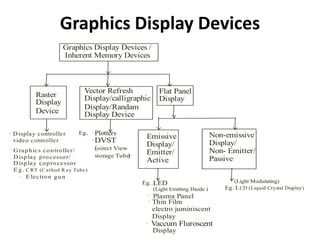
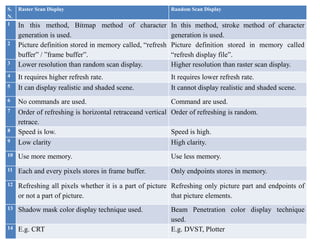
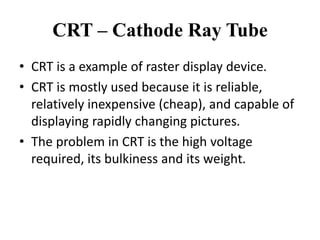
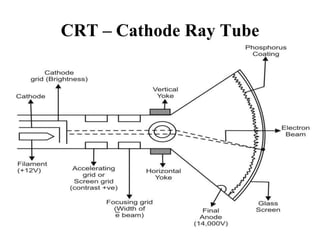
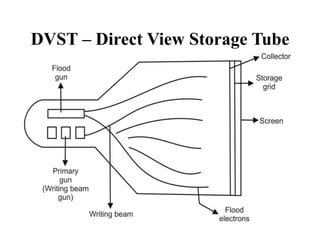
The document provides an overview of various graphics display devices including CRT (Cathode Ray Tube) and DVST (Direct View Storage Tube), detailing their construction, functions, advantages, and disadvantages. It highlights differences in display methods, with CRT offering reliable performance for rapidly changing images, while DVST allows for high-resolution displays without flicker but lacks color display capability. Key components such as the electron gun, phosphor coating, and deflection systems are also discussed in terms of their roles in image generation and display quality.