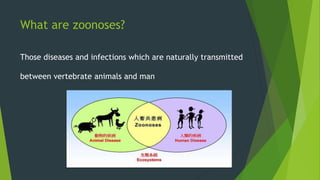
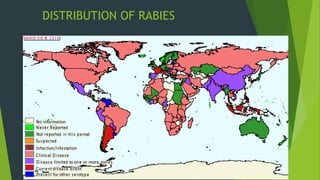
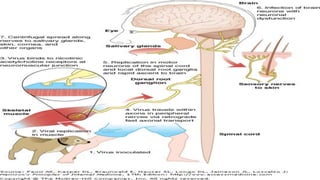
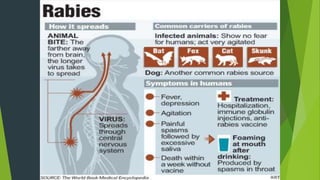
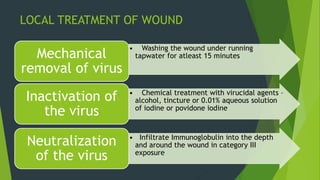
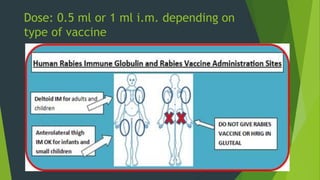
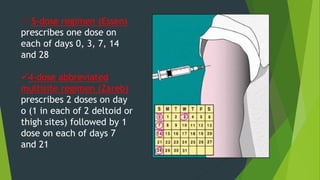
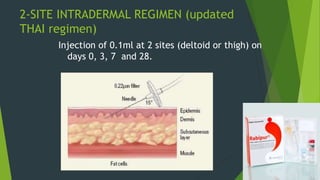
Rabies is classified as a direct zoonosis transmitted through bites or licks. It is a fatal viral infection of the central nervous system caused by lyssavirus. Rabies remains a major public health problem globally, though some areas are considered rabies-free if there are no indigenous human or animal cases reported for over 2 years. Clinical features include hydrophobia and aerophobia. Post-exposure prophylaxis involves wound cleansing, rabies immunoglobulin, and a course of anti-rabies vaccination to prevent onset of symptoms. Control relies on dog vaccination, restraint, and elimination of stray animals.