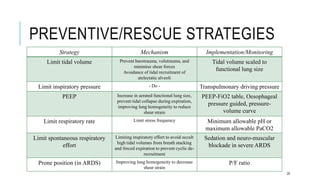
This document discusses ventilator induced lung injury (VILI). It begins by outlining the principles of beneficence, non-maleficence, justice and autonomy in medical care. It then describes the mechanisms of mechanical ventilation and various adverse effects it can cause including volutrauma, barotrauma, atelectrauma and biotrauma. The pathophysiology of VILI is explained as well as ways to assess and prevent VILI through limiting tidal volumes, inspiratory pressures, respiratory rates and using PEEP. Recent developments to monitor and prevent VILI through measures like particle flow rate monitoring and time controlled adaptive ventilation are also summarized.

























![28
Resistive pressure
Elastic pressure
P = V/ELrs + Raw * F + PEEP
[∆P]
[Ppeak − Pplat]
[(Ppeak − Pplat) = Raw*F]
P
T
[(Pplat − PEEP) = V/ELrs]
Driving pressure (∆P)
Trans airway pressure (Pta)
Trans thoracic pressure (Ptt)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vili-211122154803/85/Vili-28-320.jpg)