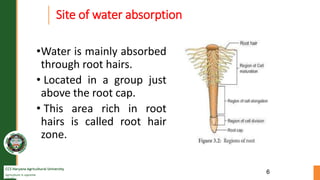
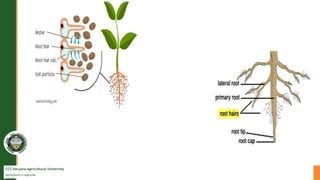
Roots absorb water through osmosis and transpiration. Root hairs absorb water from the soil through osmosis due to their cell sap having a lower water potential than the soil solution. The water moves into the root cortex and then into the stele through passage cells that lack suberin casings. It travels up the xylem vessels through transpiration pull from the leaves. There are three pathways for water movement: apoplastic through cell walls, symplastic through plasmodesmata, and transmembrane through cell membranes. Active absorption is driven by root cell osmosis while passive absorption relies on transpiration pull from the leaves.