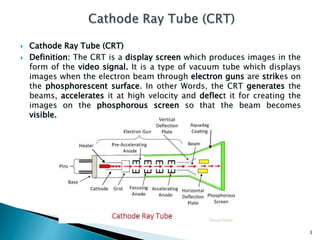
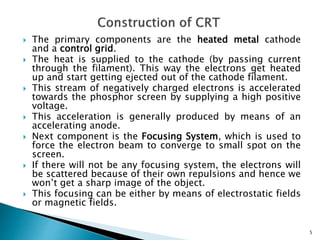
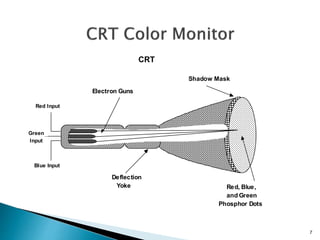
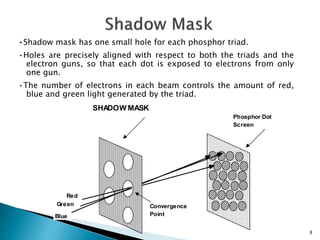
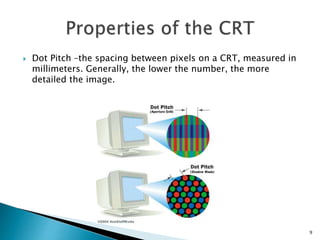
The document discusses the construction and operation of display devices, primarily focusing on cathode-ray tubes (CRTs). It details the components involved, such as the frame buffer, monitor, and display controller, as well as the role of electron guns and deflection systems in image creation. The summary also touches on the importance of pixel representation and the concept of dot pitch in display quality.