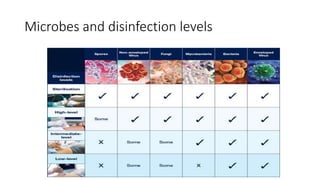
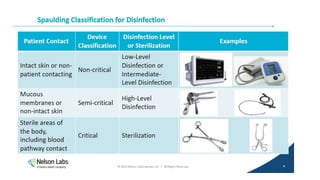
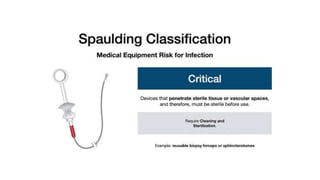
The document outlines the Spaulding classification, which categorizes medical instruments into three levels: critical, semi-critical, and non-critical based on their risk of infection. It emphasizes the importance of appropriate disinfection and sterilization methods for each category, detailing the required levels of disinfection such as sterilization, high-level, intermediate-level, and low-level disinfection. This classification aids healthcare professionals in determining the necessary disinfection protocols to prevent disease transmission during medical procedures.