The document discusses different types of water loss from plants, including transpiration, guttation, and secretion/bleeding. It provides details on each process:
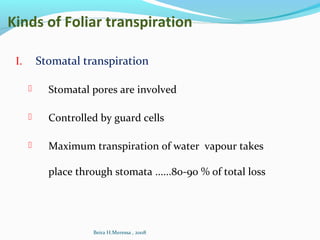
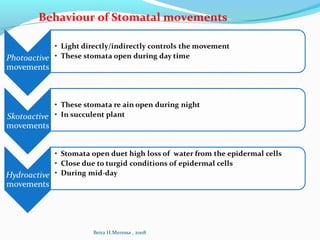
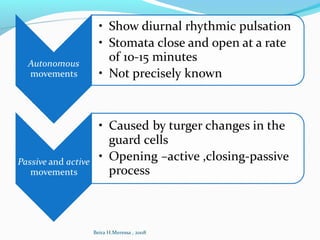
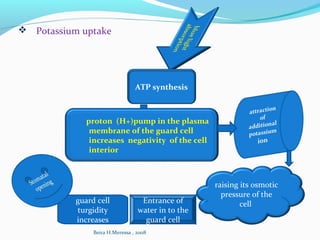
- Transpiration is the primary means of water loss, occurring through stomata. It is a controlled process that allows for gas exchange.
- Guttation involves the exudation of water from specialized pores called hydathodes, occurring primarily at night due to root pressure. The water lost contains minerals and is in liquid form.
- Secretion and bleeding refer to the loss of liquid solutions from plant glands and cuts, respectively.
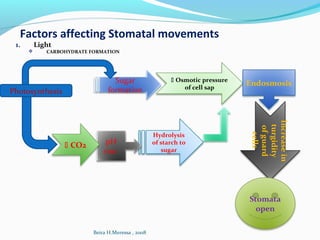
The document then examines factors that influence transpiration and guttation rates like light, temperature,