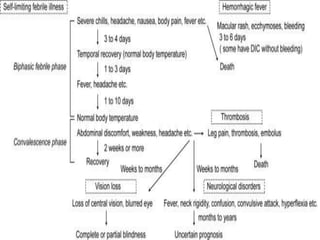
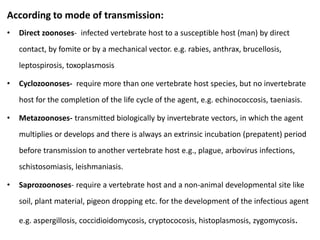
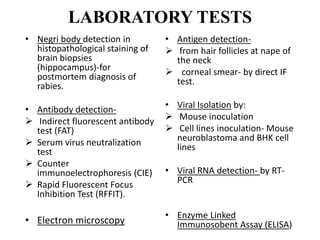
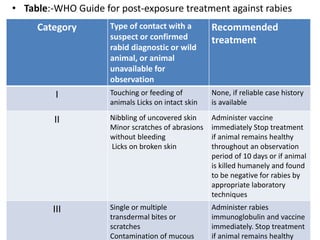
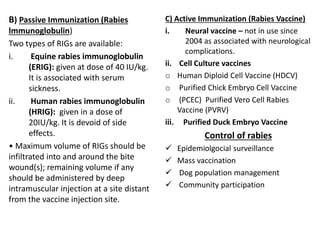
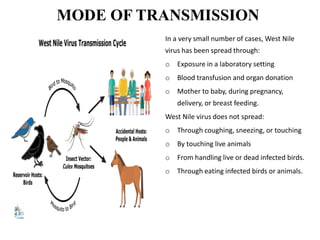
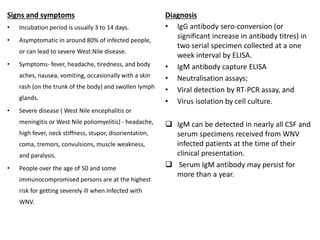
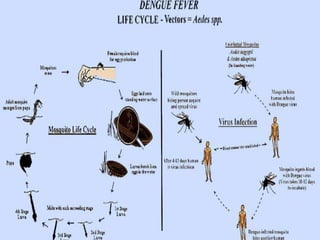
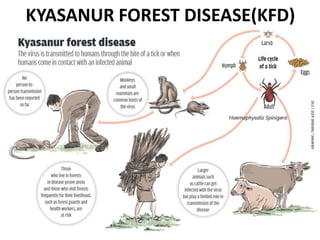
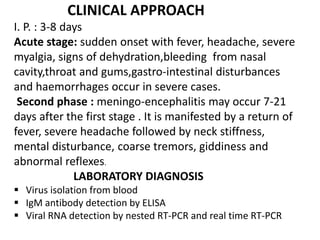
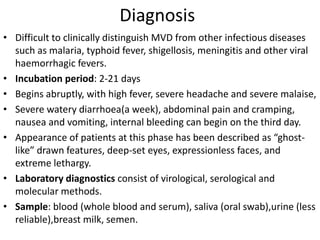
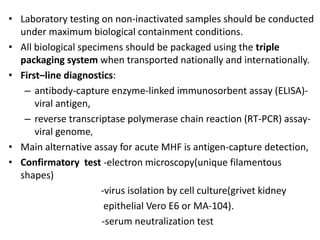
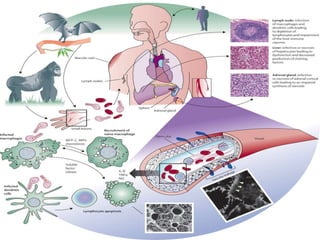
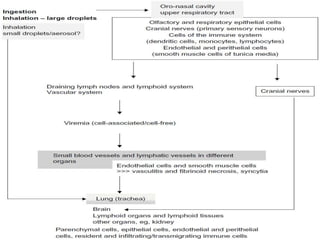
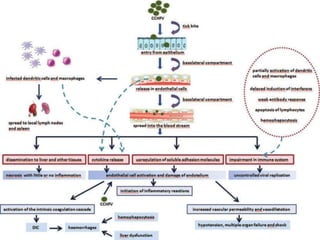
This document discusses viral zoonotic diseases, with a focus on rabies. It defines zoonoses as diseases that can be transmitted between animals and humans. Rabies virus causes progressive infection of the central nervous system. Rabies occurs worldwide except Australia and Antarctica. Transmission is typically through bites from rabid animals, most commonly dogs. Symptoms in humans include pain at the bite site, hydrophobia, and paralysis. Laboratory diagnosis involves detecting the rabies virus or antibodies. Post-exposure prophylaxis includes wound cleansing, rabies immunoglobulin, and rabies vaccines. Prevention relies on surveillance, mass dog vaccination, population control, and public education.


























































![PREVENTION AND CONTROL
• No vaccine available,
• Preventive efforts are focused on vector control ,
• Elimination of breeding sites or source reduction is important,
• Larvivorous fish (eg: gambusia, guppy), which eat mosquito larvae,
may be introduced into local endemic areas,
• Protection from mosquito bites by insect repellent DEET (N, N-
diethyl-3-methylbenzamide), IR3535 (3-[N-acetyl-N-butyl]-
aminopropionic acid ethyl ester) or icaridin (1-piperidinecarboxylic
acid, 2-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-methylpropylester)and use of insecticide-
treated mosquito nets,
• Well-planned fogging operations in high-risk villages,
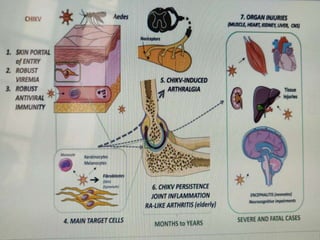
• Active epidemiological surveillance for CHIKV for promoting effective
community education and transmission control.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/viralzoonoticdisease-191004133818/85/Viral-zoonotic-disease-78-320.jpg)