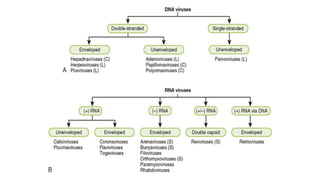
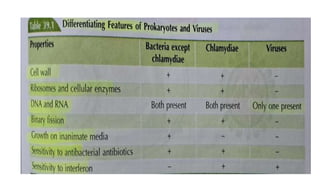
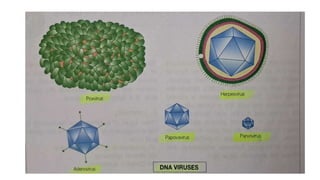
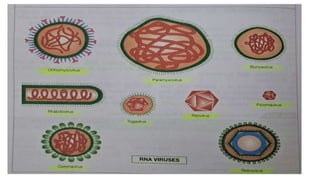
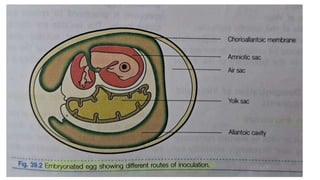
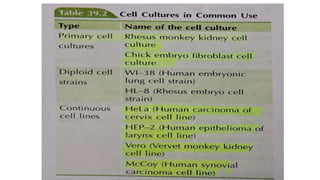
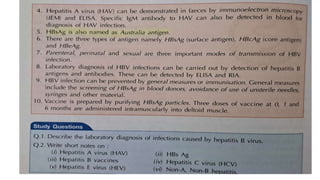
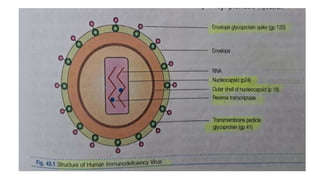
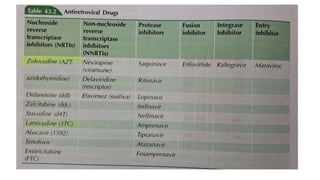
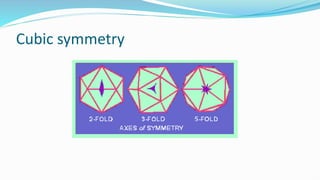
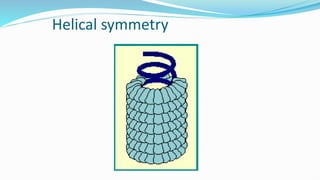
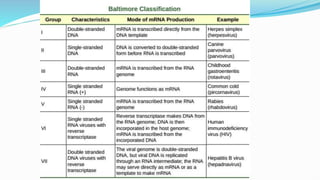
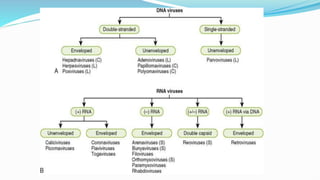
The document provides a comprehensive overview of viruses, detailing their characteristics, classification criteria based on nucleic acid type, replication methods, and host range. It explains the morphology of viruses, describing them as either rod-shaped or spherical, and outlines laboratory diagnosis methods for viral infections. Additionally, the nomenclature of viruses is discussed, including naming conventions related to diseases, geographical locations, and host organisms.