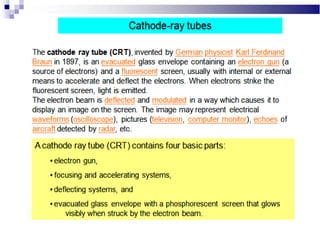
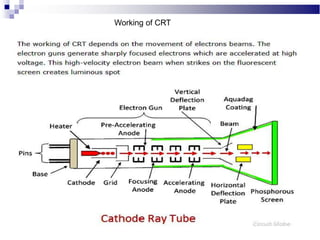
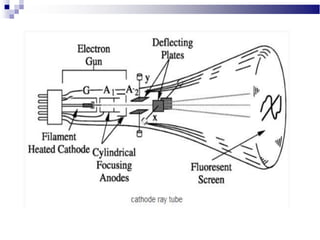
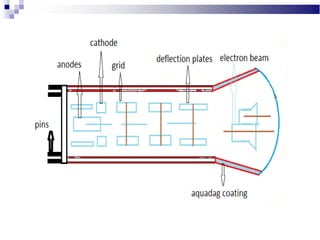
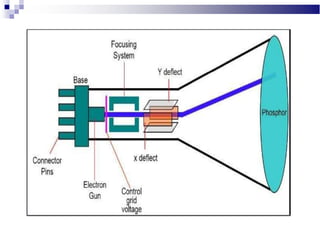
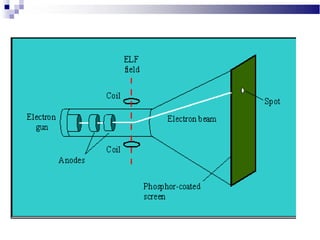
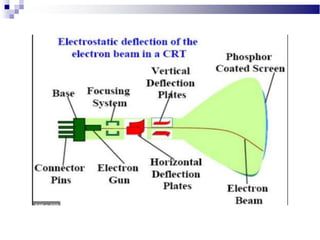
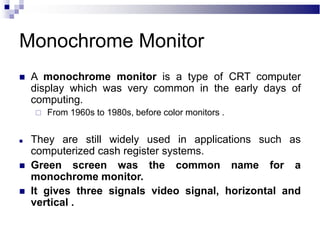
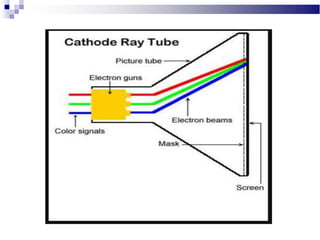
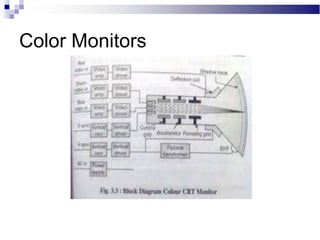
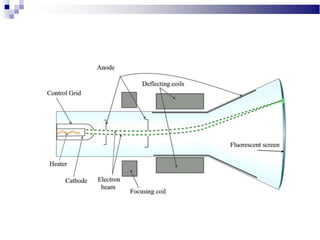
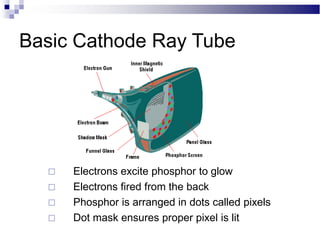
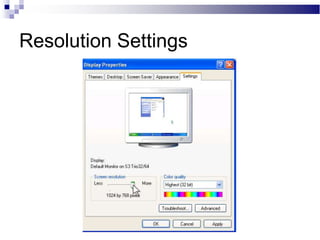
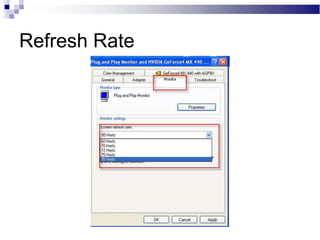
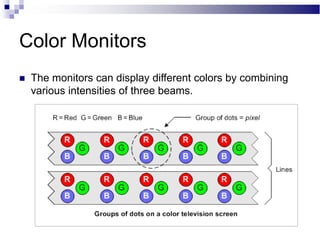
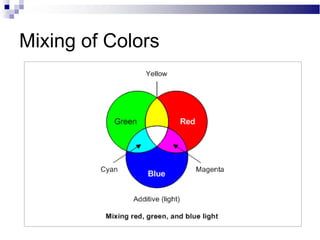
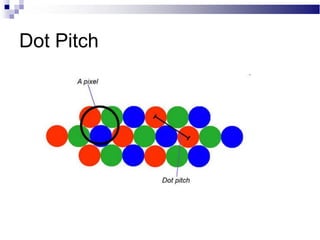
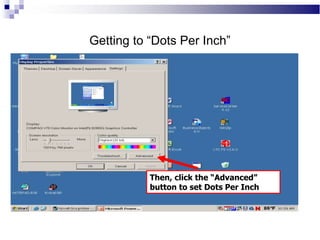
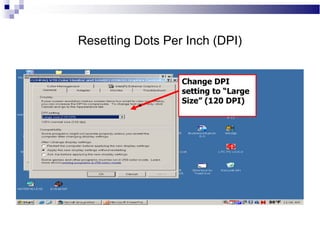
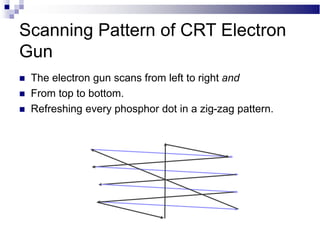
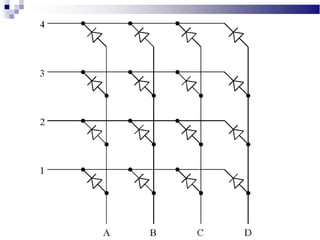
A CRT monitor works by using an electron gun to excite phosphor on the inside of a screen, causing it to glow. It contains three electron guns that fire beams of red, green, and blue to create colors by combining different intensities of the primary colors. The electron beams travel across the screen rapidly, guided by deflection coils and synchronized by horizontal and vertical sync signals to refresh the screen and prevent flickering. Key specifications that affect image quality include screen size, resolution measured in pixels, refresh rate measured in Hz, and dot pitch which affects sharpness.