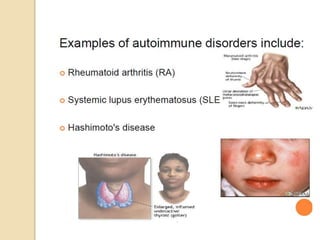
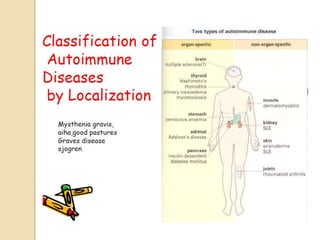
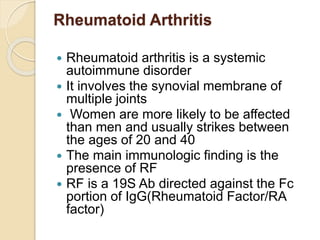
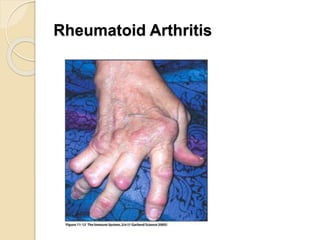
Autoimmunity involves immune responses against self-antigens, leading to conditions where the immune system attacks healthy tissue, such as Graves’ disease, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, and systemic lupus erythematosus. Causes of autoimmune diseases include sequestered antigens, neo-antigens, loss of tolerance, and cross-reacting antigens. Various types of autoimmune disorders can be classified as hemolytic, localized, or systemic, with distinct laboratory diagnostics for conditions like SLE and rheumatoid arthritis.