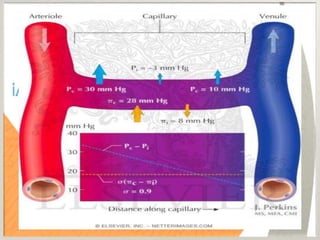
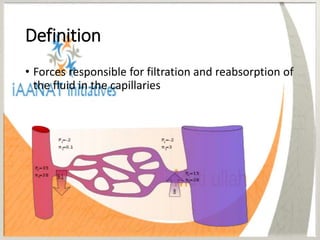
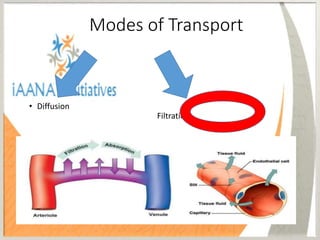
The Starling forces refer to the balance of hydrostatic and oncotic pressures that determine the filtration and reabsorption of fluid across the capillary wall. There are four Starling forces - hydrostatic pressure in the capillaries and interstitium and oncotic pressure in the capillaries and interstitium. According to the Starling principle, fluid movement across the capillary wall is dependent on the balance between the hydrostatic pressure gradient and oncotic pressure gradient. The Starling equation represents this balance, where the fluid movement equals the capillary filtration coefficient times the difference between the hydrostatic and oncotic pressures. At the arterial end, outward forces exceed inward forces, resulting in net filtration. At





![Starling Equation
• Fluid Movement =k[(Pc – Pi) – (∏c - ∏i) ]
where:
• K = Capillary Filtration Coefficient
• K depends upon permeability and the area
available](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/starlingforces-171109102759/85/Starling-forces-8-320.jpg)