Embed presentation



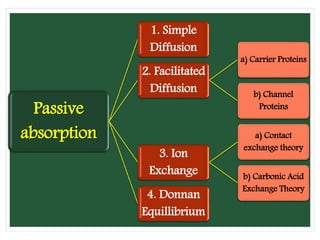
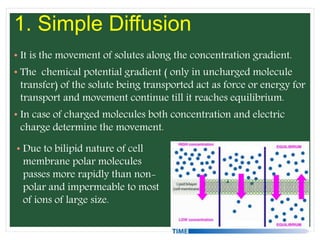
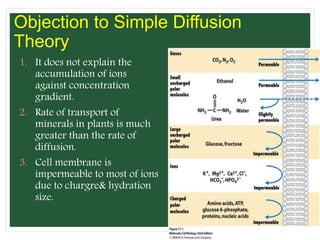
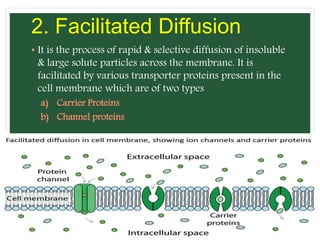



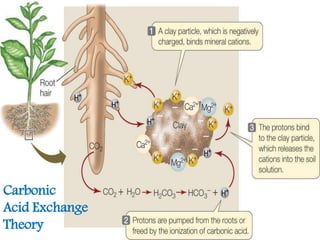


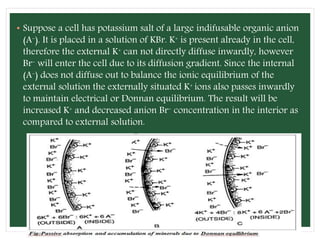

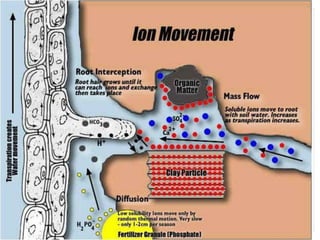

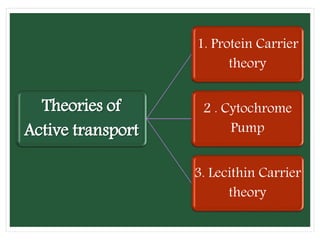

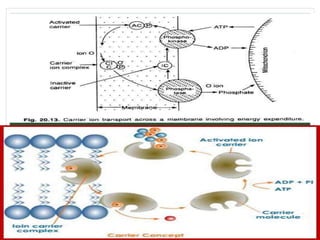



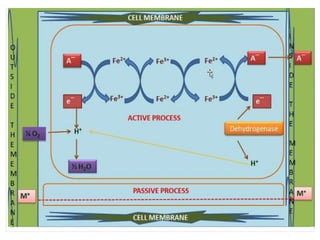


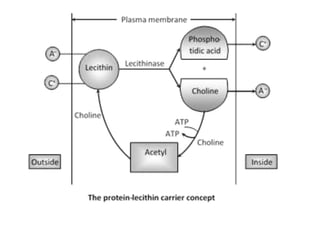
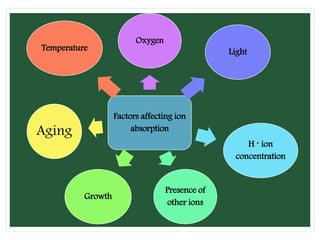






The document discusses mineral uptake in plants, detailing the processes of passive and active absorption, and explaining various theories such as simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and ion exchange. It outlines the mechanisms of active transport and factors influencing ion absorption, including temperature, pH, and interaction with other ions. Additionally, the text emphasizes the role of metabolic energy in the active absorption of ions against concentration gradients.


































