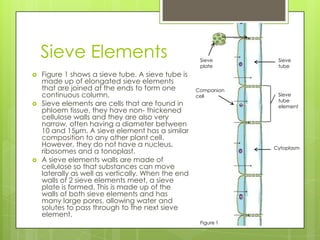
Translocation is the transport of organic substances like sugars through the phloem tissue of plants. Assimilates are produced by plant cells and loaded into sieve tube elements, with help from companion cells, for long-distance transport. Sugars move from sources, like leaves, where they are produced by photosynthesis, to sinks, like roots and fruits, where they are unloaded. Pressure gradients are created by active loading of sucrose into sieve tubes to drive mass flow of phloem sap from areas of high pressure to low pressure.