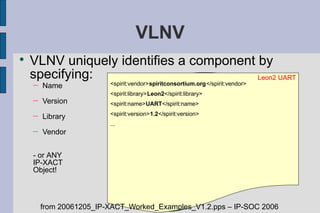
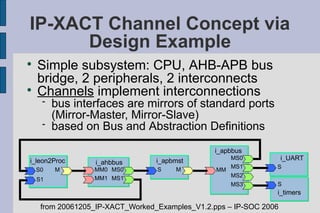
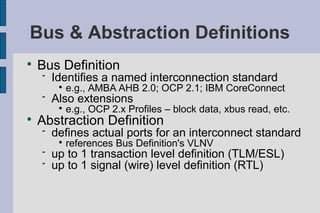
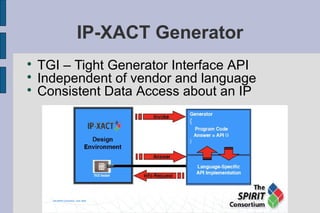
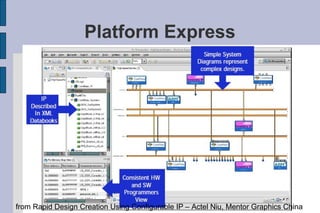
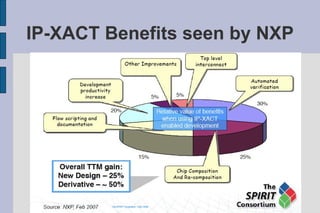
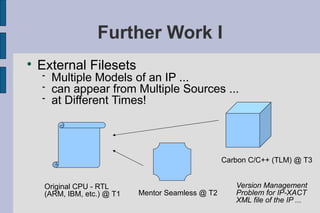
The document summarizes Gary Leonard Dare's presentation on the IP-XACT standard and SPIRIT Consortium. It discusses the SPIRIT Consortium's creation of standards including IP-XACT, its merger with Accellera, and the standardization of IP-XACT as IEEE P1685. It also notes some limitations of IP-XACT including handling external filesets and hierarchical components.