1. Paediatric musculoskeletal (MSK) examination is unique and focuses on differentiating normal from abnormal findings. It relies on inspection, palpation, and assessment of range of motion.
2. The paediatric MSK evaluation includes observation, palpation, range of motion testing, strength testing, and functional assessment. It follows the "look, feel, move" approach.
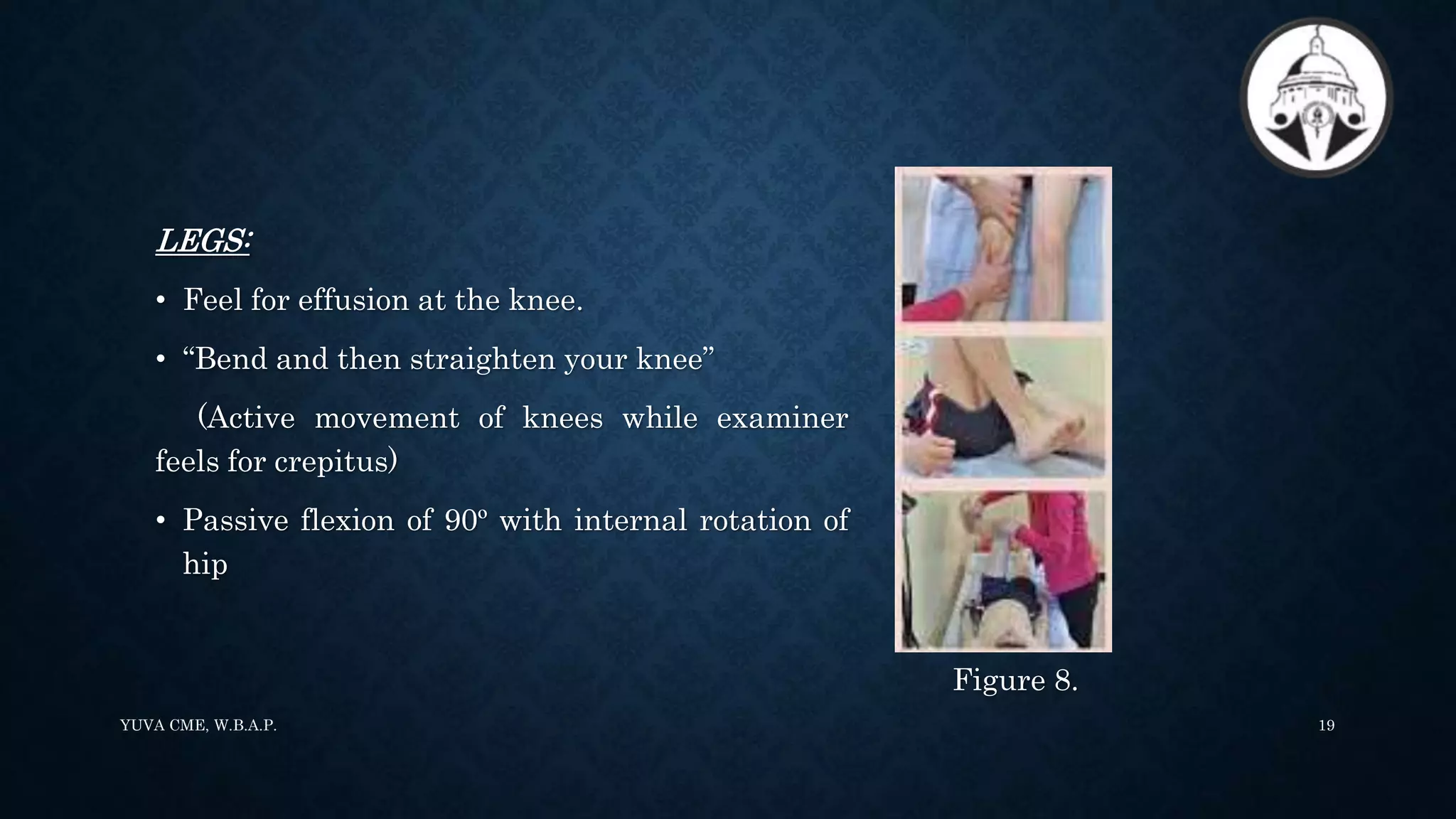
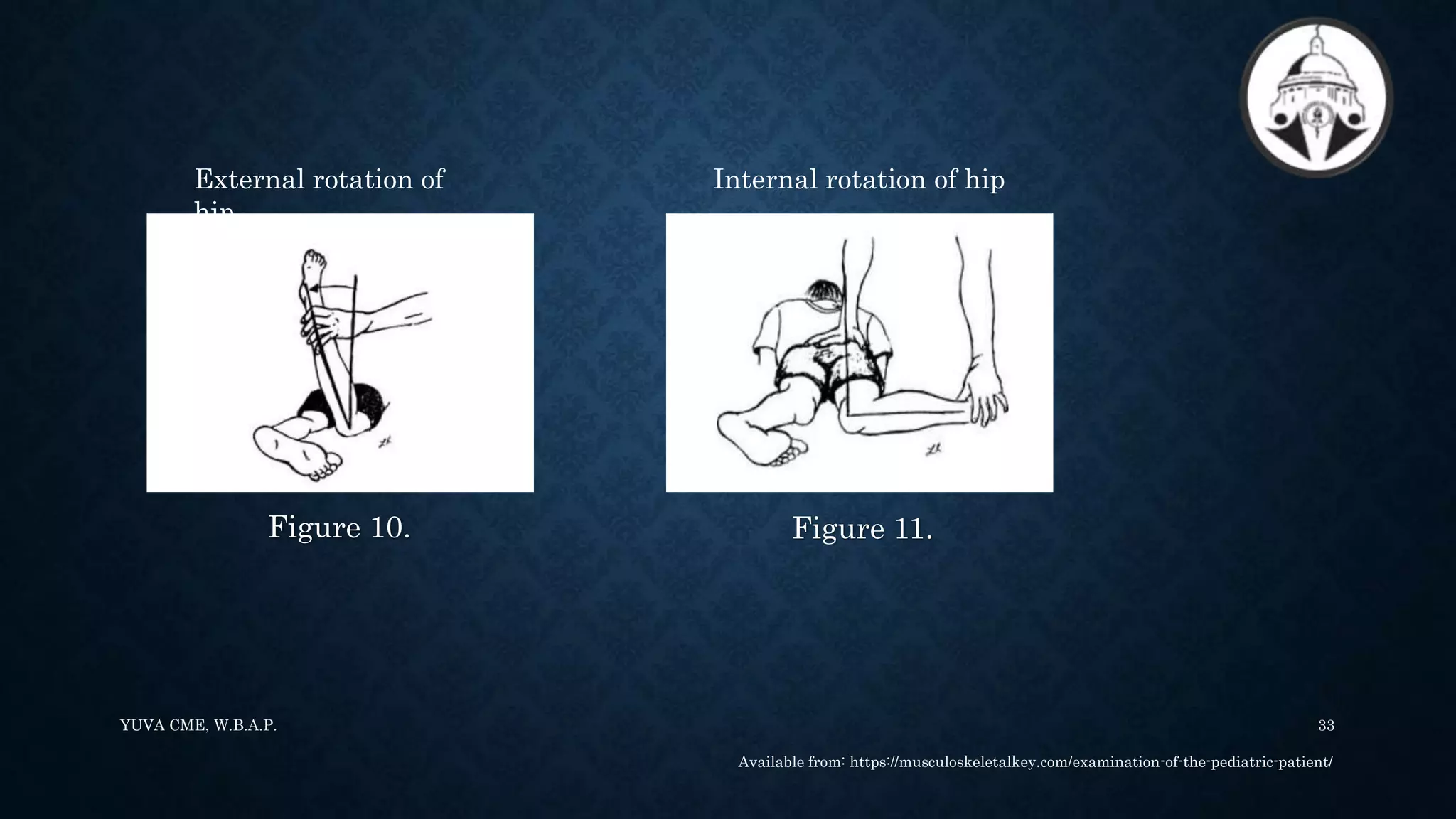
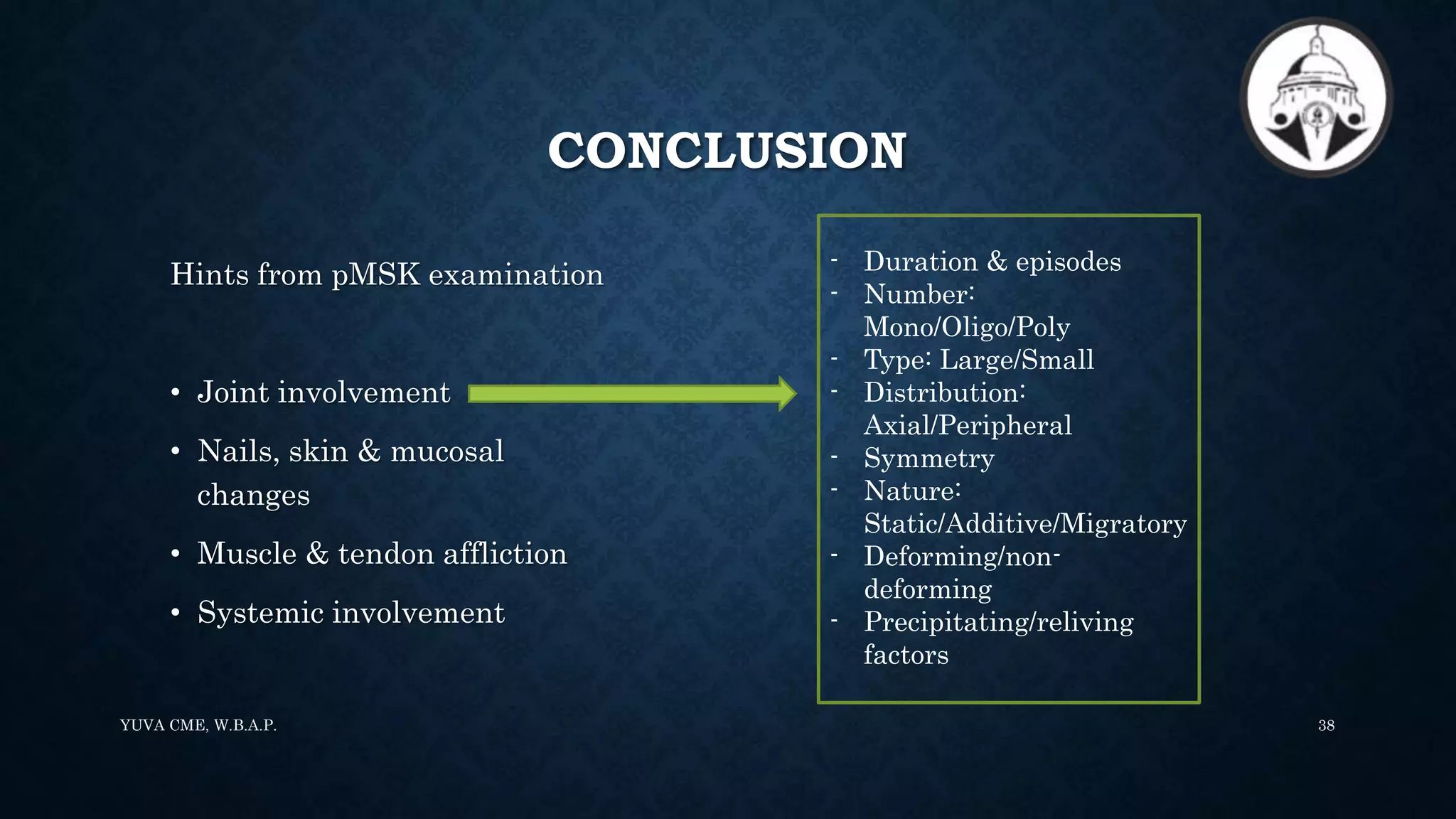
3. The paediatric Gait, Arms, Legs, and Spine (pGALS) assessment is a simple and rapid screening tool to detect musculoskeletal problems in children. It involves observation of gait and movement of various joints followed by focused examination of affected areas.