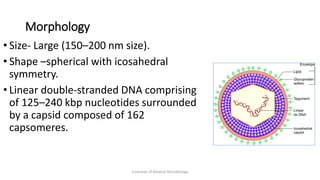
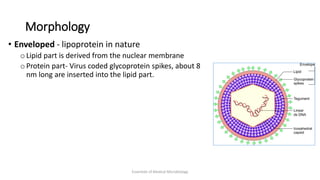
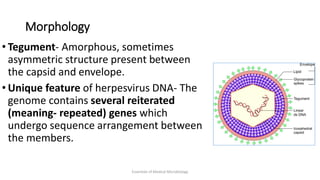
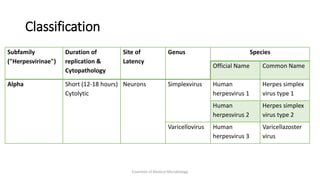
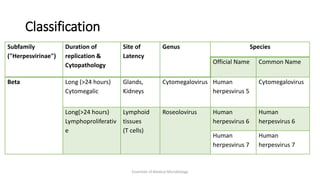
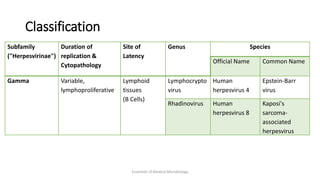
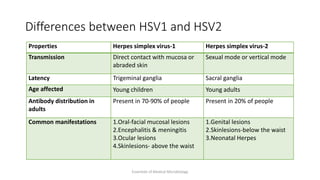
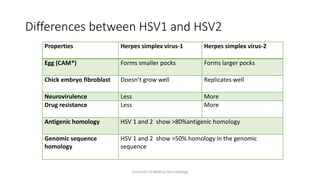
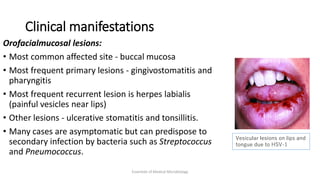
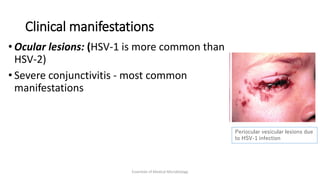
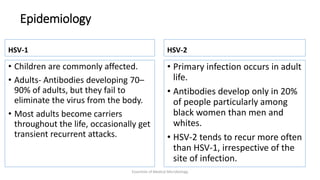
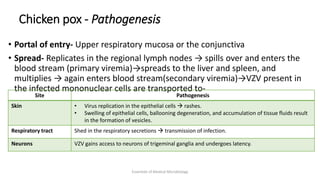
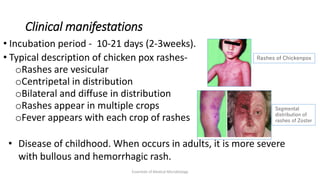
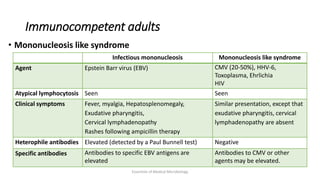
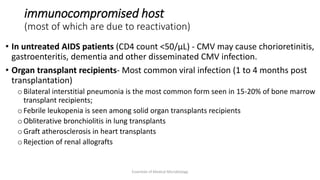
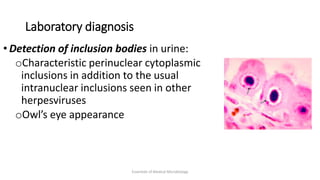
Herpesviruses are a group of viruses that establish latent or persistent infections in their hosts and can undergo periodic reactivation. They are large, enveloped viruses that contain double-stranded DNA. Herpesviruses establish lifelong latent infections primarily in neuronal tissues. During latency, the virus does not replicate but can reactivate later to cause recurrent lesions. Important human herpesviruses include herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2, which cause lesions above and below the waist respectively and establish latency in different neuronal tissues, and varicella zoster virus, which causes chickenpox during initial infection and shingles during reactivation.