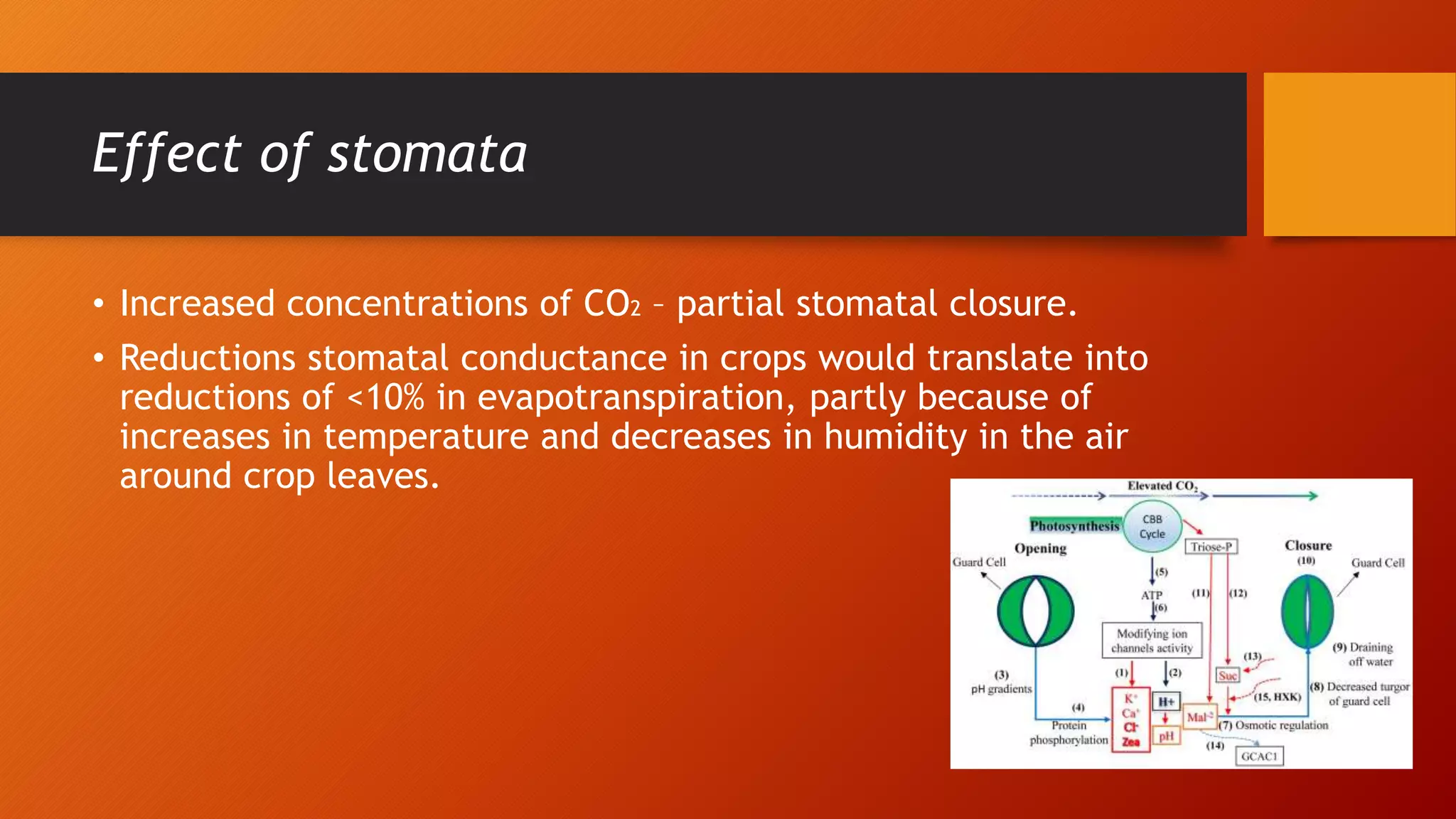
The document discusses the effects of increasing atmospheric CO2 concentration on the environment, plant growth, and agricultural productivity. It highlights the negative impacts of CO2 on ocean acidity and marine life, while also acknowledging the potential benefits for plants, such as enhanced photosynthesis and increased water-use efficiency. Additionally, it notes the influence of CO2 on nitrogen content, rooting patterns, and crop duration, emphasizing the complexities of its effects on various species.