill and boards) o low thermal conductivity Disadvantages o releases particulates into the air which may be inhaled by those installing or removing it, and may cause cancer and other serious afflictions. o wet fiberglass insulation loses all R-value and has almost no insulating properties until it dries out.
- 58. Cellulose o Cellulose insulation is perhaps one of the most eco-friendly forms of insulation, used in wall and roof cavities to insulate, draught proof and reduce noise. o Cellulose, a plant-based insulator, is the oldest form of home insulation. o Has been produced from sawdust, cotton, straw, hemp, and other plant materials with low thermal-conductivity. o Today, it is produced from recycled newspapers that are later treated with chemicals that reduce its ignition potential. o Cellulose has an R-value between R-3.1 and R-3.7. Advantages o Because of the compactness of the material, cellulose contains next to no oxygen within it, so the amount of damage that a fire can cause. o Cellulose is a cheap and effective means of insulating. Disadvantages o Some people may have allergies to newspaper dust. o Needs skilled worker, relative to, say, fiberglass.
- 59. Polyurethane Foam o Nowadays, polyurethane foams use non-chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) gas for use as a blowing agent. o They are relatively light. o They have an R-value of approximately R-6.3 per inch of thickness. o There are also low density foams that can be sprayed into areas that have no insulation. These types of polyurethane insulation tend to have approximately R-3.6 rating per inch of thickness. o Another advantage of this type of insulation is that it is fire resistant. Use The two component high pressure system is generally used in new home construction. It is a quick expanding type of spray foam. The two component low pressure spray foam is another system that is used primarily for remodel jobs where there are existing walls with drywall already in place.
- 60. Advantages o It has good thermal insulating properties, low moisture-vapour permeability. o High resistance to water absorption, relatively high mechanical strength and low density. o In addition, it is relatively easy and economical to install o Cost Effective : Spray polyurethane insulation is more cost-effective than foam board or batt insulation because a little goes a long way. Spray insulation can go around pipes and into cracks and other hard-to-reach places
- 61. Polystyrene o Polystyrene is a waterproof thermoplastic foam which is an excellent sound and temperature insulation material. o EPS and XPS are resistant to moisture o It comes in two types, expanded (EPS) and extruded (XEPS) also known as Styrofoam. The two types differ in performance ratings and cost. The more costly XEPS has a R-value of R-5.5 while EPS is R-4. o Typically the foam is created or cut into blocks, ideal for wall insulation. o The foam is flammable and needs to be coated in a fireproofing chemical called Hexabromocyclododecane (HBCD).
- 62. Insulating material “R” value per inch (2.54 cm) Advantages Disadvantages Polyurethane, board 6.25 Very good R-value, can be used with fibreglass resins Not always easily available, relatively expensive Polyurethane, spray on 7.0 Very good R-value, can be used with fibreglass resins, easy application with spray equipment Not always easily available, expensive, requires special spray equipment Polyurethane, poured (two-part chemical) 7.0 Very good R-value, can be used with fibreglass resins, relative ease of application Not always easily available, expensive, requires very careful volume calculations Polystyrene, sheets (smooth) Trade name “Styrofoam” 5.0 Readily available, low cost, reasonable R-value Cannot be used with fibreglass resins unless protected, easily damaged Polystyrene, foamed in place and expanded moulded beads. Known as Isopor, Polypor, etc. 3.75 to 4.0 Reasonable R-values, lower cost than smooth surfaced sheets Cannot be used with fibreglass resins unless protected, easily damaged Cork board 3.33 Availability in many markets, reasonable cost, can be covered with fibreglass Lower R-values than polyurethane for styrene foams Fibreglass wool batts 3.3 Low cost, ease of installation Readily absorbs water or other fluids, loses insulating value when wet Rock wool batts 3.7 As above As above Comparison of insulation materials
- 64. COMPANIES SELLING INSULATION Texsa India Ltd. Head office : Gurgaon 122 016 Haryana Jaipur Plant : RIICO Industrial Area Phase-1, Rajasthan, India Insulation India Poonamalle High road,Chennai-600 077, Tamilnadu, India ROXUL ROCKWOOL Technical Insulation India Pvt. Ltd. J.B.Nagar, Andheri (East), Mumbai - 400 059, India Lloyd insulations Delhi: Punj Star Premises, Kalkaji Industries Area, New Delhi - 110019. ECOTHERM INSULATION PVT. LTD. An ISO:9001:2008 Company Regd Office: Modern park,Kolkata -700075 (India)
