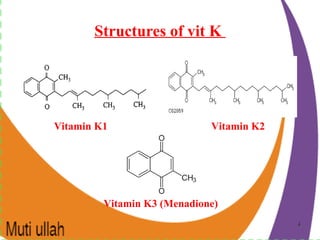
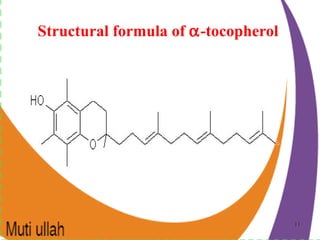
Vitamin K is essential for blood clotting as it enables the formation of prothrombin in the liver. It exists in different forms including phylloquinone (vitamin K1) in plants and menaquinone (vitamin K2) produced by intestinal bacteria. The daily requirement of vitamin K is 120 μg for adult males and 90 μg for adult females. A deficiency of vitamin K can cause hemorrhagic disease in newborns who lack intestinal bacteria and a true deficiency in adults is rare. Vitamin E consists of tocopherols, with alpha-tocopherol being the most biologically active form. It is an important antioxidant found in plant oils and protects polyunsaturated fatty