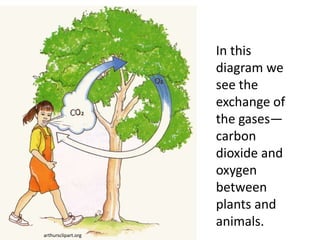
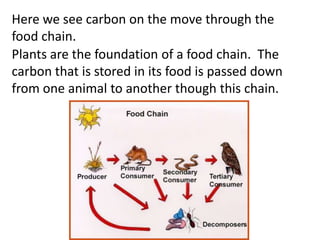
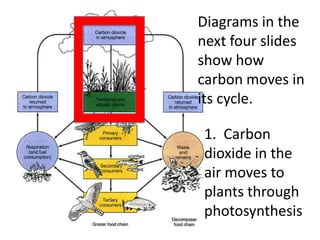
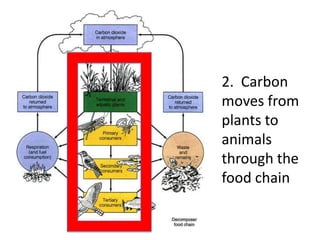
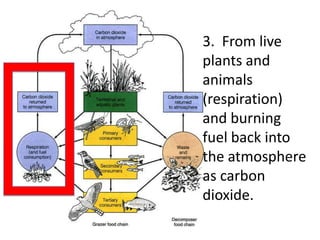
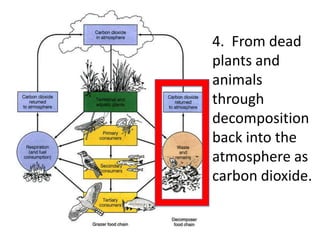
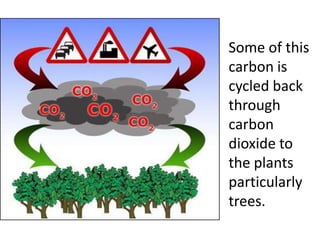
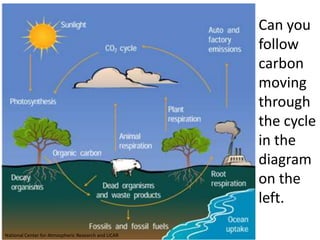
The carbon cycle is a continuous movement of carbon through living organisms, the atmosphere, oceans, and Earth's crust, essential for life on Earth. Carbon moves through processes such as photosynthesis, respiration, and decomposition, influencing the flow of carbon dioxide and oxygen between plants and animals. Fossil fuels, formed from the remains of living organisms, play a significant role in this cycle by releasing carbon dioxide into the atmosphere when burned, highlighting the interconnection of energy use and the carbon cycle.